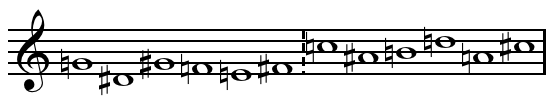|
Stockhausen
Karlheinz Stockhausen (; 22 August 1928 – 5 December 2007) was a German composer, widely acknowledged by critics as one of the most important but also controversial composers of the 20th and early 21st centuries. He is known for his groundbreaking work in electronic music, having been called the "father of electronic music", for introducing controlled chance (Aleatoric music, aleatory techniques) into Serialism, serial composition, and for musical spatial music, spatialization. Stockhausen was educated at the Hochschule für Musik Köln and the University of Cologne, later studying with Olivier Messiaen in Paris and with Werner Meyer-Eppler at the University of Bonn. As one of the leading figures of the Darmstadt School, his compositions and theories were and remain widely influential, not only on composers of art music, but also on jazz and popular music. His works, composed over a period of nearly sixty years, eschew traditional forms. In addition to electronic musicboth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stockhausen 1994 WDR
Karlheinz Stockhausen (; 22 August 1928 – 5 December 2007) was a German composer, widely acknowledged by critics as one of the most important but also controversial composers of the 20th-century classical music, 20th and early 21st-century classical music, 21st centuries. He is known for his groundbreaking work in electronic music, having been called the "father of electronic music", for introducing controlled chance (Aleatoric music, aleatory techniques) into Serialism, serial composition, and for musical spatial music, spatialization. Stockhausen was educated at the Hochschule für Musik Köln and the University of Cologne, later studying with Olivier Messiaen in Paris and with Werner Meyer-Eppler at the University of Bonn. As one of the leading figures of the Darmstadt School, his compositions and theories were and remain widely influential, not only on composers of art music, but also on jazz and popular music. His works, composed over a period of nearly sixty years, esc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klavierstücke (Stockhausen)
The ''Klavierstücke'' (German for "Piano Pieces") constitute a series of nineteen compositions by German composer Karlheinz Stockhausen. Stockhausen has said the ''Klavierstücke'' "are my ''drawings''". Originating as a set of four small pieces composed between February and June 1952, Stockhausen later formulated a plan for a large cycle of 21 ''Klavierstücke'', in sets of 4 + 6 + 1 + 5 + 3 + 2 pieces. He composed the second set in 1954–55 (''VI'' was subsequently revised several times and ''IX'' and ''X'' were finished only in 1961), and the single ''Klavierstück XI'' in 1956. Beginning in 1979, he resumed composing ''Klavierstücke'' and finished eight more, but appears to have abandoned the plan for a set of 21 pieces. The pieces from ''XV'' onward are for the synthesizer or similar electronic instruments, which Stockhausen had come to regard as the natural successor to the piano. The dimensions vary considerably, from a duration of less than half a minute for ''Klaviers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Momente
''Momente'' (Moments) is a work by the German composer Karlheinz Stockhausen, written between 1962 and 1969, scored for solo soprano, four mixed choirs, and thirteen instrumentalists (four trumpets, four trombones, three percussionists, and two electric keyboards). A "cantata with radiophonic and theatrical overtones", it is described by the composer as "practically an opera of Mother Earth surrounded by her chicks". It was Stockhausen's first piece composed on principles of modular transposability, and his first musical form to be determined from categories of sensation or perception rather than by numerical units of musical terminology, which marks a significant change in the composer's musical approach from the abstract forms of the 1950s. History Stockhausen began work on ''Momente'' in January 1962, with a performance planned for the following May. He had been invited by Baron Francesco Agnello to withdraw for the period of composition of the work to his palazzo in Siculia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hymnen
''Hymnen'' (German for " Anthems") is an electronic and concrete work, with optional live performers, by Karlheinz Stockhausen, composed in 1966–67, and elaborated in 1969. In the composer's catalog of works, it is No. 22. The extended work is based on national anthems. It is structured in four Regions: Region I is dedicated to Pierre Boulez and uses "The Internationale" and "La Marseillaise", Region II is dedicated to Henri Pousseur and uses the "Deutschlandlied", a group of African anthems, the beginning of the Russian anthem, and a fragment of the "Horst-Wessel-Lied", Region III is dedicated to John Cage and uses the continuation of the Russian anthem, The Star-Spangled Banner, and the "Marcha Real", Region IV is dedicated to Luciano Berio and uses the "Swiss Psalm". Stockhausen wrote three versions, one for electronic and concrete music alone, one for electronic and concrete music with soloists, and finally an orchestral version of Region III, which can be performed by its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gruppen
''Gruppen'' ( German for "Groups") for three orchestras (1955–57) is amongst the best-known compositions of German composer Karlheinz Stockhausen, and is Work Number 6 in the composer's catalog of works. ''Gruppen'' is "a landmark in 20th-century music ... probably the first work of the post-war generation of composers in which technique and imagination combine on the highest level to produce an undisputable masterpiece". History Early in 1955 Stockhausen received a commission from WDR for a new orchestral composition, but his ongoing work on '' Gesang der Jünglinge'' prevented him from starting right away. In August and September, he took the opportunity to retreat to an inexpensive rented room in the attic of a parsonage in Paspels, Switzerland, recommended to him by a colleague, Paul Gredinger. Surrounded by the splendour of the Graubünden alps, he created the entire plan of ''Gruppen'', "with a completely new conception of musical time". The surroundings provided mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikrophonie (Stockhausen)
''Mikrophonie'' is the title given by Karlheinz Stockhausen to two of his compositions, written in 1964 and 1965, in which "normally inaudible vibrations ... are made audible by an active process of sound detection (comparable to the auscultation of a body by a physician); the microphone is used actively as a musical instrument, in contrast to its former passive function of reproducing sounds as faithfully as possible". Together with Stockhausen's immediately preceding work ''Mixtur'', for five orchestra groups, four sine-wave generators, four ring modulators, they form a triptych of Live electronic music, live-electronic works, where electronic transformations are accomplished during the performance (as opposed to studio-produced electronic music on tape). Similar to a group of three of the composer's works from the previous decade, ''Gruppen'', ''Zeitmaße'', and ''Gesang der Jünglinge'', there is one work each for orchestral, chamber, and vocal forces. Derivation of the term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kontakte
''Kontakte'' (, 'contacts') is an electronic music work by Karlheinz Stockhausen, realized in 1958–60 at the '' Westdeutscher Rundfunk'' (WDR) electronic-music studio in Cologne with the assistance of Gottfried Michael Koenig. The score is Nr. 12 in the composer's catalogue of works, and is dedicated to . Work history The title of the work "refers both to contacts between instrumental and electronic sound groups and to contacts between self-sufficient, strongly characterized moments. In the case of four-channel loudspeaker reproduction, it also refers to contacts between various forms of spatial movement". The composition exists in two forms: (1) for electronic sounds alone, designated "Nr. in the composer's catalog of works, and (2) for electronic sounds, piano, and percussion, designated "Nr. . A further, theatrical work, '' Originale'' (Nr. ), composed in 1961, incorporates all of the second version of ''Kontakte''. Section and subsection numbers The score is divided i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimmung
''Stimmung'', for six vocalists and six microphones, is a piece by Karlheinz Stockhausen, written in 1968 and commissioned by the City of Cologne for the Collegium Vocale Köln. Its average length is seventy-four minutes, and it bears the work number 24 in the composer's catalog. It is a tonal and yet also a serial composition. It is "the first major Western composition to be based entirely on the production of vocal harmonics", the first "to use overtones as a ''primary'' element". An additional innovation is "the unique kind of rhythmic polyphony which arises from the gradual transformation/assimilation of rhythmic models". Title The German word ''Stimmung'' has several meanings, including " tuning" and " mood". The word is the noun formed from the verb ''stimmen'', which means "to harmonize, to be correct", and related to ''Stimme'' (voice). The primary sense of the title "implies not only the outward tuning of voices or instruments, but also the inward tuning of one's so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gesang Der Jünglinge
''Gesang der Jünglinge'' (literally "Song of the Youths") is an electronic music work by Karlheinz Stockhausen. It was realized in 1955–56 at the Westdeutscher Rundfunk studio in Cologne and is Work Number 8 in the composer's catalog. The vocal parts were supplied by 12-year-old Josef Protschka. It is exactly 13 minutes, 14 seconds long. The work, normally described as "the first masterpiece of electronic music" and "an opus, in the most emphatic sense of the term", is significant in that it seamlessly integrates electronic sounds with the human voice by means of matching voice resonances with pitch and creating sounds of phonemes electronically. In this way, for the first time ever it successfully brought together the two opposing worlds of the purely electronically generated German ''elektronische Musik'' and the French ''musique concrète'', which transforms recordings of acoustical events. ''Gesang der Jünglinge'' is also noted for its early use of spatiality; it was o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kontra-Punkte
''Kontra-Punkte'' (Counter-Points, or Against-Points) is a composition for ten instruments by Karlheinz Stockhausen which resolves contrasts among six instrumental timbres, as well as extremes of note values and dynamic levels, into a homogeneous ending texture. Stockhausen described it: "Counter-Points: a series of the most concealed and also the most conspicuous transformations and renewals—with no predictable end. The same thing is never heard twice. Yet there is a distinct feeling of never falling out of an unmistakable construction of the utmost homogeneity. An underlying force that holds things together—related proportions: a structure. Not the same ''Gestalten'' in a changing light. But rather this: various ''Gestalten'' in the same light, that permeates everything." History The first, untitled version, written in 1952–53, was a sparse-textured, " punctual" composition scored for flute, E-flat clarinet, contrabass clarinet, contrabassoon, trumpet, contrabass tuba, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serialism
In music, serialism is a method of composition using series of pitches, rhythms, dynamics, timbres or other musical elements. Serialism began primarily with Arnold Schoenberg's twelve-tone technique, though some of his contemporaries were also working to establish serialism as a form of post-tonal thinking. Twelve-tone technique orders the twelve notes of the chromatic scale, forming a row or series and providing a unifying basis for a composition's melody, harmony, structural progressions, and variations. Other types of serialism also work with sets, collections of objects, but not necessarily with fixed-order series, and extend the technique to other musical dimensions (often called " parameters"), such as duration, dynamics, and timbre. The idea of serialism is also applied in various ways in the visual arts, design, and architecture, and the musical concept has also been adapted in literature. Integral serialism or total serialism is the use of series for aspects su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Music
Electronic music broadly is a group of music genres that employ electronic musical instruments, circuitry-based music technology and software, or general-purpose electronics (such as personal computers) in its creation. It includes both music made using electronic and electromechanical means (electroacoustic music). Pure electronic instruments depend entirely on circuitry-based sound generation, for instance using devices such as an electronic oscillator, theremin, or synthesizer: no acoustic waves need to be previously generated by mechanical means and then converted into electrical signals. On the other hand, electromechanical instruments have mechanical parts such as strings or hammers that generate the sound waves, together with electric elements including pickup (music technology), magnetic pickups, power amplifiers and loudspeakers that convert the acoustic waves into electrical signals, process them and convert them back into sound waves. Such electromechanical devices in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |