|
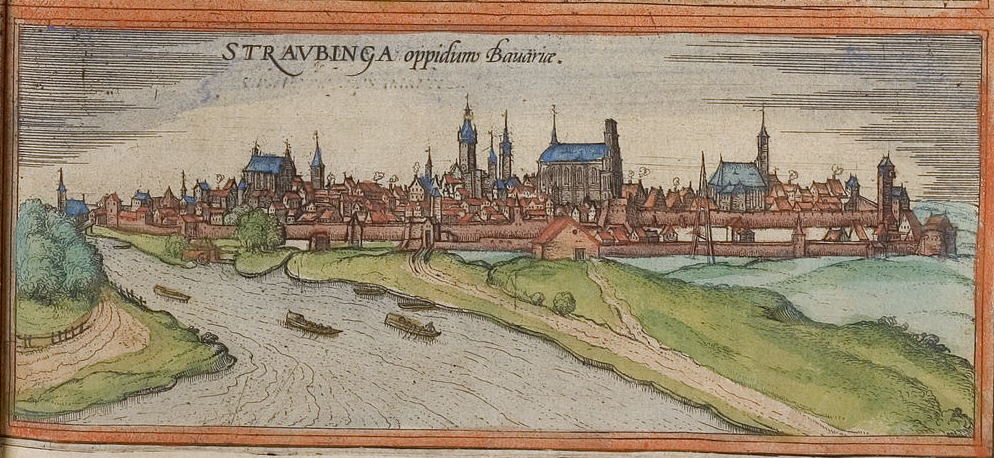
Straubing
Straubing (; Central Bavarian: ''Strauwing'') is an independent city in Lower Bavaria, southern Germany. It is seat of the Districts of Germany, district of Straubing-Bogen. Annually in August the Gäubodenvolksfest, the second largest fair in Bavaria, is held. The city is located on the Danube forming the centre of the Gäuboden. History The area of Straubing has been continuously settled since the Neolithic. The conquest by the Roman Empire, Romans in 16–14 BC had a dramatic impact on the whole region. Even today many traces of the 400-year Roman occupation can be found: for example, the famous 'Römerschatz' (Roman treasure) which was excavated in 1950 and which is shown in the Gäubodenmuseum. ''Sorviodurum'', as the Romans called it, was an important military support base. After the fall of the Roman Empire Straubing became a centre of settlement of the Bavarii, mostly around St. Peter's Church, Straubing, St. Peter's Church (built in the 9th century) between Allachbach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Bavaria-Straubing
Bavaria-Straubing denotes the widely scattered territorial inheritance in the Wittelsbach house of Bavaria that were governed by independent dukes of Bavaria-Straubing between 1353 and 1432; a map (''illustration'') of these marches and outliers of the Holy Roman Empire, vividly demonstrates the fractionalisation of lands where primogeniture did not obtain. In 1255 the Duchy of Bavaria had been divided into and . The two parts were reunited in 1340 but in 1349, after Emperor Louis IV's death, his sons re-divided Bavaria: Lower Bavaria passed to Stephan II (died 1375), William (died 1389) and Albert (died 1404). In 1353, by the , Lower Bavaria was further partitioned into Bavaria-Landshut and Bavaria-Straubing: William and Albert received a part of the Lower Bavarian inheritance, with a capital in Straubing and rights to Hainaut and Holland.Stephan II received the rest of Lower Bavaria. Jacqueline never ruled Bavaria. She bore the title, but women could not rule in Bavaria. She ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gäubodenvolksfest
The Gäubodenvolksfest in Straubing is one of the largest Volksfests (beer festival and travelling funfair) in the Germany, German state of Bavaria. It is an annual event, spanning eleven days mid-August. History The Gäubodenvolksfest was founded in the year 1812 by Maximilian I Joseph of Bavaria, Maximilian I Joseph, King of Bavaria, as an agricultural festival to foster an annual gathering of the people in the Danube region. The festival went on hiatus in 1915–1918, 1940–1945, and 2020–2021. Description The Gäubodenvolksfest is a modern and family-friendly festival with several attractions, including carousels and roller coasters. There are also several large beer tents that span a 100,000 m2 area. The event has maintained the historic character of Bavarian festivals, and attracts approximately 1.4 million visitors every year. Many visitors wear traditional Bavarian clothing (''Tracht'') for the occasion. The festival combines Bavarian tradition with progre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straubing-Bogen
Straubing-Bogen is a Districts of Germany, ''Landkreis'' (district) in the eastern part of Bavaria, Germany. Neighboring districts are (from the north clockwise) Cham (district), Cham, Regen (district), Regen, Deggendorf (district), Deggendorf, Dingolfing-Landau, Landshut (district), Landshut and Regensburg (district), Regensburg. The independent town of Straubing is surrounded by the district. The seat of the government of the district (Landratsamt) is located in Straubing. The only towns within the district itself are Bogen, Germany, Bogen and Geiselhöring. Geography The main river is the Danube, which crosses the district from the west to the east. There are two major geographical regions in the district. One is the Gäuboden with the Danube region and lowlands, the other are the mountains of the Bavarian Forest (''Bayerische Wald''). History The district was created in 1972 by merging the previous districts of Straubing and Bogen and parts of the Mallersdorf district. Coat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agnes Bernauer
Agnes Bernauer (c. 1410 – 12 October 1435) was the mistress and perhaps also the first wife of Albert, later Albert III, Duke of Bavaria. Because his father, Ernest, ruling Duke of Bavaria at the time, considered this liaison with a commoner unbefitting his son's social standing, he clashed with his son over the matter and finally arranged to have Agnes condemned for witchcraft and drowned in the Danube in 1435. Her life and death have been depicted in numerous literary works, the most well known being Friedrich Hebbel's tragedy of the same name and the folk musical ''Die Bernauerin'' by the composer Carl Orff. Biography Agnes Bernauer was probably born around 1410; nothing is known of her childhood and youth. She is traditionally considered to have been the daughter of the Augsburg barber surgeon Kaspar Bernauer, whose existence has, however, not yet been proved. Since Ernest's son Albert participated in a tournament in Augsburg in February 1428, it is generally assumed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest, Duke Of Bavaria
Ernest of Bavaria-Munich (), (Munich, 1373 – 2 July 1438 in Munich), from 1397 Duke of Bavaria-Munich. Biography Ernest was a son of John II and ruled the duchy of Bavaria-Munich together with his brother William III. He restrained uprisings of the citizenry of Munich in 1396 and 1410 and forced his uncle Stephen III to confine his reign to Bavaria-Ingolstadt in 1402. Afterwards Ernest still fought several times successfully against the dukes of Bavaria-Ingolstadt Stephen III and his son Louis VII the Bearded as ally of Henry XVI of Bavaria-Landshut. He was a member of the Parakeet Society and of the League of Constance. After the extinction of the Wittelsbach dukes of Bavaria-Straubing, counts of Holland and Hainaut, Ernest and his brother William struggled with Henry and Louis but finally received half of Bavaria-Straubing including the city of Straubing in 1429. As ally of the House of Luxembourg Ernest backed his deposed brother in law Wenceslaus against t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Bavaria
Lower Bavaria (, ; ) is one of the seven administrative regions of Bavaria, Germany, located in the east of the state. It consists of nine districts and 258 municipalities (including three cities). Geography Lower Bavaria is subdivided into two regions () – Landshut and Donau-Wald. Recent election results mark it as the most conservative part of Germany, generally giving huge margins to the CSU. This part of Bavaria includes the Bavarian Forest, a well-known tourist destination in Germany, and the Lower Bavarian Upland. ''Landkreise''(districts) # Deggendorf # Dingolfing-Landau # Freyung-Grafenau # Kelheim # Landshut # Passau # Regen # Rottal-Inn # Straubing-Bogen ''Kreisfreie Städte''(district-free towns) # Landshut # Passau # Straubing Population Economy The gross domestic product (GDP) of the region was €48.5 billion in 2018, accounting for 1.4% of German economic output. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was €36,100 or 120% of the EU27 avera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William V, Count Of Hainaut
William I, Duke of Bavaria-Straubing (Frankfurt am Main, 12 May 1330 – 15 April 1389, Le Quesnoy), was the second son of Emperor Louis IV and Margaret II of Hainaut. He was also known as William V, Count of Holland, as William III, Count of Hainaut and as William IV Count of Zeeland. Biography In 1345 William's father was conferring Hainaut, Holland, Zeeland and Friesland upon his wife Margaret, and shortly later also upon their son William. After his father's death in 1347, William ruled Bavaria, Holland and Hainaut together with his five brothers until 1349. With the first division of the Wittelsbach possessions in 1349 he received Hainaut, Holland and Lower Bavaria together with his brothers Stephen II and Albert I. After the next division of Bavaria in 1353, he ruled together with his younger brother Albert I in Bavaria-Straubing, Holland and Hainaut. William had engaged in a long struggle with his mother Margaret, obtaining Holland and Zeeland from her in 1354, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gäuboden
The Gäuboden (; also referred to in German as the Dungau) is a region in Lower Bavaria in southern Germany without any clear geographic or cultural boundaries, that covers an area about 15 kilometres wide south of the River Danube and the Bavarian Forest, beginning opposite Wörth an der Donau and stretching as far as Künzing. The largest town in the region is Straubing, which is often called the centre of the Gäuboden. The Gäuboden is one of the largest loess A loess (, ; from ) is a clastic rock, clastic, predominantly silt-sized sediment that is formed by the accumulation of wind-blown dust. Ten percent of Earth's land area is covered by loesses or similar deposition (geology), deposits. A loess ... regions in southern Germany. Literature * Franz Krojer: ''Aufschluss des Gäubodens.'' Differenz, München 2006. * Erwin Rutte: ''Rhein – Main – Donau. Eine geologische Geschichte.'' Thobecke, Sigmaringen 1987, . * Dieter Vogel (Hrsg.): ''Der Gäuboden. Heimatbuch. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis I Wittelsbach, Duke Of Bavaria
Louis I (; 23 December 1173 – 15 September 1231), called the Kelheimer or of Kelheim, since he was born and died at Kelheim, was the Duke of Bavaria from 1183 and Count Palatine of the Rhine from 1214. He was the only surviving son of Otto I, Duke of Bavaria (the first duke from the House of Wittelsbach) by his wife Agnes of Loon. He married Ludmilla of Bohemia, a daughter of Duke Frederick of Bohemia. Life Early years Soon after his father's death in 1183, Louis was appointed under the guardianship of his uncle Conrad of Wittelsbach, Archbishop of Mainz, and Emperor Frederick Barbarossa. His mother, Agnes, an energetic and enterprising leader, had taken over the regency of Bavaria in the meantime, securing her son's inheritance. Upon his coming-of-age, in 1189, at sixteen years old, at the beginning of his reign, he had already fallen in the midst of a conflict which triggered the nearly simultaneous extinction of the Burgrave of Regensburg and the Count of Sulzbach i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest south into the Black Sea. A large and historically important river, it was once a frontier of the Roman Empire. In the 21st century, it connects ten European countries, running through their territories or marking a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , passing through or bordering Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Romania, Bulgaria, Moldova, and Ukraine. Among the many List of cities and towns on the river Danube, cities on the river are four national capitals: Vienna, Bratislava, Budapest, and Belgrade. Its drainage basin amounts to and extends into nine more countries. The Danube's longest headstream, the Breg (river), Breg, rises in Furtwangen im Schwarzwald, while the river carries its name from its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Bavaria
The Duchy of Bavaria () was a frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It was settled by Bavarians, Bavarian tribes and ruled by List of rulers of Bavaria, dukes (''duces'') under Francia, Frankish overlordship. A new duchy was created from this area during the decline of the Carolingian Empire in the late ninth century. It became one of the stem duchies of the East Francia, East Frankish realm, which evolved as the Kingdom of Germany and the Holy Roman Empire. During internal struggles in the Ottonian dynasty, the Bavarian territory was considerably diminished by the separation of the newly established Duchy of Carinthia in 976. Between 1070 and 1180, the Holy Roman Emperors were again strongly opposed by Bavaria, especially by the Duke, ducal House of Welf. In the final conflict between the Welf and Hohenstaufen dynasties, Duke Henry the Lion was banned and deprived of his Bavarian and Duchy of Saxony, Saxon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
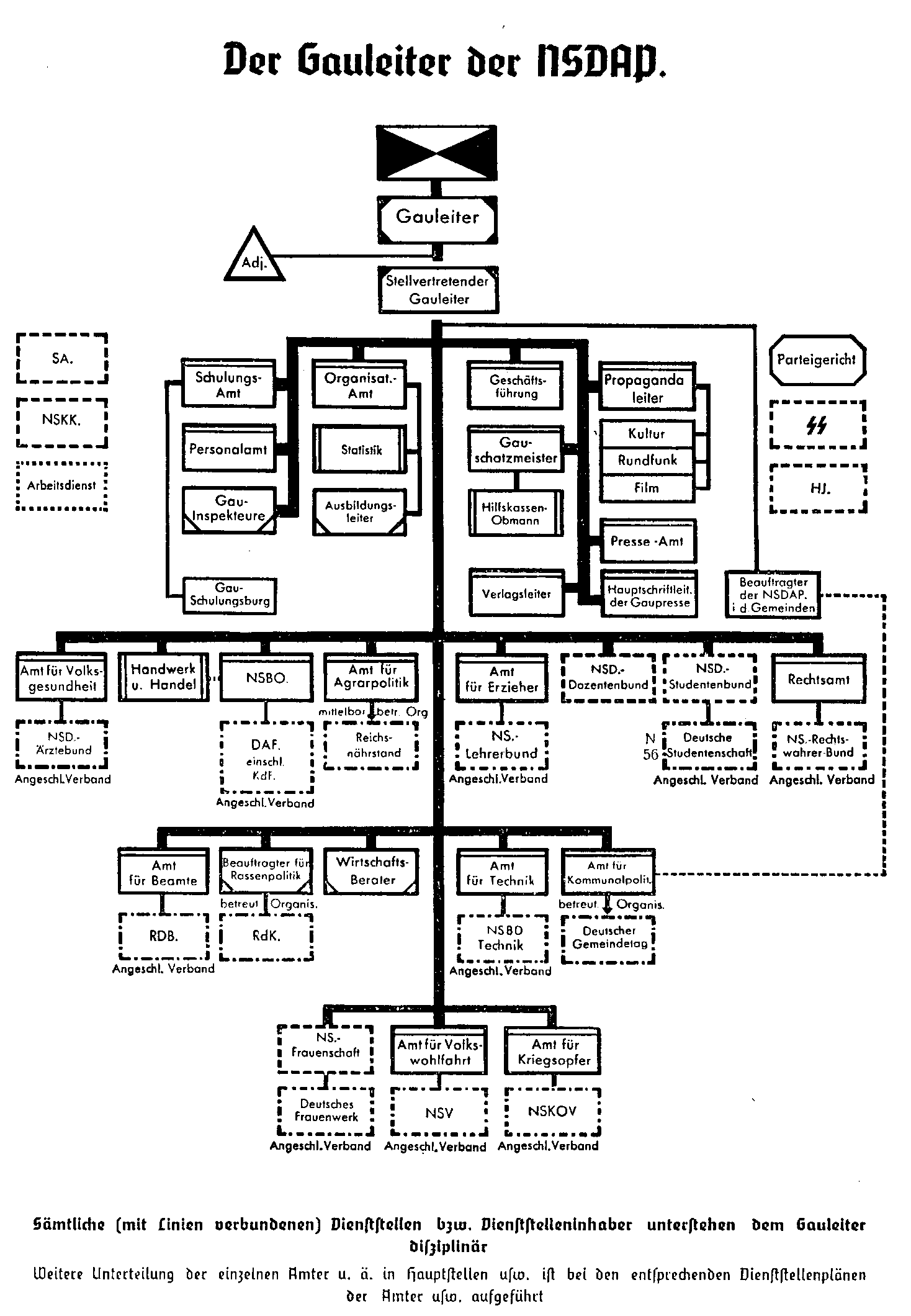
Gauleiter
A ''Gauleiter'' () was a regional leader of the Nazi Party (NSDAP) who served as the head of a ''Administrative divisions of Nazi Germany, Gau'' or ''Reichsgau''. ''Gauleiter'' was the third-highest Ranks and insignia of the Nazi Party, rank in the Nazi political leadership, subordinate only to ''Reichsleiter'' and to the ''Führer'' himself. The position was effectively abolished with the fall of the Nazi regime on 8 May 1945. History and development Origin and early years The first use of the term ''Gauleiter'' by the Nazi Party was in 1925 around the time Adolf Hitler re-founded the Party on 27 February, after the lifting of the ban that had been imposed on it in the aftermath of the Beer Hall Putsch of 9 November 1923. The word can be singular or plural in German usage, depending on its context, and derives from the German words ''Gau (territory), Gau'' and ''leiter'' (''leader''). The word ''Gau'' is an old term for a region of the German ''Reich'' (Empire). The Frankis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |