|
Steroidogenic Enzyme
__NOTOC__ Steroidogenic enzymes are enzymes that are involved in steroidogenesis and steroid biosynthesis. They are responsible for the biosynthesis of the steroid hormones, including sex steroids (androgens, estrogens, and progestogens) and corticosteroids (glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids), as well as neurosteroids, from cholesterol. Steroidogenic enzymes are most highly expressed in classical steroidogenic tissues, such as the testis, ovary, and adrenal cortex, but are also present in other tissues in the body. List of steroidogenic enzymes * Steroid desmolases ** Cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme (20,22-desmolase) – steroid synthesis ** 17,20-Lyase (17,20-desmolase) – androgen synthesis * Steroid hydroxylases ** 11β-Hydroxylase – corticosteroid synthesis ** 17α-Hydroxylase – androgen and glucocorticoid synthesis ** 18-Hydroxylase (aldosterone synthase) – mineralocorticoid synthesis ** 21-Hydroxylase – corticosteroid synthesis ** Cytochrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroidogenesis
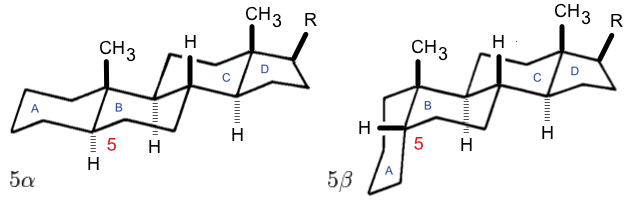
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules. Examples include the lipid cholesterol, sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, anabolic steroids, and the anti-inflammatory corticosteroid drug dexamethasone. Hundreds of steroids are found in fungi, plants, and animals. All steroids are manufactured in cells from a sterol: cholesterol (animals), lanosterol ( opisthokonts), or cycloartenol (plants). All three of these molecules are produced via cyclization of the triterpene squalene. Structure The steroid nucleus ( core structure) is called gonane (cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene). It is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in four fused rings: three six-member cyclohexane rings (rings A, B and C in the first illustrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testis
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, primarily testosterone. The release of testosterone is regulated by luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary gland. Sperm production is controlled by follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) from the anterior pituitary gland and by testosterone produced within the gonads. Structure Appearance Males have two testicles of similar size contained within the scrotum, which is an extension of the abdominal wall. Scrotal asymmetry, in which one testicle extends farther down into the scrotum than the other, is common. This is because of the differences in the vasculature's anatomy. For 85% of men, the right testis hangs lower than the left one. Measurement and volume The volume of the testicle can be estimated by palpating it and compari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CYP3
Cytochromes P450 (P450s or CYPs) are a superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that mostly, but not exclusively, function as monooxygenases. However, they are not omnipresent; for example, they have not been found in ''Escherichia coli''. In mammals, these enzymes oxidize steroids, fatty acids, xenobiotics, and participate in many biosyntheses. By hydroxylation, CYP450 enzymes convert xenobiotics into hydrophilic derivatives, which are more readily excreted. P450s are, in general, the terminal oxidase enzymes in electron transfer chains, broadly categorized as P450-containing systems. The term "P450" is derived from the spectrophotometric peak at the wavelength of the absorption maximum of the enzyme (450 nm) when it is in the reduced state and complexed with carbon monoxide. Most P450s require a protein partner to deliver one or more electrons to reduce the iron (and eventually molecular oxygen). Nomenclature Genes encoding P450 enzymes, and the enzyme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (P450s or CYPs) are a Protein superfamily, superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor that mostly, but not exclusively, function as monooxygenases. However, they are not omnipresent; for example, they have not been found in ''Escherichia coli''. In mammals, these enzymes oxidize steroids, fatty acids, xenobiotics, and participate in many biosyntheses. By hydroxylation, CYP450 enzymes convert xenobiotics into hydrophilic derivatives, which are more readily excreted. P450s are, in general, the terminal oxidase enzymes in electron transfer chains, broadly categorized as P450-containing systems. The term "P450" is derived from the spectrophotometry, spectrophotometric peak at the wavelength of the absorption spectroscopy, absorption maximum of the enzyme (450 nanometre, nm) when it is in the redox, reduced state and complexed with carbon monoxide. Most P450s require a protein partner to deliver one or more electrons to reduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
21-Hydroxylase
Steroid 21-hydroxylase is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CYP21A2'' gene. The protein is an enzyme that hydroxylates steroids at the C21 position on the molecule. Naming conventions for enzymes are based on the substrate acted upon and the chemical process performed. Biochemically, this enzyme is involved in the biosynthesis of the adrenal gland hormones aldosterone and cortisol, which are important in blood pressure regulation, sodium homeostasis and blood sugar control. The enzyme converts progesterone and 17α-hydroxyprogesterone into 11-deoxycorticosterone and 11-deoxycortisol, respectively, within metabolic pathways which in humans ultimately lead to aldosterone and cortisol creation—deficiency in the enzyme may cause congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Steroid 21-hydroxylase is a member of the cytochrome P450 family of monooxygenase enzymes that use an iron-containing heme cofactor to oxidize substrates. In humans, the enzyme is localized in endoplasmic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18-Hydroxylase
Aldosterone synthase, also called steroid 18-hydroxylase, corticosterone 18-monooxygenase or P450C18, is a steroid hydroxylase cytochrome P450 enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of the mineralocorticoid aldosterone and other steroids. The enzyme catalyzes sequential hydroxylations of the steroid angular methyl group at C18 after initial 11β-hydroxylation (the enzyme has steroid 18-hydroxylase activity as well as steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase activity). It is encoded by the gene in humans. Aldosterone synthase is a protein which is only expressed in the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex and is primarily regulated by the renin–angiotensin system. It is the sole enzyme capable of synthesizing aldosterone in humans and plays an important role in electrolyte balance and blood pressure. Genetics Aldosterone synthase is encoded on chromosome 8q22 by the ''CYP11B2'' gene. The gene contains 9 exons and spans roughly 7000 base pairs of DNA. ''CYP11B2'' is closely related with '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroid Hydroxylase
A steroid hydroxylase is a class of hydroxylase enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of steroids. See also * Steroidogenic enzyme Additional images File:Steroidogenesis.svg, Steroidogenesis Image:Steroid numbering.svg, Steroid nomenclature — numbering of carbons Image:DHEA1.svg, Production of DHEA from Cholesterol References External links * EC 1.14 Steroids {{1.14-enzyme-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CYP17A1
Cytochrome P450 17A1 (steroid 17α-monooxygenase, 17α-hydroxylase, 17-alpha-hydroxylase, 17,20-lyase, 17,20-desmolase) is an enzyme of the hydroxylase type that in humans is encoded by the ''CYP17A1'' gene on chromosome 10. It is ubiquitously expressed in many tissues and cell types, including the zona reticularis and zona fasciculata (but not zona glomerulosa) of the adrenal cortex as well as gonadal tissues. It has both 17α-hydroxylase and 17,20-lyase activities, and is a key enzyme in the steroidogenic pathway that produces progestins, mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, androgens, and estrogens. More specifically, the enzyme acts upon pregnenolone and progesterone to add a hydroxyl (-OH) group at carbon 17 position (C17) of the steroid D ring (the 17α-hydroxylase activity, ), or acts upon 17α-hydroxyprogesterone and 17α-hydroxypregnenolone to split the side-chain off the steroid nucleus (the 17,20- lyase activity, ). Structure Gene The ''CYP17A1'' gene resi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholesterol Side-chain Cleavage Enzyme
Cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme is commonly referred to as P450scc, where "scc" is an abbreviation for side-chain cleavage. P450scc is a mitochondrial enzyme that catalyzes conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone. This is the first reaction in the process of steroidogenesis in all mammalian tissues that specialize in the production of various steroid hormones. P450scc is a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes (family 11, subfamily A, polypeptide 1) and is encoded by the gene. Nomenclature The systematic name of this enzyme class is cholesterol, reduced-adrenal-ferredoxin:oxygen oxidoreductase (side-chain-cleaving). Other names include: * C27-side-chain cleavage enzyme * cholesterol 20-22-desmolase * cholesterol C20-22 desmolase * cholesterol desmolase * cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme * cholesterol side-chain-cleaving enzyme * cytochrome P-450scc * desmolase, steroid 20-22 * enzymes, cholesterol side-chain-cleaving * steroid 20-2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |