|
Standerton, Mpumalanga
Standerton is a large commercial and agricultural town lying on the banks of the Vaal River in Mpumalanga, South Africa, which specialises in cattle, dairy, maize and poultry farming. The town was established in 1876 and named after Boer leader Commandant A. H. Stander. During the First Boer War a British garrison in the town was besieged by the Boers for three months. General Jan Smuts won this seat during elections and went on to assist in setting up the League of Nations. Standerton is the seat of the Lekwa Local Municipality. History Standerton was founded in 1878 on a farm called ''Grootverlangen'' and named after its owner Commandant Adriaan Henrik Stander. The South African Republic's Volksraad approved the formation of a town at the drift in 1876 and proclaimed two years later. It was granted municipal status in 1903. The crossing over the Vaal River, now bridged, was known as ''Stander's Drift'' and a hill close to the town was called ''Standerskop'' were also named after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Ocean; to the north by the neighbouring countries of Namibia, Botswana, and Zimbabwe; to the east and northeast by Mozambique and Eswatini; and it encloses Lesotho. Covering an area of , the country has Demographics of South Africa, a population of over 64 million people. Pretoria is the administrative capital, while Cape Town, as the seat of Parliament of South Africa, Parliament, is the legislative capital, and Bloemfontein is regarded as the judicial capital. The largest, most populous city is Johannesburg, followed by Cape Town and Durban. Cradle of Humankind, Archaeological findings suggest that various hominid species existed in South Africa about 2.5 million years ago, and modern humans inhabited the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telephone Numbers In South Africa
Telephone numbers in South Africa are administered by the Independent Communications Authority of South Africa. On 16 January 2007, the country switched to a closed numbering plan. It became mandatory to dial the full nine-digit national telephone number. For calls within the country, this is prefixed by trunk code ''0'' (zero), which is often included in listings of the area code. Area codes within the system are generally organized geographically. Special services by Telkom have numbers with special formats. When dialed from another country, the national number is prefixed with the appropriate international access code and the telephone country code 27. Background History Numbers were allocated when South Africa had only four provinces, meaning that ranges are now split across the current nine provinces. Namibia South-West Africa (including Walvis Bay) was integrated into the South African numbering plan. However, the International Telecommunication Union (ITU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
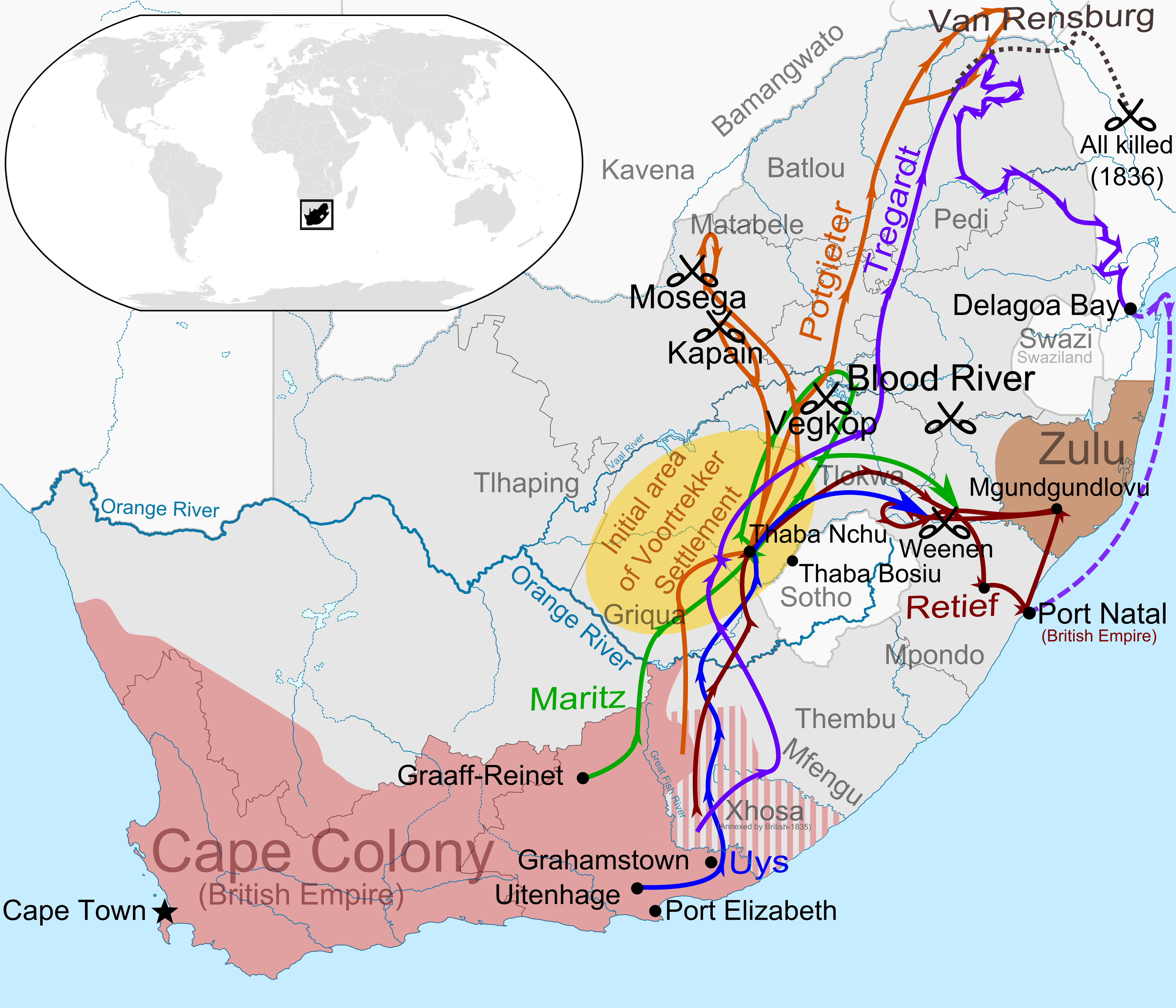
Great Trek
The Great Trek (, ) was a northward migration of Dutch-speaking settlers who travelled by wagon trains from the Cape Colony into the interior of modern South Africa from 1836 onwards, seeking to live beyond the Cape's British colonial administration. The Great Trek resulted from the culmination of tensions between rural descendants of the Cape's original White South Africans, European settlers, known collectively as Boers, and the British Empire, British. It was also reflective of an increasingly common trend among individual Boer communities to pursue an isolationism, isolationist and semi-nomadic lifestyle away from the developing administrative complexities in Cape Town. Boers who took part in the Great Trek identified themselves as ''voortrekkers'', meaning "pioneers" or "pathfinders" in Dutch language, Dutch and Afrikaans language, Afrikaans. The Great Trek led directly to the founding of several autonomous Boer republics, namely the South African Republic (also known sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afrikaner
Afrikaners () are a Southern African ethnic group descended from predominantly Dutch settlers who first arrived at the Cape of Good Hope in 1652.Entry: Cape Colony. ''Encyclopædia Britannica Volume 4 Part 2: Brain to Casting''. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. 1933. James Louis Garvin, editor. Until 1994, they dominated South Africa's politics as well as the country's commercial agricultural sector. Afrikaans, a language which evolved from the Dutch dialect of South Holland, is the mother tongue of Afrikaners and most Cape Coloureds. According to the South African National Census of 2022, 10.6% of South Africans claimed to speak Afrikaans as a first language at home, making it the country's third-largest home language after Zulu and Xhosa. The arrival of Portuguese explorer Vasco da Gama at Calicut, India, in 1498 opened a gateway of free access to Asia from Western Europe around the Cape of Good Hope. This access necessitated the founding and safeguarding of tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voortrekker
The Great Trek (, ) was a northward migration of Dutch-speaking settlers who travelled by wagon trains from the Cape Colony into the interior of modern South Africa from 1836 onwards, seeking to live beyond the Cape's British colonial administration. The Great Trek resulted from the culmination of tensions between rural descendants of the Cape's original European settlers, known collectively as Boers, and the British. It was also reflective of an increasingly common trend among individual Boer communities to pursue an isolationist and semi-nomadic lifestyle away from the developing administrative complexities in Cape Town. Boers who took part in the Great Trek identified themselves as ''voortrekkers'', meaning "pioneers" or "pathfinders" in Dutch and Afrikaans. The Great Trek led directly to the founding of several autonomous Boer republics, namely the South African Republic (also known simply as the Transvaal), the Orange Free State and the Natalia Republic. It also led ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volksraad (South African Republic)
The ''Volksraad of the South African Republic'' (English: "People's Council" of the South African Republic, ) was the parliament of the former South African Republic (ZAR), it existed from 1840 to 1877, and from 1881 to 1902 in part of what is now South Africa. The body ceased to exist after the British Empire's victory in the Second Anglo-Boer War. The ''Volksraad'' sat in session in Ou Raadsaal in Church Square, Pretoria. Unicameral body In 1840, at the beginning of the Natalia Republic, an adjunct ''Volksraad'' was created in Potchefstroom for settlers west of the Drakensberg. The Potchefstroom ''Volksraad'' continued despite the British annexation of the Natalia Republic in 1843. It eventually passed the Thirty-three Articles, the precursor to the 1858 constitution (''Grondwet''), in 1849. In 1858 the ''Grondwet'' permanently established the ''Volksraad'' as the supreme authority of the nation. Volksraad was initially a unicameral body. It consisted of three members for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
League Of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace Conference that ended the World War I, First World War. The main organisation ceased operations on 18 April 1946 when many of its components were relocated into the new United Nations (UN) which was created in the aftermath of the World War II, Second World War. As the template for modern global governance, the League profoundly shaped the modern world. The League's primary goals were stated in its Covenant of the League of Nations, eponymous Covenant. They included preventing wars through collective security and Arms control, disarmament and settling international disputes through negotiation and arbitration. Its other concerns included labour conditions, just treatment of native inhabitants, Human trafficking, human and Illegal drug tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Jan Smuts
Field Marshal Jan Christian Smuts, (baptismal name Jan Christiaan Smuts, 24 May 1870 11 September 1950) was a South African statesman, military leader and philosopher. In addition to holding various military and cabinet posts, he served as Prime Minister of South Africa, Prime Minister of the Union of South Africa from 1919 to 1924 and 1939 to 1948. Smuts was born to Afrikaner parents in the British Cape Colony. He was educated at Stellenbosch University, Victoria College, Stellenbosch before reading law at Christ's College, Cambridge on a scholarship. He was called to the bar at the Middle Temple in 1894 but returned home the following year. In the leadup to the Second Boer War, Smuts practised law in Pretoria, the capital of the South African Republic. He led the republic's delegation to the Bloemfontein Conference and served as an officer in a commando unit following the outbreak of war in 1899. In 1902, he played a key role in negotiating the Treaty of Vereeniging, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Boer War
The First Boer War (, ), was fought from 16 December 1880 until 23 March 1881 between the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and Boers of the Transvaal (as the South African Republic was known while under British administration). The war resulted in a Boer victory and eventual independence of the South African Republic. The war is also known as the ''First Anglo–Boer War'', the ''Transvaal War'' or the ''Transvaal Rebellion.'' Background In the 19th century, Britain at some times attempted to set up a single unified state in southern Africa, and at other times wanted to control less territory. The British Empire's expansion in South Africa was accelerated due to the desire to control trade routes between British Raj, India via the Cape of Good Hope, the discovery of diamonds in Kimberley, Northern Cape, Kimberley in 1867, and the Scramble for Africa, race against other European powers to control as much of Africa as possible. The British annexati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boer
Boers ( ; ; ) are the descendants of the proto Afrikaans-speaking Free Burghers of the eastern Cape frontier in Southern Africa during the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries. From 1652 to 1795, the Dutch East India Company controlled the Dutch Cape Colony, which the United Kingdom incorporated into the British Empire in 1806. The name of the group is derived from Trekboer then later "boer", which means "farmer" in Dutch and Afrikaans. In addition, the term also applied to those who left the Cape Colony during the 19th century to colonise the Orange Free State, and the Transvaal (together known as the Boer Republics), and to a lesser extent Natal. They emigrated from the Cape to live beyond the reach of the British colonial administration, with their reasons for doing so primarily being the new Anglophone common law system being introduced into the Cape and the British abolition of slavery in 1833. The term ''Afrikaners'' or ''Afrikaans people'' is generally used in moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poultry
Poultry () are domesticated birds kept by humans for the purpose of harvesting animal products such as meat, Eggs as food, eggs or feathers. The practice of animal husbandry, raising poultry is known as poultry farming. These birds are most typically members of the superorder Galloanserae (fowl), especially the order Galliformes (which includes chickens, quails, and domestic turkey, turkeys). The term also includes waterfowls of the family Anatidae (ducks and geese) but does not include wild birds hunted for food known as game (hunting), game or wild meat, quarry. Recent genomic studies involving the four extant junglefowl species reveals that the domestication of chicken, the most populous poultry species, occurred around 8,000 years ago in Southeast Asia. This was previously believed to have occurred around 5,400 years ago, also in Southeast Asia. The process may have originally occurred as a result of people hatching and rearing young birds from eggs collected from the wild, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
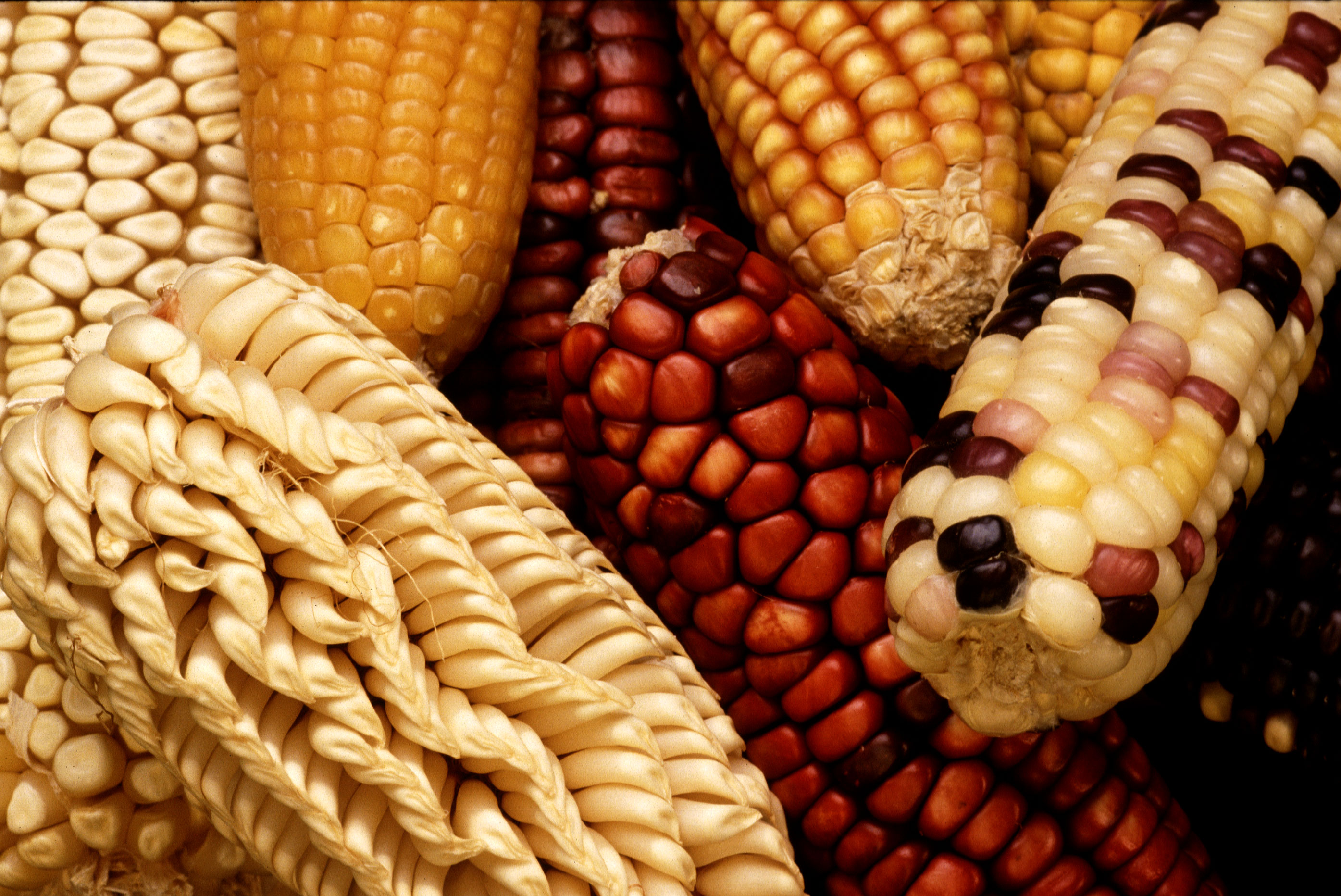
Maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native Americans planted it alongside beans and squashes in the Three Sisters polyculture. The leafy stalk of the plant gives rise to male inflorescences or tassels which produce pollen, and female inflorescences called ears. The ears yield grain, known as kernels or seeds. In modern commercial varieties, these are usually yellow or white; other varieties can be of many colors. Maize relies on humans for its propagation. Since the Columbian exchange, it has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat and rice. Much maize is used for animal feed, whether as grain or as the whole plant, which can either be baled or made into the more palatable silage. Sugar-rich varieties called sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |