|
Stobi
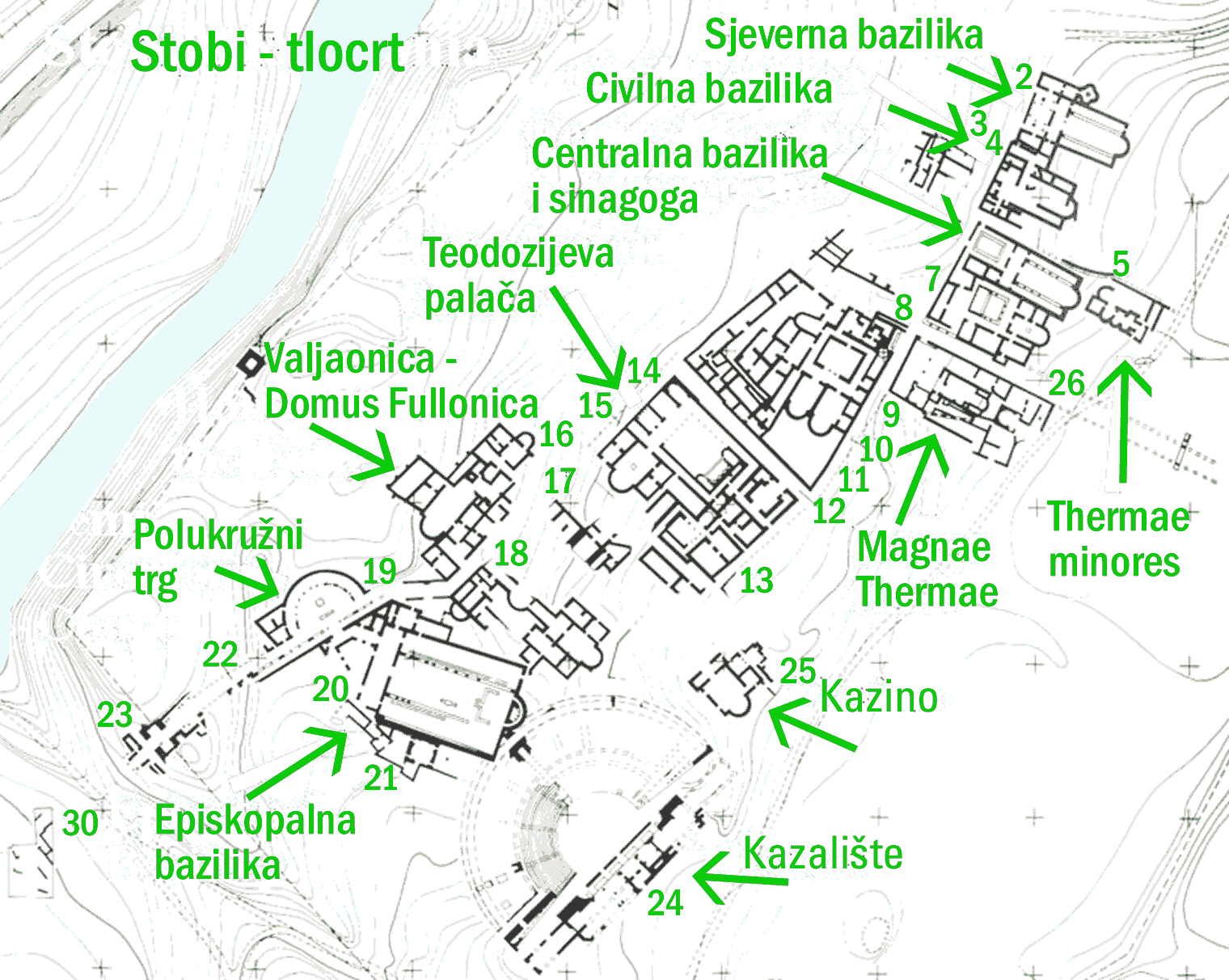
Stobi or Stoboi (; ; ; ), was an ancient town of Paeonia (kingdom), Paeonia, later conquered by Macedon, and finally turned into the capital of the Ancient Rome, Roman province of Macedonia Salutaris. It is located near Gradsko, North Macedonia, Gradsko, North Macedonia, on the main road that leads from the Danube to the Aegean Sea and is considered by many to be the most famous archaeological site in North Macedonia. Stobi was built where the Crna River (Vardar), Erigon (Crna River) joins the Vardar, Axios (Vardar), making it strategically important as a center for both trade and warfare. The pre-Roman period Stobi developed from a Paeonian settlement established in the Archaic Greece, Archaic period. Located on the northern side of a terrace, the early town covered an area of about . Its proximity to the junction of the Erigón and Axiós Rivers as well as its position in the fertile central Vardar valley allowed it quickly to develop a flourishing economy and to establish t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stobi Theater
Stobi or Stoboi (; ; ; ), was an ancient town of Paeonia, later conquered by Macedon, and finally turned into the capital of the Roman province of Macedonia Salutaris. It is located near Gradsko, North Macedonia, on the main road that leads from the Danube to the Aegean Sea and is considered by many to be the most famous archaeological site in North Macedonia. Stobi was built where the Erigon (Crna River) joins the Axios (Vardar), making it strategically important as a center for both trade and warfare. The pre-Roman period Stobi developed from a Paeonian settlement established in the Archaic period. Located on the northern side of a terrace, the early town covered an area of about . Its proximity to the junction of the Erigón and Axiós Rivers as well as its position in the fertile central Vardar valley allowed it quickly to develop a flourishing economy and to establish trade. Nearby Mount Klepa was a lucrative source of marble. The initial Paeonian population was late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Macedonia Salutaris
Macedonia (; ) was a province of ancient Rome, encompassing the territory of the former Antigonid Kingdom of Macedonia, which had been conquered by the Roman Republic in 168 BC at the conclusion of the Third Macedonian War. The province was created in 146 BC, after the Roman general Quintus Caecilius Metellus defeated Andriscus of Macedon, the last self-styled King of Macedonia in the Fourth Macedonian War. The province incorporated the former Kingdom of Macedonia with the addition of Epirus, Thessaly, and parts of Illyria, Paeonia and Thrace. During the Republican period, the province was of great military significance, as the main bulwark protecting the Aegean region from attacks from the north. The Via Egnatia, which crossed the province from west to east was of great strategic importance, providing the main overland link between Rome and its domains in the Eastern Mediterranean. In this period, campaigns against the Dardani and Scordisci to the north and the Thracians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Crna River (Vardar)
The Crna River ( Macedonian: Црна Река ;"Black River"), also known in English as Cherna (), is a river in North Macedonia. It is a right tributary of the Vardar River. It runs through much of the south and west of the country. Its source is in the mountains on the western part of North Macedonia, northwest of Demir Hisar. It enters the Pelagonia valley at the village of Buchin and then flows through the village Sopotnica, and southwards through the plains east of Bitola. At Brod ( Novaci Municipality) it turns northeast. It leaves the Pelagonia valley at the Staravina village and goes in the biggest canyon in North Macedonia, the Skočivir valley and flows into the Vardar River between Rosoman and Gradsko. Thus, the river makes a bend of almost 180 degrees east of Bitola. This bend was part of the Macedonian front in World War I. It was known to the allied forces as the ''Cerna Bend'' or ''Cerna Loop'', and two major battles were fought here: the Battle of the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gradsko, North Macedonia
Gradsko (, ) is a village (despite the word ''grad'' meaning "town") located in the central part of North Macedonia. It is the seat of the Gradsko municipality. It is located very close to the main motorway which links Gevgelija on North Macedonia's border with Greece. History It was the ancient Paeonian capital of Stobi. Demographics On the 1927 ethnic map of Leonhard Schulze-Jena, the village is shown as a Christian Bulgarian village.Schultze Jena, Leonhard. Makedonien: Landschafts- und Kulturbilder. Jena, Verlag von Gustav Fischer, 1927 According to the 2002 census, the village had a total of 2,219 inhabitants. Ethnic groups in the village include:Macedonian Census (2002) ''Book 5 - Total population according to the Ethnic Affiliation, Mother Tongue and Religion'' The State Statistical Office, Skopje, 2002, p. 87. * Macedonians 1,920 * Turks 7 *Serbs 14 * Romani 48 *Albanians 6 *Bosniaks 215 *Others 9 Twin towns * Zugló, Hungary, since 2025 Transport The settlement is se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Paeonia (kingdom)
In antiquity, Paeonia or Paionia () was the land and kingdom of the Paeonians (or Paionians; ). The exact original boundaries of Paeonia, like the early history of its inhabitants, are obscure, but it is known that it roughly corresponds to most of present-day North Macedonia and north-central parts of Greek Macedonia (i.e. probably the Greek municipalities of Paionia (excluding the village of Evropos), Almopia, Sintiki, Irakleia, and Serres), and a small part of south-western Bulgaria. Ancient authors placed it south of Dardania (an area corresponding to modern-day Kosovo and northern North Macedonia), west of the Thracian mountains, and east of the southernmost Illyrians. It was separated from Dardania by the mountains through which the Vardar river passes from the field of Scupi (modern Skopje) to the valley of Bylazora (near modern Sveti Nikole). In the Iliad, the Paeonians are portrayed as allies of the Trojans. During the Persian invasion of Greece, the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
North Macedonia
North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe. It shares land borders with Greece to the south, Albania to the west, Bulgaria to the east, Kosovo to the northwest and Serbia to the north. It constitutes approximately the northern third of the larger geographical Macedonia (region), region of Macedonia. Skopje, the capital and largest city, is home to a quarter of the country's population of over 1.83 million. The majority of the residents are ethnic Macedonians (ethnic group), Macedonians, a South Slavs, South Slavic people. Albanians in North Macedonia, Albanians form a significant minority at around 25%, followed by Turks in North Macedonia, Turks, Romani people in North Macedonia, Roma, Serbs in North Macedonia, Serbs, Bosniaks in North Macedonia, Bosniaks, Aromanians in North Macedonia, Aromanians and a few other minorities. The region's history begins with the Paeonia (kingdom), kingdom of Paeonia. In the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ius Italicum
''Ius Italicum'' or ''ius italicum'' (Latin, Italian or Italic law) was a law in the early Roman Empire that allowed the emperors to grant cities outside Italy the legal fiction that they were on Italian soil. This meant that the city would be governed under Roman law rather than local law, and it would have a greater degree of autonomy in their relations with provincial governors. As Roman citizens, people were able to buy and sell property, were exempt from land tax and the poll tax, and were entitled to protection under Roman law. ''Ius Italicum'' was the highest liberty a municipality or province could obtain and was considered very favorable. Emperors, such as Augustus and Septimius Severus, made use of the law during their reign. Augustus' enactment of the law Emperor Augustus was one of the first Emperors to implement the law of ''Ius Italicum'' during his reign. During Emperor Augustus' reign he gave land-grants to veterans who participated in civil wars to reward them f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |