|
Statistic
A statistic (singular) or sample statistic is any quantity computed from values in a sample which is considered for a statistical purpose. Statistical purposes include estimating a population parameter, describing a sample, or evaluating a hypothesis. The average (or mean) of sample values is a statistic. The term statistic is used both for the function and for the value of the function on a given sample. When a statistic is being used for a specific purpose, it may be referred to by a name indicating its purpose. When a statistic is used for estimating a population parameter, the statistic is called an '' estimator''. A population parameter is any characteristic of a population under study, but when it is not feasible to directly measure the value of a population parameter, statistical methods are used to infer the likely value of the parameter on the basis of a statistic computed from a sample taken from the population. For example, the sample mean is an unbiased estimato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Hypothesis Testing
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of statistical inference used to decide whether the data at hand sufficiently support a particular hypothesis. Hypothesis testing allows us to make probabilistic statements about population parameters. History Early use While hypothesis testing was popularized early in the 20th century, early forms were used in the 1700s. The first use is credited to John Arbuthnot (1710), followed by Pierre-Simon Laplace (1770s), in analyzing the human sex ratio at birth; see . Modern origins and early controversy Modern significance testing is largely the product of Karl Pearson ( ''p''-value, Pearson's chi-squared test), William Sealy Gosset ( Student's t-distribution), and Ronald Fisher ("null hypothesis", analysis of variance, " significance test"), while hypothesis testing was developed by Jerzy Neyman and Egon Pearson (son of Karl). Ronald Fisher began his life in statistics as a Bayesian (Zabell 1992), but Fisher soon grew disenchanted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Statistic
In statistics, the ''k''th order statistic of a statistical sample is equal to its ''k''th-smallest value. Together with rank statistics, order statistics are among the most fundamental tools in non-parametric statistics and inference. Important special cases of the order statistics are the minimum and maximum value of a sample, and (with some qualifications discussed below) the sample median and other sample quantiles. When using probability theory to analyze order statistics of random samples from a continuous distribution, the cumulative distribution function is used to reduce the analysis to the case of order statistics of the uniform distribution. Notation and examples For example, suppose that four numbers are observed or recorded, resulting in a sample of size 4. If the sample values are :6, 9, 3, 8, the order statistics would be denoted :x_=3,\ \ x_=6,\ \ x_=8,\ \ x_=9,\, where the subscript enclosed in parentheses indicates the th order statistic of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median
In statistics and probability theory, the median is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample, a population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as "the middle" value. The basic feature of the median in describing data compared to the mean (often simply described as the "average") is that it is not skewed by a small proportion of extremely large or small values, and therefore provides a better representation of a "typical" value. Median income, for example, may be a better way to suggest what a "typical" income is, because income distribution can be very skewed. The median is of central importance in robust statistics, as it is the most resistant statistic, having a breakdown point of 50%: so long as no more than half the data are contaminated, the median is not an arbitrarily large or small result. Finite data set of numbers The median of a finite list of numbers is the "middle" number, when those numbers are list ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-statistic
In statistics, the ''t''-statistic is the ratio of the departure of the estimated value of a parameter from its hypothesized value to its standard error. It is used in hypothesis testing via Student's ''t''-test. The ''t''-statistic is used in a ''t''-test to determine whether to support or reject the null hypothesis. It is very similar to the z-score but with the difference that ''t''-statistic is used when the sample size is small or the population standard deviation is unknown. For example, the ''t''-statistic is used in estimating the population mean from a sampling distribution of sample means if the population standard deviation is unknown. It is also used along with p-value when running hypothesis tests where the p-value tells us what the odds are of the results to have happened. Definition and features Let \hat\beta be an estimator of parameter ''β'' in some statistical model. Then a ''t''-statistic for this parameter is any quantity of the form : t_ = \f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Descriptive Statistic
A descriptive statistic (in the count noun sense) is a summary statistic that quantitatively describes or summarizes features from a collection of information, while descriptive statistics (in the mass noun sense) is the process of using and analysing those statistics. Descriptive statistic is distinguished from inferential statistics (or inductive statistics) by its aim to summarize a sample, rather than use the data to learn about the population that the sample of data is thought to represent. This generally means that descriptive statistics, unlike inferential statistics, is not developed on the basis of probability theory, and are frequently nonparametric statistics. Even when a data analysis draws its main conclusions using inferential statistics, descriptive statistics are generally also presented. For example, in papers reporting on human subjects, typically a table is included giving the overall sample size, sample sizes in important subgroups (e.g., for each treatment o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
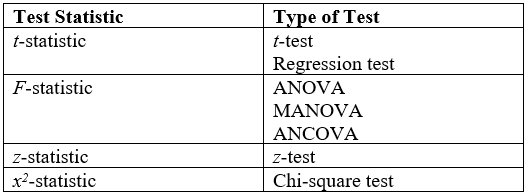
Test Statistic A test statistic is a statistic (a quantity derived from the sample) used in statistical hypothesis testing.Berger, R. L.; Casella, G. (2001). ''Statistical Inference'', Duxbury Press, Second Edition (p.374) A hypothesis test is typically specified in terms of a test statistic, considered as a numerical summary of a data-set that reduces the data to one value that can be used to perform the hypothesis test. In general, a test statistic is selected or defined in such a way as to quantify, within observed data, behaviours that would distinguish the null from the alternative hypothesis, where such an alternative is prescribed, or that would characterize the null hypothesis if there is no explicitly stated alternative hypothesis. An important property of a test statistic is that its sampling distribution under the |