|
Stamping Press
A stamping press is a metalworking machine tool used to stamping (metalworking), shape or cut metal by deformation (engineering), deforming it with a die (manufacturing), die. A stamping press uses precision-made male and female dies to shape the final product. It is a modern-day counterpart to the hammer and anvil. Components A press has a bolster plate, and a ram. Presses come in various types of frame configurations, C-Frame where the front & left and right sides are open, straight-side, or H-Frame for stronger higher tonnage applications. It is very important to size the press and tonnage based on the type of applications, blanking, forming, progressive, or transfer. Strong consideration should be given to avoiding off-center load conditions to prevent premature wear to the press. Bolster Plate The bolster plate is mounted on top of the press bed and is a large block of metal upon which the bottom portion of a die is clamped; the bolster plate is stationary. Large presses ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Press Animation
Power may refer to: Common meanings * Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work" ** Engine power, the power put out by an engine ** Electric power, a type of energy * Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events Mathematics, science and technology Computing * IBM POWER (software), an IBM operating system enhancement package * IBM POWER architecture, a RISC instruction set architecture * Power ISA, a RISC instruction set architecture derived from PowerPC * IBM Power microprocessors, made by IBM, which implement those RISC architectures * Power.org, a predecessor to the OpenPOWER Foundation Mathematics * Exponentiation, "''x'' to the power of ''y''" * Power function * Power of a point * Statistical power Physics * Magnification, the factor by which an optical system enlarges an image * Optical power, the degree to which a lens converges or diverges light Social sciences and politics * Economic power, encompassing several concepts that economists use, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
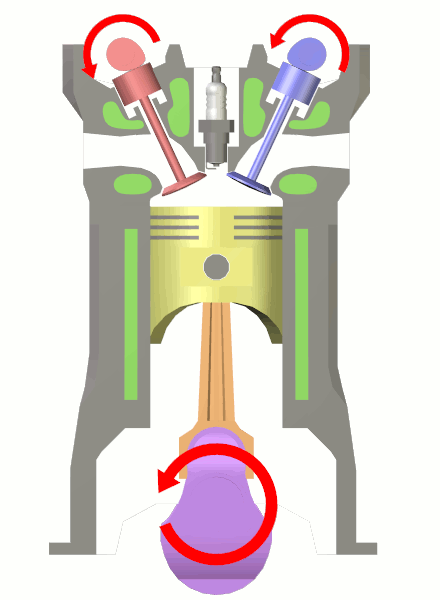
Eccentric (mechanism)
In mechanical engineering, an eccentric is a circular disk (''eccentric sheave'') solidly fixed to a rotating axle with its centre offset from that of the axle (hence the word " eccentric", out of the center). It is used most often in steam engines, and used to convert rotary motion into linear reciprocating motion to drive a sliding valve or pump ram. To do so, an eccentric usually has a groove at its circumference closely fitted a circular collar (''eccentric strap''). An attached ''eccentric rod'' is suspended in such a way that its other end can impart the required reciprocating motion. A return crank fulfills the same function except that it can only work at the end of an axle or on the outside of a wheel whereas an eccentric can also be fitted to the body of the axle between the wheels. Unlike a cam, which also converts rotary into linear motion at almost any rate of acceleration and deceleration, an eccentric or return crank can only impart an approximation of simple har ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metalworking Tools
Metalworking is the process of shaping and reshaping metals in order to create useful objects, parts, assemblies, and large scale structures. As a term, it covers a wide and diverse range of processes, skills, and tools for producing objects on every scale: from huge ships, buildings, and bridges, down to precise engine parts and delicate jewellery. The historical roots of metalworking predate recorded history; its use spans cultures, civilizations and millennia. It has evolved from shaping soft, native metals like gold with simple hand tools, through the smelting of ores and hot forging of harder metals like iron, up to and including highly technical modern processes such as machining and welding. It has been used as an industry, a driver of trade, individual hobbies, and in the creation of art; it can be regarded as both a science and a craft. Modern metalworking processes, though diverse and specialized, can be categorized into one of three broad areas known as forming, cuttin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Tools
A machine tool is a machine for handling or machining metal or other rigid materials, usually by cutting, boring, grinding, shearing, or other forms of deformations. Machine tools employ some sort of tool that does the cutting or shaping. All machine tools have some means of constraining the workpiece and provide a guided movement of the parts of the machine. Thus, the relative movement between the workpiece and the cutting tool (which is called the toolpath) is controlled or constrained by the machine to at least some extent, rather than being entirely "offhand" or " freehand". It is a power-driven metal cutting machine which assists in managing the needed relative motion between cutting tool and the job that changes the size and shape of the job material. The precise definition of the term ''machine tool'' varies among users. While all machine tools are "machines that help people to make things", not all factory machines are machine tools. Today machine tools are typically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonnage Monitor
A tonnage monitor is a meter used on a stamping press to measure the force applied by the ram. In a press, the cutting and forming tools in the die will wear down, requiring increasing effort to stamp the part. A tonnage monitor allows the user to observe this degradation and decide when it is time to sharpen and adjust the die. It generally uses strain gauges attached to the frame or tie rods of the press. The gauges provide an electric signal by means of piezoelectric effect Piezoelectricity (, ) is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials—such as crystals, certain ceramics, and biological matter such as bone, DNA, and various proteins—in response to applied stress (mechanics), mechanical s ... as they are stretched during press operation. The tonnage monitor may provide any of the following additional features: * Warning indication when the load exceeds a setpoint * A press stop signal to halt the press at the top of the stroke for when the load e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raw Material
A raw material, also known as a feedstock, unprocessed material, or primary commodity, is a basic material that is used to produce goods, finished goods, energy, or intermediate materials/Intermediate goods that are feedstock for future finished products. As feedstock, the term connotes these materials are bottleneck assets and are required to produce other products. The term raw material denotes materials in unprocessed or minimally processed states such as raw latex, crude oil, cotton, coal, raw biomass, iron ore, plastic, air, lumber, logs, and water. The term secondary raw material denotes waste material which has been recycled and injected back into use as productive material. Raw material in supply chain Supply chains typically begin with the acquisition or extraction of raw materials. For example, the European Commission notes that food supply chains commence in the agricultural phase of food production. A 2022 report on changes affecting international trade noted that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programmable Logic Controller
A programmable logic controller (PLC) or programmable controller is an industrial computer that has been ruggedized and adapted for the control of manufacturing processes, such as assembly lines, machines, robotic devices, or any activity that requires high reliability, ease of programming, and process fault diagnosis. PLCs can range from small modular devices with tens of Input/output, inputs and outputs (I/O), in a housing integral with the processor, to large rack-mounted modular devices with thousands of I/O, and which are often networked to other PLC and SCADA systems. They can be designed for many arrangements of digital and analog I/O, extended temperature ranges, immunity to electrical noise, and resistance to vibration and impact. PLCs were first developed in the automobile manufacturing industry to provide flexible, rugged and easily programmable controllers to replace hard-wired relay logic systems. Dick Morley, who invented the first PLC, the Modicon 084, for Gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dead Centre (engineering)
In a reciprocating engine, the dead centre is the position of a piston in which it is either furthest from, or nearest to, the crankshaft. The former is known as top dead centre (TDC) while the latter is known as bottom dead centre (BDC). More generally, the dead centre is any position of a crank where the applied force is straight along its axis, meaning no turning force can be applied. Many sorts of machines are crank driven, including unicycles, bicycles, tricycles, various types of machine presses, gasoline engines, diesel engines, steam locomotives, and other steam engines. Crank-driven machines rely on the energy stored in a flywheel to overcome the dead centre, or are designed, in the case of multi-cylinder engines, so that dead centres can never exist on all cranks at the same time. A steam locomotive is an example of the latter, the connecting rods being arranged such that the dead centre for each cylinder occurs out of phase with the other one (or more) cylinders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
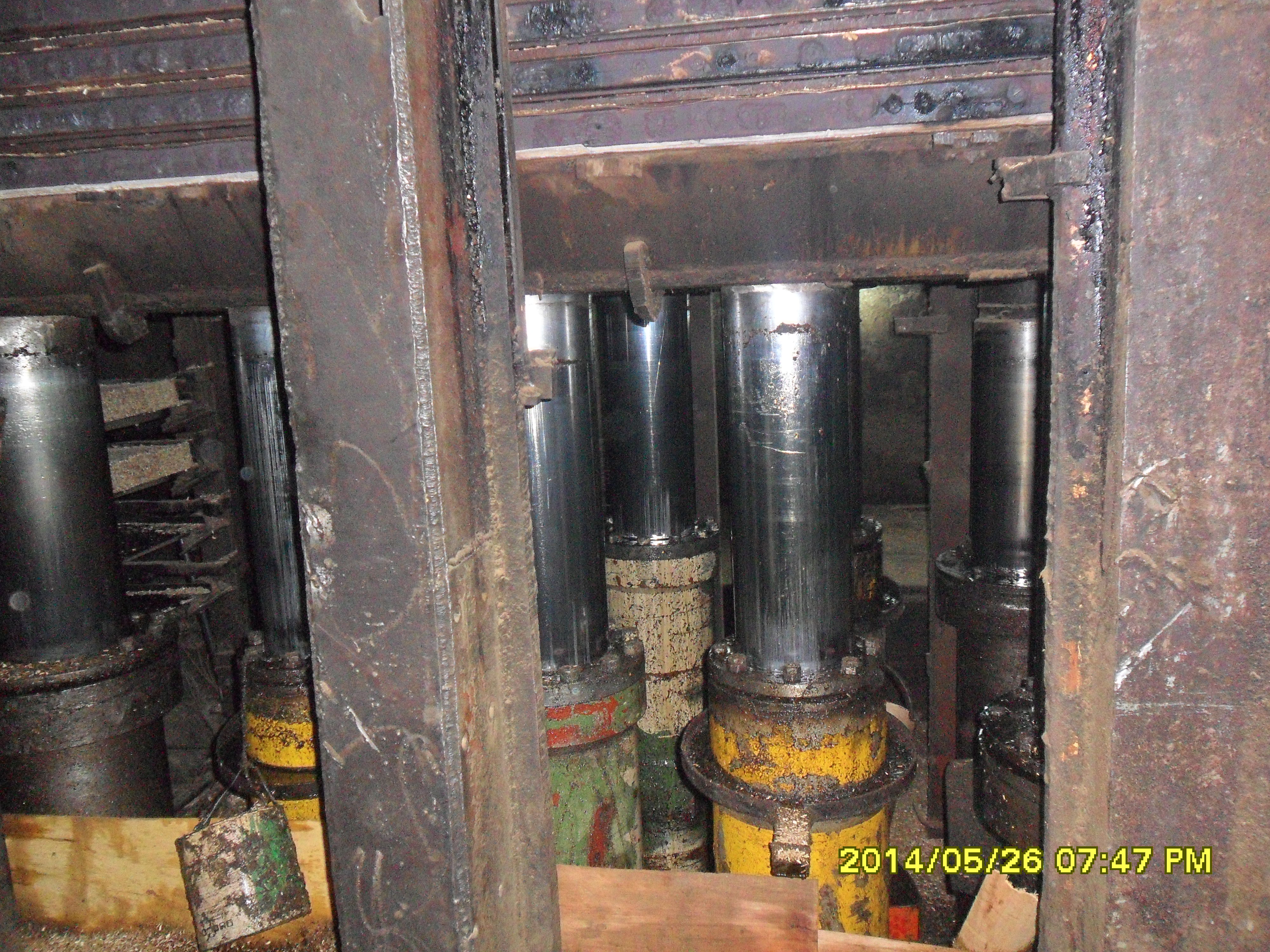
Hydraulic Cylinders
A hydraulic cylinder (also called a linear hydraulic motor) is a mechanical actuator that is used to give a unidirectional force through a unidirectional stroke. It has many applications, notably in construction equipment (engineering vehicles), manufacturing machinery, elevators, and civil engineering. A hydraulic cylinder is a hydraulic actuator that provides linear motion when hydraulic energy is converted into mechanical movement. It can be likened to a muscle in that, when the hydraulic system of a machine is activated, the cylinder is responsible for providing the motion. Operation Hydraulic cylinders get their power from pressurized hydraulic fluid, which is incompressible. Typically oil is used as hydraulic fluid. The hydraulic cylinder consists of a cylinder barrel, in which a piston connected to a piston rod moves back and forth. The barrel is closed on one end by the cylinder bottom (also called the cap) and the other end by the cylinder head (also called the gland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crankshaft
A crankshaft is a mechanical component used in a reciprocating engine, piston engine to convert the reciprocating motion into rotational motion. The crankshaft is a rotating Shaft (mechanical engineering), shaft containing one or more crankpins, that are driven by the pistons via the connecting rods. The crankpins are also called ''rod bearing journals'', and they rotate within the "big end" of the connecting rods. Most modern crankshafts are located in the engine block. They are made from steel or cast iron, using either a forging, casting (metalworking), casting or machining process. Design The crankshaft is located within the engine block and held in place via main bearings which allow the crankshaft to rotate within the block. The up-down motion of each piston is transferred to the crankshaft via connecting rods. A flywheel is often attached to one end of the crankshaft, in order to smoothen the power delivery and reduce vibration. A crankshaft is subjected to enormou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Press
A forming press, commonly shortened to press, is a machine tool that changes the shape of a work-piece by the application of pressure. The operator of a forming press is known as a press-tool setter, often shortened to tool-setter. Presses can be classified according to * their mechanism: Hydraulic press, hydraulic, Machine (mechanical) , mechanical, Pneumatics, pneumatic; * their function: forging presses, stamping presses, press brakes, punch press, etc. * their structure, e.g. Knuckle-joint press, screw press, Expeller pressing, Expeller press * their controllability: conventional vs. Servo press, servo-presses Shop Press Typically consisting of a simple rectangular frame, often fabrication (metal), fabricated from Structural channel, C-channel or tubing, containing a Jack (device)#Bottle jack, bottle jack or hydraulic cylinder to apply pressure via a ram to a work-piece. Often used for general-purpose forming work in the auto mechanic shop, machine shop, garage or basem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |