|
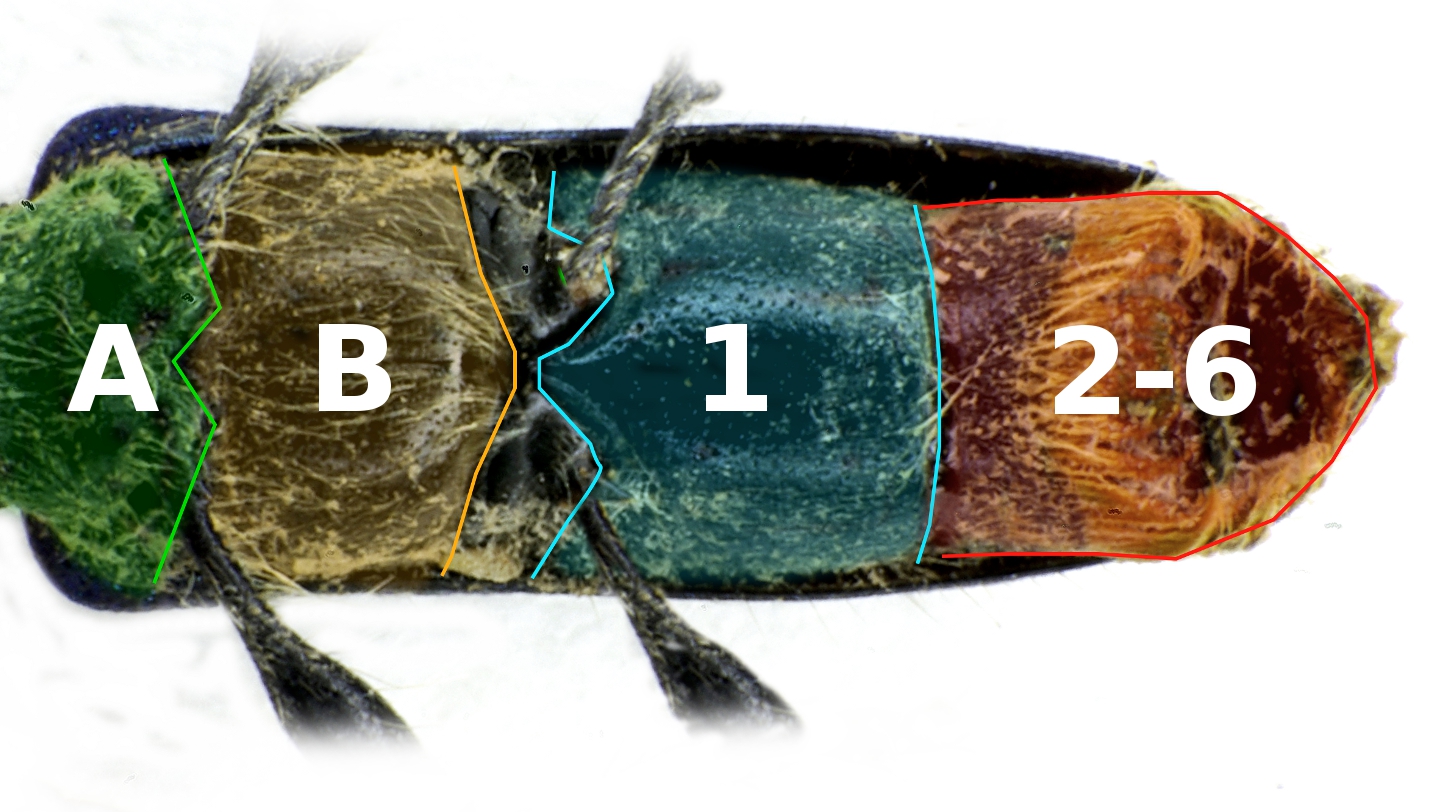
Sternum (arthropod)
The sternum (: sterna) is the ventral portion of a segment of an arthropod thorax or abdomen. In insects, the sterna are usually single, large sclerites, and external. However, they can sometimes be divided in two or more, in which case the subunits are called sternites, and may also be modified on the terminal abdominal segments so as to form part of the functional genitalia, in which case they are frequently reduced in size and development, and may become internalized and/or membranous. For a detailed explanation of the terminology, see Kinorhynchs have tergal and sternal plates too, though seemingly not homologous with those of arthropods.Sørensen, M. V. et al. Phylogeny of Kinorhyncha based on morphology and two molecular loci. PLoS One 10, 1–33 (2015). Ventrites are externally visible sternites. Usually the first sternite is covered up, so that ventrite numbers do not correspond to sternite numbers. The term is also used in other arthropod groups such as crustace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthropods including decapods (shrimps, prawns, crabs, lobsters and crayfish), seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, opossum shrimps, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods (insects and entognathans) emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed pan-group referred to as Pancrustacea. The three classes Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda and Remipedia are more closely related to the hexapods than they are to any of the other crustaceans ( oligostracans and multicrustaceans). The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalothorax
The cephalothorax, also called prosoma in some groups, is a tagma of various arthropods, comprising the head and the thorax fused together, as distinct from the abdomen behind. (The terms ''prosoma'' and ''opisthosoma'' are equivalent to ''cephalothorax'' and ''abdomen'' in some groups. The terms ''prosoma'' and ''opisthosoma'' may be preferred by some researchers in cases such as arachnids, where there is neither fossil nor embryonic evidence animals in this class have ever had separate heads and thoraxes, and where the ''opisthosoma'' contains organs atypical of a true ''abdomen'', such as a heart and respiratory organs.) The word ''cephalothorax'' is derived from the Greek words for head (, ') and thorax (, '). This fusion of the head and thorax is seen in chelicerates and crustaceans; in other groups, such as the Hexapoda (including insect Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spider
Spiders (order (biology), order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight limbs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude spider silk, silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all Order (biology), orders of organisms. Spiders are found worldwide on every continent except Antarctica, and have become established in nearly every land habitat. , 53,034 spider species in 136 Family (biology), families have been recorded by Taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. However, there has been debate among scientists about how families should be classified, with over 20 different classifications proposed since 1900. Anatomy, Anatomically, spiders (as with all arachnids) differ from other arthropods in that the usual body segmentation (biology), segments are fused into two Tagma (biology), tagmata, the cephalothorax or prosoma, and the opisthosoma, or abdomen, and joined by a small, cylindr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
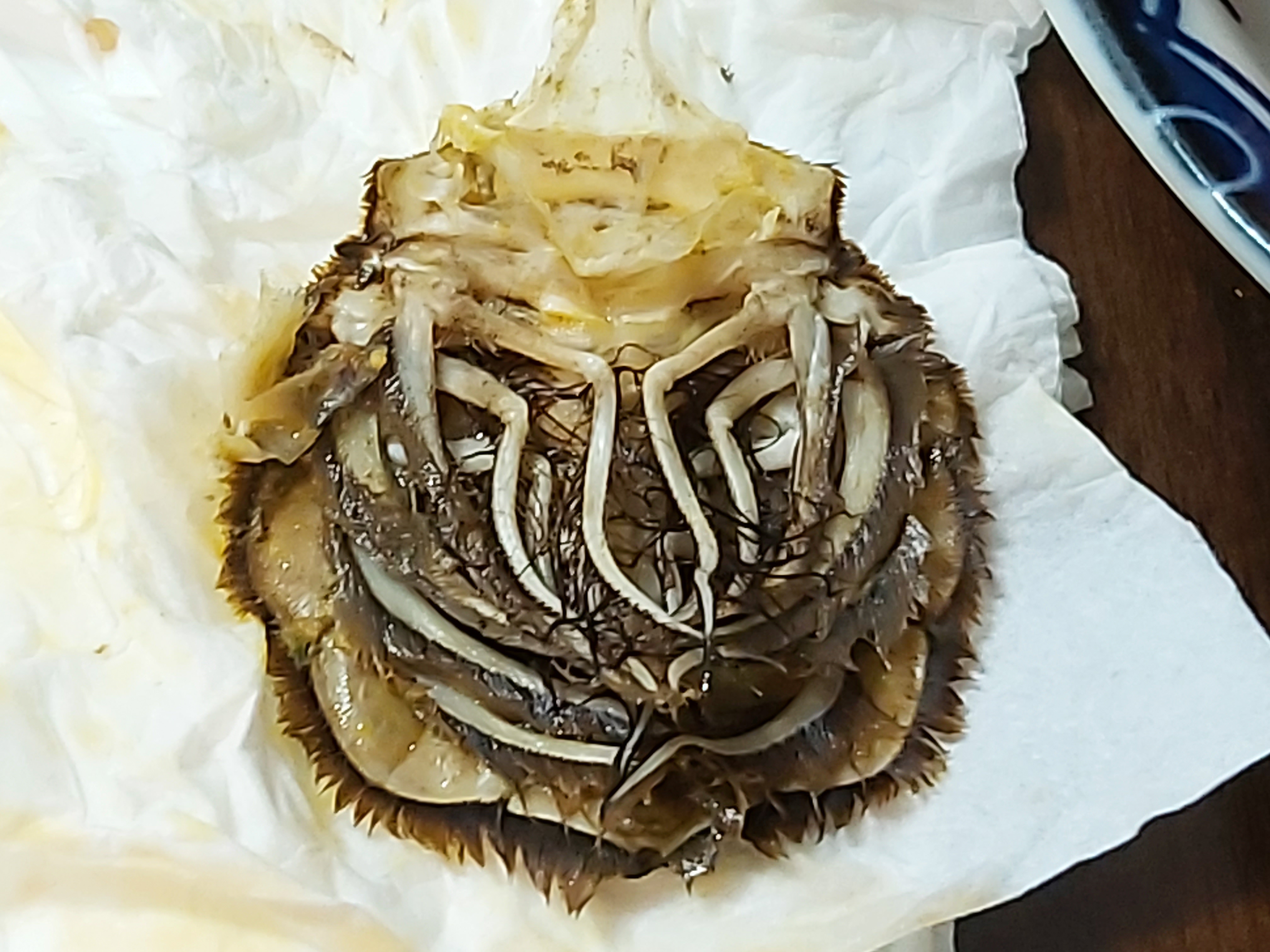
Pleopod
The anatomy of a decapod consists of 20 body segments grouped into two main body parts: the cephalothorax and the pleon (abdomen). Each segment – often called a somite – may possess one pair of appendages, although in various groups these may be reduced or missing. Cephalothorax Head # antennules # antennae # mandibles # first maxillae # second maxillae The head also bears the (usually stalked) compound eyes. The distal portion of a mandible or maxilla which has a sensory function is known as a palp. Thorax / pereon #first maxillipeds #second maxillipeds #third maxillipeds #first pereiopods #second pereiopods #third pereiopods #fourth pereiopods #fifth pereiopods Maxillipeds are appendages modified to function as mouthparts. Particularly in the less advanced decapods, these can be very similar to the pereiopods. Pereiopods are primarily walking legs and are also used for gathering food. They are also the ten legs from which decapods take their name. Those pereiopods which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myriapod
Myriapods () are the members of subphylum Myriapoda, containing arthropods such as millipedes and centipedes. The group contains about 13,000 species, all of them terrestrial. Although molecular evidence and similar fossils suggests a diversification in the Cambrian Period, the oldest known fossil record of myriapods dates between the Late Silurian and Early Devonian, with '' Pneumodesmus'' preserving the earliest known evidence of air-breathing on land. Other early myriapod fossil species around the similar time period include '' Kampecaris obanensis'' and '' Archidesmus'' sp. The phylogenetic classification of myriapods is still debated. The scientific study of myriapods is myriapodology, and those who study myriapods are myriapodologists. Anatomy Myriapods have a single pair of antennae and, in most cases, simple eyes. Exceptions are the two classes of symphylans and pauropods, the millipede order Polydesmida and the centipede order Geophilomorpha, which are all ey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arachnid
Arachnids are arthropods in the Class (biology), class Arachnida () of the subphylum Chelicerata. Arachnida includes, among others, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, pseudoscorpions, opiliones, harvestmen, Solifugae, camel spiders, Amblypygi, whip spiders and Uropygi, vinegaroons. Adult arachnids have eight Arthropod leg, legs attached to the cephalothorax. In some species the frontmost pair of legs has converted to a sensory function, while in others, different appendages can grow large enough to take on the appearance of extra pairs of legs. Almost all Extant taxon, extant arachnids are terrestrial animal, terrestrial, living mainly on land. However, some inhabit freshwater environments and, with the exception of the pelagic zone, marine environments as well. They comprise over 110,000 named species, of which 51,000 are species of spiders. The term is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek word (''aráchnē'', 'spider'), from the myth of the hubristic human weaver Arachne, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinorhynchs
Kinorhyncha (, ' "snout") is a phylum (biology), phylum of small marine invertebrates that are widespread in mud or sand at all depths as part of the meiobenthos. They are commonly called mud dragons. Modern species are or less, but Cambrian forms could reach . Anatomy Kinorhynchs are limbless animals, with a body consisting of a head, neck, and a trunk of eleven segments. They are the only members of Ecdysozoa, except from the panarthropoda, with a segmented body. Juveniles have eight or nine segments, depending on genus, with the last two or three being added later during growth. A Cambrian species, Eokinorhynchus rarus, had about twice as many segments as present forms. Like other ecdysozoans they do not have external cilia, but instead have a number of spines along the body, plus up to seven circles of spines around the head. These spines are used for animal locomotion, locomotion, withdrawing the head and pushing forward, then gripping the substrate with the spines wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Location
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether a vertebrate is a biped or a quadruped, due to the difference in the neuraxis, or if an invertebrate is a non-bilaterian. A non-bilaterian has no anterior or posterior surface for example but can still have a descriptor used such as proximal or distal in relation to a body part that is nearest to, or furthest from its middle. International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standards for subdisciplines of anatomy. For example, '' Termi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genitalia
A sex organ, also known as a reproductive organ, is a part of an organism that is involved in sexual reproduction. Sex organs constitute the primary sex characteristics of an organism. Sex organs are responsible for producing and transporting gametes, as well as facilitating fertilization and supporting the development and birth of offspring. Sex organs are found in many species of animals and plants, with their features varying depending on the species. Sex organs are typically differentiated into male and female types. In animals (including humans), the male sex organs include the testicles, epididymides, and penis; the female sex organs include the clitoris, ovaries, oviducts, and vagina. The testicle in the male and the ovary in the female are called the ''primary sex organs''. All other sex-related organs are known as ''secondary sex organs''. The outer parts are known as the genitals or external genitalia, visible at birth in both sexes, while the inner parts are refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jones & Bartlett Publishers
Jones & Bartlett Learning, a division of Ascend Learning, is a scholarly publisher. The name comes from Donald W. Jones, the company's founder, and Arthur Bartlett, the first editor. History In 1988, the company was named by ''New England Business Magazine'' as one of the 100 fastest-growing companies in New England. In 1989, they opened their first office in London. In 1993, they opened an office in Singapore, and an office in Toronto in 1994. Their corporate headquarters moved to Sudbury, Massachusetts in 1995. In 2011, Jones & Bartlett Learning moved its offices in Sudbury and Maynard, Massachusetts to Burlington, Massachusetts, sharing a building with other Ascend Learning corporate offices. See also * National Healthcareer Association The National Healthcareer Association (NHA) is a national professional certification agency for healthcare workers in the United States. Granting credentials in more than 8 allied health specialties, it is an organizational member of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |