|
Stereotactic
Stereotactic surgery is a minimally invasive form of surgery, surgical intervention that makes use of a three-dimensional coordinates, coordinate system to locate small targets inside the body and to perform on them some action such as ablation, biopsy, lesion, injection, Deep brain stimulation, stimulation, implantation, radiosurgery (SRS), etc. In theory, any organ system inside the body can be subjected to stereotactic surgery. However, difficulties in setting up a reliable frame of reference (such as bone landmarks, which bear a constant spatial relation to soft tissues) mean that its applications have been, traditionally and until recently, limited to neurosurgery, brain surgery. Besides the brain, biopsy and surgery of the breast are done routinely to locate, sample (biopsy), and remove tissue. Plain X-ray images (radiography, radiographic mammography), computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging can be used to Image-guided surgery, guide the procedure. Another acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiosurgery
Radiosurgery is surgery using radiation, that is, the destruction of precisely selected areas of tissue using ionizing radiation rather than excision with a blade. Like other forms of radiation therapy (also called radiotherapy), it is usually used to treat cancer. Radiosurgery was originally defined by the Swedish neurosurgeon Lars Leksell as "a single high dose fraction of radiation, stereotactically directed to an intracranial region of interest". In stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), the word "stereotactic" refers to a three-dimensional coordinate system that enables accurate correlation of a virtual target seen in the patient's diagnostic images with the actual target position in the patient. Stereotactic radiosurgery may also be called stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) or stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) when used outside the central nervous system (CNS). History Stereotactic radiosurgery was first developed in 1949 by the Swedish neurosurgeon Lars Leksell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
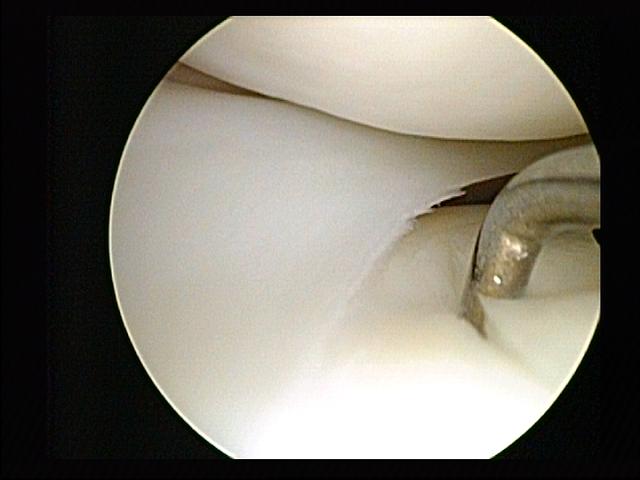
Vestibular Schwannoma
A vestibular schwannoma (VS), also called acoustic neuroma, is a benign tumor that develops on the vestibulocochlear nerve that passes from the inner ear to the brain. The tumor originates when Schwann cells that form the insulating myelin sheath on the nerve malfunction. Normally, Schwann cells function beneficially to protect the nerves which transmit balance and sound information to the brain. However, sometimes a mutation in the tumor suppressor gene, NF2, located on chromosome 22, results in abnormal production of the cell protein named ''Merlin'', and Schwann cells multiply to form a tumor. The tumor originates mostly on the vestibular division of the nerve rather than the cochlear division, but hearing as well as balance will be affected as the tumor enlarges. The great majority of these VSs (95%) are unilateral, in one ear only. They are called "sporadic" (i.e., by-chance, non-hereditary). Although non-cancerous, they can do harm or even become life-threatening if they gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurosurgery
Neurosurgery or neurological surgery, known in common parlance as brain surgery, is the specialty (medicine), medical specialty that focuses on the surgical treatment or rehabilitation of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the Human brain, brain, spinal cord, peripheral nervous system, and cerebrovascular system. Neurosurgery as a medical specialty also includes non-surgical management of some neurological conditions. Education and context In different countries, there are different requirements for an individual to legally practice neurosurgery, and there are varying methods through which they must be educated. In most countries, neurosurgeon training requires a minimum period of seven years after graduating from medical school. United Kingdom In the United Kingdom, students must gain entry into medical school. The MBBS qualification (Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery) takes four to six years depending on the student's route. The newly qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a type of neurostimulation therapy in which an implantable pulse generator is stereotactic surgery, surgically implanted subcutaneous tissue, below the skin of the chest and connected by Lead (electronics), leads to the brain to deliver controlled electrical charge, electrical impulses. These charges therapeutically disrupt and promote dysfunctional nervous system circuits bidirectionally in both ante- and retrograde signaling, retrograde directions. Though first developed for Parkinsonian tremor, the technology has since been adapted to a wide variety of chronic neurologic disorders. The usage of electrical stimulation to treat neurologic disorders dates back thousands of years to ancient Greece and Early Dynastic Period (Egypt), dynastic Egypt. The distinguishing feature of DBS, however, is that by taking advantage of the portability of lithium-ion battery technology, it is able to be used long term without the patient having to be Electrical wir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computed Tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry to measure X-ray attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, it can also be used to form images of non-living objects. The 1979 N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to form images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimally Invasive
Minimally invasive procedures (also known as minimally invasive surgeries) encompass surgical techniques that limit the size of incisions needed, thereby reducing wound healing time, associated pain, and risk of infection. Surgery by definition is invasive, and many operations requiring incisions of some size are referred to as ''open surgery''. Incisions made during open surgery can sometimes leave large wounds that may be painful and take a long time to heal. Advancements in medical technologies have enabled the development and regular use of minimally invasive procedures. For example, endovascular aneurysm repair, a minimally invasive surgery, has become the most common method of repairing abdominal aortic aneurysms in the US as of 2003. The procedure involves much smaller incisions than the corresponding open surgery procedure of open aortic surgery. Interventional radiologists were the forerunners of minimally invasive procedures. Using imaging techniques, radiologist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigeminal Neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN or TGN), also called Fothergill disease, tic douloureux, trifacial neuralgia, is a chronic pain, long-term pain disorder that affects the trigeminal nerve, the nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing. It is a form of neuropathic pain. There are two main types: typical and atypical trigeminal neuralgia. The typical form results in episodes of severe, sudden, shock-like pain in one side of the face that lasts for seconds to a few minutes. Groups of these episodes can occur over a few hours. The atypical form results in a constant burning pain that is less severe. Episodes may be triggered by any touch to the face. Both forms may occur in the same person. Pain from the disease has been linked to mental health issues, especially depression (mood), depression. The exact cause is unknown, but believed to involve loss of the myelin of the trigeminal nerve. This might occur due to Nerve compression syndrome, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image-guided Surgery
Image-guided surgery (IGS) is any surgical procedure where the surgeon uses tracked surgical instruments in conjunction with preoperative or intraoperative images in order to directly or indirectly guide the procedure. Image guided surgery systems use cameras, ultrasonic, electromagnetic or a combination of fields to capture and relay the patient's anatomy and the surgeon's precise movements in relation to the patient, to computer monitors in the operating room or to augmented reality headsets (augmented reality surgical navigation technology). This is generally performed in real-time though there may be delays of seconds or minutes depending on the modality and application. Image-guided surgery helps surgeons perform safer and less invasive procedures and has become a recognized standard of care in managing disorders including cranial, otorhinolaryngology, spine, orthopedic, and cardiovascular. Benefits The benefits of Image-guided surgery include greater control of the surgical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pituitary Adenoma
Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland. Most pituitary tumors are benign, approximately 35% are invasive and just 0.1% to 0.2% are carcinomas.Pituitary Tumors Treatment (PDQ®)–Health Professional Version NIH National Cancer Institute Pituitary adenomas represent from 10% to 25% of all intracranial neoplasia, neoplasms, with an estimated prevalence, prevalence rate in the general population of approximately 17%. Non-invasive and non-secreting pituitary adenomas are considered to be Benign tumors, benign in the literal as well as the clinical sense, though a 2011 meta-analysis of available research showed that research to either support or refute this assumption was scant and of questionable qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glioblastoma
Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is the most aggressive and most common type of cancer that originates in the brain, and has a very poor prognosis for survival. Initial signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nonspecific. They may include headaches, personality changes, nausea, and symptoms similar to those of a stroke. Symptoms often worsen rapidly and may progress to unconsciousness. The cause of most cases of glioblastoma is not known. Uncommon risk factors include genetic disorders, such as neurofibromatosis and Li–Fraumeni syndrome, and previous radiation therapy. Glioblastomas represent 15% of all brain tumors. They are thought to arise from astrocytes. The diagnosis typically is made by a combination of a CT scan, MRI scan, and tissue biopsy. There is no known method of preventing the cancer. Treatment usually involves surgery, after which chemotherapy and radiation therapy are used. The medication temozolomide is frequently used a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whole Brain Radiotherapy
Whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) is a treatment option for patients with brain metastases. In WBRT, radiation therapy is administered broadly, to the whole brain, over multiple treatments. Usage WBRT has been shown to alleviate symptoms, decrease the use of corticosteroids needed to control tumor-associated edema, and potentially improve overall survival. However, WBRT has been reported to increase the risk of cognitive decline. However, single trials suggest that WBRT with memantine or hippocampal sparing may delay cognitive decline, though these methods did not improve survival or quality of life. WBRT may be administered in combination with stereotactic radiosurgery Stereotactic surgery is a minimally invasive form of surgery, surgical intervention that makes use of a three-dimensional coordinates, coordinate system to locate small targets inside the body and to perform on them some action such as ablation, ... (SRS), surgery, or systemic therapies. Based on data, WBR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |