|
Stem Cell Transplantation
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood, in order to replicate inside a patient and produce additional normal blood cells. HSCT may be autologous (the patient's own stem cells are used), syngeneic (stem cells from an identical twin), or allogeneic (stem cells from a donor). It is most often performed for patients with certain cancers of the blood or bone marrow, such as multiple myeloma, leukemia, some types of lymphoma and immune deficiencies. In these cases, the recipient's immune system is usually suppressed with radiation or chemotherapy before the transplantation. Infection and graft-versus-host disease are major complications of allogeneic HSCT. HSCT remains a dangerous procedure with many possible complications; it is reserved for patients with life-threatening diseases. As survival following the procedure has increas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organ Transplantation
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organs may be transported from a donor site to another location. Organs and/or tissues that are transplanted within the same person's body are called autografts. Transplants that are recently performed between two subjects of the same species are called allografts. Allografts can either be from a living or cadaveric source. Organs that have been successfully transplanted include the heart, kidneys, liver, lungs, pancreas, intestine, thymus and uterus. Tissues include bones, tendons (both referred to as musculoskeletal grafts), corneae, skin, heart valves, nerves and veins. Worldwide, the kidneys are the most commonly transplanted organs, followed by the liver and then the heart. J. Hartwell Harrison performed the first organ removal for transplant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
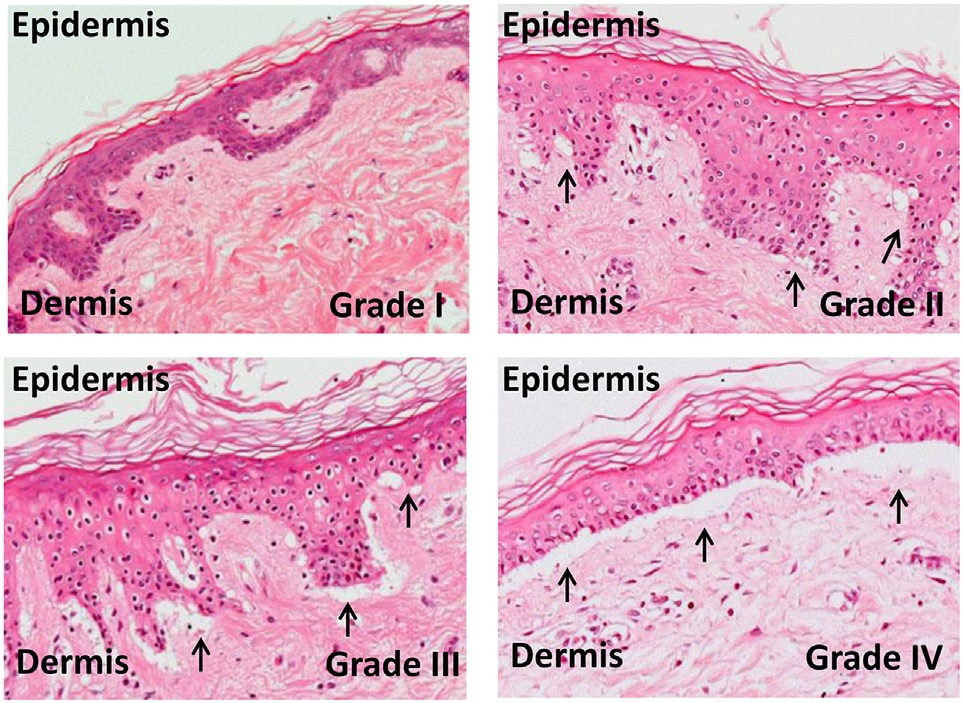
Graft-versus-host Disease
Graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) is a syndrome, characterized by inflammation in different organs. GvHD is commonly associated with bone marrow transplants and stem cell transplants. White blood cells of the donor's immune system which remain within the donated tissue (the graft) recognize the recipient (the host) as foreign (non-self). The white blood cells present within the transplanted tissue then attack the recipient's body's cells, which leads to GvHD. This should not be confused with a transplant rejection, which occurs when the immune system of the transplant recipient rejects the transplanted tissue; GvHD occurs when the donor's immune system's white blood cells reject the recipient. The underlying principle ( alloimmunity) is the same, but the details and course may differ. GvHD can also occur after a blood transfusion, known as ''Transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease'' or TA-GvHD if the blood products used have not been gamma irradiated or treated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroblastoma
Neuroblastoma (NB) is a type of cancer that forms in certain types of nerve tissue. It most frequently starts from one of the adrenal glands but can also develop in the head, neck, chest, abdomen, or Vertebral column, spine. Symptoms may include bone pain, a lump in the abdomen, neck, or chest, or a painless bluish lump under the skin. Typically, neuroblastoma occurs due to a genetic mutation occurring in the first trimester of pregnancy. Rarely, it may be due to a mutation heredity, inherited. Environmental factors have not been found to be involved. Diagnosis is based on a tissue biopsy. Occasionally, it may be found in a baby by ultrasound during pregnancy. At diagnosis, the cancer has usually already Metastasis, spread. The cancer is divided into low-, intermediate-, and high-risk groups based on a child's age, cancer stage, and what the cancer looks like. Treatment and outcomes depends on the risk group a person is in. Treatments may include observation, surgery, radiatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), also known as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a group of blood cancers that includes all types of lymphomas except Hodgkin lymphomas. Symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and tiredness. Other symptoms may include bone pain, chest pain, or itchiness. Some forms are slow-growing while others are fast-growing. Unlike Hodgkin lymphoma, which spreads contiguously, NHL is largely a systemic illness. Signs and symptoms The signs and symptoms of non-Hodgkin lymphoma vary depending upon its location within the body. Symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and tiredness. Other symptoms may include bone pain, chest pain, or itchiness. Some forms are slow growing, while others are fast growing. Enlarged lymph nodes may cause lumps to be felt under the skin when they are close to the surface of the body. Lymphomas in the skin may also result in lumps, which are commonly itchy, red, or purple. Ly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hodgkin Lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the lymph nodes. The condition was named after the English physician Thomas Hodgkin, who first described it in 1832. Symptoms may include fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Often, non-painful lymphadenopathy, enlarged lymph nodes occur in the neck, under the arm, or in the groin. Persons affected may feel tired or be itchy. The two major types of Hodgkin lymphoma are classic Hodgkin lymphoma and nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. About half of cases of Hodgkin lymphoma are due to Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) and these are generally the classic form. Other risk factors include a family history of the condition and having HIV/AIDS. Diagnosis is conducted by confirming the presence of cancer and identifying Reed–Sternberg cells in lymph node biopsies. The virus-posi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia
Juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML) is a rare form of chronic leukemia (cancer of the blood) that affects children, commonly those aged four and younger. The name JMML now encompasses all diagnoses formerly referred to as juvenile chronic myeloid leukemia (JCML), chronic myelomonocytic leukemia of infancy, and infantile monosomy 7 syndrome. The average age of patients at diagnosis is two (2) years old. The World Health Organization has included JMML as a subcategory of myelodysplastic and myeloproliferative disorders. Signs and symptoms The following symptoms are typical ones that lead to testing for JMML, though children with JMML may exhibit any combination of them: * pallor * fever * infection * bleeding * cough * poor weight gain * a maculopapular rash (discolored but not raised, or small and raised but not containing pus) * lymphadenopathy * moderate hepatomegaly * marked splenomegaly * leukocytosis * absolute monocytosis * anemia * thrombocytopenia Most of these c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a cancer of the Lymphocyte, lymphoid line of blood cells characterized by the development of large numbers of lymphoblast, immature lymphocytes. Symptoms may include feeling tired, pale skin color, fever, easy bleeding or bruising, lymphadenopathy, enlarged lymph nodes, or bone pain. As an acute leukemia, ALL progresses rapidly and is typically fatal within weeks or months if left untreated. In most cases, the cause is unknown. Genetic risk factors may include Down syndrome, Li–Fraumeni syndrome, or neurofibromatosis type 1. Environmental risk factors may include significant radiation exposure or prior chemotherapy. Evidence regarding electromagnetic fields or pesticides is unclear. Some hypothesize that an abnormal immune response to a common infection may be a trigger. The underlying mechanism involves multiple genetic mutations that results in rapid cell division. The excessive immature lymphocytes in the bone marrow interfere with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), also known as chronic myeloid leukemia, is a cancer of the white blood cells. It is a form of leukemia characterized by the increased and unregulated growth of myeloid cells in the bone marrow and the accumulation of these cells in the blood. CML is a clonal bone marrow stem cell disorder in which a proliferation of mature granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils) and their precursors is found; characteristic increase in basophils is clinically relevant. It is a type of myeloproliferative neoplasm associated with a characteristic chromosomal translocation called the Philadelphia chromosome. CML is largely treated with targeted drugs called tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (TKIs) which have led to dramatically improved long-term survival rates since 2001. These drugs have revolutionized treatment of this disease and allow most patients to have a good quality of life when compared to the former chemotherapy drugs. In Western countries, CM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with haematopoiesis, normal blood cell production. Symptoms may include Fatigue, feeling tired, shortness of breath, Bruise, easy bruising and bleeding, and increased risk of infection. Occasionally, spread may occur to the brain, skin, or gums. As an acute leukemia, AML progresses rapidly, and is typically fatal within weeks or months if left untreated. Risk factors include getting older, being male, smoking, previous chemotherapy or radiation therapy, myelodysplastic syndrome, and exposure to the chemical benzene. The underlying mechanism involves replacement of normal bone marrow with leukemia cells, which results in a anemia, drop in red blood cells, thrombocytopenia, platelets, and normal leukopenia, white blood cells. Diagnosis is generally based on bone marrow aspiration and specific bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Spectrum Of Target Antigens Associated With Tumor Immunity And Allo-immunity After Allogeneic HSCT
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucopolysaccharidosis
Mucopolysaccharidoses are a group of metabolic disorders caused by the absence or malfunctioning of lysosomal enzymes needed to break down molecules called glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). These long chains of sugar carbohydrates occur within the cells that help build bone, cartilage, tendons, corneas, skin and connective tissue. GAGs (formerly called mucopolysaccharides) are also found in the fluids that lubricate joints. Individuals with mucopolysaccharidosis either do not produce enough of one of the eleven enzymes required to break down these sugar chains into simpler molecules, or they produce enzymes that do not work properly. Over time, these GAGs collect in the cells, blood and connective tissues. The result is permanent, progressive cellular damage which affects appearance, physical abilities, organ and system functioning. The mucopolysaccharidoses are part of the lysosomal storage disease family, a group of genetic disorders that result when the lysosome organelle in anim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |