|
Stanley Bay, New Zealand
Stanley Point (previously Stanley Bay) is a small suburb located on the North Shore, New Zealand, North Shore of Auckland, New Zealand, near Devonport, another suburb. It is mostly residential. The Devonport Naval Base lies to the east of the bay on the south side of the Stanley Bay peninsula and is connected to storage facilities on the north side at Ngataringa Bay by a tunnel. Name The suburb was known as Stanley Bay until December 2007 when New Zealand Geographic Board, The New Zealand Geographic Board (Ngā Pou Taunaha o Aotearoa) officially named the suburb as Stanley Point. The area is named after Owen Stanley, captain of , who conducted a survey of the Waitematā Harbour in 1841. During the construction of the Calliope Dock in the 1880s, Stanley Bay was home to a Māori people, Māori village for the labourers who worked on the dock construction. Demographics Stanley Point covers and had an estimated population of as of with a population density of people per km2. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auckland
Auckland ( ; ) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. It has an urban population of about It is located in the greater Auckland Region, the area governed by Auckland Council, which includes outlying rural areas and the islands of the Hauraki Gulf, and which has a total population of as of It is the List of cities in New Zealand, most populous city of New Zealand and the List of cities in Oceania by population, fifth-largest city in Oceania. The city lies between the Hauraki Gulf to the east, the Hunua Ranges to the south-east, the Manukau Harbour to the south-west, and the Waitākere Ranges and smaller ranges to the west and north-west. The surrounding hills are covered in rainforest and the landscape is dotted with 53 volcanic centres that make up the Auckland Volcanic Field. The central part of the urban area occupies a narrow isthmus between the Manukau Harbour on the Tasman Sea and the Waitematā Harbour on the Pacific Ocean. Auckland is one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2013 New Zealand Census
The 2013 New Zealand census was the thirty-third national census. "The National Census Day" used for the census was on Tuesday, 5 March 2013. The population of New Zealand was counted as 4,242,048 – an increase of 214,101 or 5.3% over the 2006 census. The 2013 census forms were the same as those developed for the 2011 census which was cancelled due to the February 2011 major earthquake in Christchurch. There were no new topics or questions. New Zealand's next census was conducted in March 2018. Collection methods The results from the post-enumeration survey showed that the 2013 census recorded 97.6 percent of the residents in New Zealand on census night. However, the overall response rate was 92.9 percent, with a non-response rate of 7.1 percent made up of the net undercount and people who were counted in the census but had not received a form. Results Population and dwellings Population counts for New Zealand regions. Note: All figures are for the census usually resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irreligion In New Zealand
Irreligion in New Zealand refers to atheism, agnosticism, deism, religious scepticism and secular humanism in New Zealand society. Post-war New Zealand has become a highly secular country, meaning that religion does not play a major role in the lives of most people. Although New Zealand has no established religion, Christianity had been the most common religion since widespread European settlement in the 19th century. Demographics Statistics New Zealand gathers information on religious affiliation in the five-yearly census. Completing a census form is compulsory by law for every person in New Zealand on census night but respondents are able to object to answering the question of religious affiliation, and around 6% do object. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism In New Zealand
Buddhism is New Zealand's third-largest religion after Christianity and Hinduism standing at 1.5% of the population of New Zealand. Buddhism originates in Asia and was introduced to New Zealand by immigrants from East Asia. History The first Buddhists in New Zealand were Chinese diggers in the Otago goldfields in the mid-1860s. Their numbers were small, and the 1926 census, the first to include Buddhism, recorded only 169. Buddhism grew significantly as a religion in New Zealand during the 1970s and 1980s with the arrival of Southeast Asian immigrants and refugees, coinciding with increased interest in Buddhist teaching from Western communities. Buddhist associations began forming, such as the Zen Society of New Zealand in 1972 (originally known as the Denkyo-ji Society), often fundraising to organise In the 1970s travel to Asian countries and visits by Buddhist teachers sparked an interest in the religious traditions of Asia, and significant numbers of New Zealanders adopte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori Religious Beliefs
Māori or Maori can refer to: Relating to the Māori people * Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group * Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand * Māori culture * Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the Cook Islands * Cook Islands Māori, the language of the Cook Islanders Ships * SS ''Maori'' (1893), a steamship of the Shaw Savill Line, shipwrecked 1909 * , a Royal Navy Tribal-class destroyer, sunk in 1915 * , a Royal Navy Tribal-class destroyer, launched 1936 and sunk 1942 * TEV ''Maori III'', a Union Steam Ship Company inter-island ferry, 1952–74 Sports teams * New Zealand Māori cricket team * New Zealand Māori rugby league team * New Zealand Māori rugby union team Other * ''Maori'', a 1988 novel by Alan Dean Foster * Mayotte Mayotte ( ; , ; , ; , ), officially the Department of Mayotte (), is an Overseas France, overseas Overseas departments and regions of France, department and region and single territorial collecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam In New Zealand
Islam is the third-largest Religion in New Zealand, religion in New Zealand (1.5%) after Christianity in New Zealand, Christianity (32.3%) and Hinduism in New Zealand, Hinduism (2.9%). Small numbers of Muslim immigrants from South Asia and eastern Europe settled in New Zealand from the early 1900s until the 1960s. Large-scale Muslim immigration began in the 1970s with the arrival of Indo-Fijians, Indian Fijians, followed in the 1990s by refugees from various war-torn countries. According to the 2023 New Zealand census, there are 75,144 Muslim New Zealanders, representing 1.5% of the total population. The first Islamic centre in New Zealand opened in 1959 and there are now several mosques and two Islamic schools. The majority of Muslims in New Zealand are Sunni, with significant Shia and Ahmadiyya minorities. The Ahmadiyya Community has translated the Qur'an into the Māori language. History Early migration, 19th century The earliest Muslim presence in New Zealand dates bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism In New Zealand
Hinduism is the second largest religion in New Zealand. It is also one of the fastest-growing religions in the country. According to the 2023 census, Hindus form 2.9% of the population of New Zealand. There are about 153,534 Hindus in New Zealand. Hindus from all over India continue to immigrate today, with the largest Indian ethnic subgroup being Gujaratis, Haryanvi and Dravidians. A later wave of immigrants also includes Hindu immigrants who were of Indian descent from nations that were historically under European colonial rule, such as Fiji. Today there are Hindu temples in all major New Zealand cities. History Early settlement In 1836 the missionary William Colenso saw Māori women near Whangārei using a broken bronze bell to boil potatoes. The inscription is in very old Tamil script. This discovery has led to speculation that Tamil-speaking Hindus may have visited New Zealand hundreds of years ago. However, the first noted settlement of Hindus in New Zealand da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity In New Zealand
Christianity in New Zealand dates to the arrival of missionary, missionaries from the Church Missionary Society who were welcomed onto the beach at Rangihoua Bay in December 1814. It soon became the predominant belief amongst the indigenous people, with over half of Māori people, Māori regularly attending church services within the first 30 years. Christianity remains New Zealand's largest religious group, but no one denomination is dominant and there is no official state church. According to the 2018 New Zealand census, 2018 census 38.17% of the population identified as Christians, Christian. The largest Christian groups are Anglican Church in New Zealand, Anglican, Catholic Church in New Zealand, Catholic and Presbyterian Church in New Zealand, Presbyterian. Christian organisations are the leading non-government providers of social services in New Zealand. History The first Christian church service, service conducted in New Zealand waters was probably to be carried out by F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Sign Language
New Zealand Sign Language or NZSL () is the main language of the deaf community in New Zealand. It became an official language of New Zealand in April 2006 under the New Zealand Sign Language Act 2006. The purpose of the act was to create rights and obligations in the use of NZSL throughout the legal system and to ensure that the Deaf community had the same access to government information and services as everybody else. According to the 2013 Census, over 20,000 New Zealanders know NZSL. New Zealand Sign Language has its roots in British Sign Language (BSL), and may be technically considered a dialect of British, Australian and New Zealand Sign Language (BANZSL). There are 62.5% similarities found in British Sign Language and NZSL, compared with 33% of NZSL signs found in American Sign Language. Like other natural sign languages, it was devised by and for deaf people, with no linguistic connection to a spoken or written language. NZSL uses the same two-handed manual alphabet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asian New Zealanders
Asian New Zealanders are New Zealanders of Asian ancestry (including naturalised New Zealanders who are immigrants from specific regions in Asia and descendants of such immigrants). At the 2023 census, 861,573 New Zealanders identified as being of Asian ethnicity, making up 17.3% of New Zealand's population. The first Asians in New Zealand were Chinese workers who migrated to New Zealand to work in the gold mines in the 1860s. The modern period of Asian immigration began in the 1970s when New Zealand relaxed its restrictive policies to attract migrants from Asia. Terminology Under Statistics New Zealand classification, the term refers to a pan-ethnic group that includes diverse populations who have ancestral origins in East Asia (e.g. Chinese, Korean, Japanese), Southeast Asia (e.g. Filipino, Vietnamese, Malaysian), and South Asia (e.g. Nepalese, Indian (incl. Indo-Fijians), Sri Lankan, Bangladeshi, Pakistani). New Zealanders of West Asian and Central Asi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
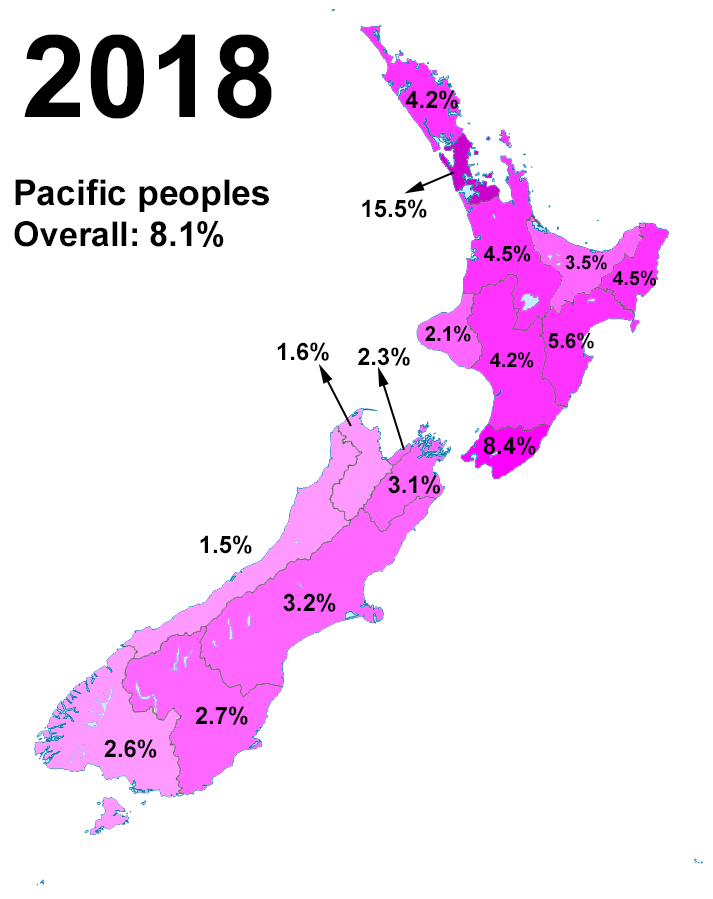
Pasifika New Zealanders
Pasifika New Zealanders (also called Pacific Peoples) are a pan-ethnic group of New Zealanders associated with, and descended from, the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Islands (also known as Pacific Islander#New Zealand, Pacific Islanders) outside New Zealand itself. They form the fourth-largest ethnic grouping in the country, after European New Zealanders, European descendants, indigenous Māori people, Māori, and Asian New Zealanders. Over 380,000 people identify as being of Pacific origin, representing 8% of the country's population, with the majority residing in Auckland. History Prior to the Second World War Pasifika in New Zealand numbered only a few hundred. Wide-scale Pasifika migration to New Zealand began in the 1950s and 1960s, typically from countries associated with the Commonwealth and the Realm of New Zealand, including Western Samoa (modern-day Samoa), the Cook Islands and Niue. In the 1970s, governments (both New Zealand Labour Party, Labour and New Zealand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pākehā
''Pākehā'' (or ''Pakeha''; ; ) is a Māori language, Māori-language word used in English, particularly in New Zealand. It generally means a non-Polynesians, Polynesian New Zealanders, New Zealander or more specifically a European New Zealanders, European New Zealander. It is not a legal term and has no definition under New Zealand law. ''Papa'a'' has a similar meaning in Cook Islands Māori. Etymology and history The etymology of is uncertain. The most likely sources are the Māori words or , which refer to an oral tale of a "mythical, human like being, with fair skin and hair who possessed canoes made of reeds which changed magically into sailing vessels". When Europeans first arrived they rowed to shore in longboats, facing backwards: In traditional Māori canoes or , paddlers face the direction of travel. This is supposed to have led to the belief by some, that the sailors were ''patupaiarehe'' (supernatural beings). There have been several dubious interpretati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |