|
Stability And Growth Pact
The Stability and Growth Pact (SGP) is an agreement, among all the 27 member states of the European Union (EU), to facilitate and maintain the stability of the Economic and Monetary Union of the European Union, Economic and Monetary Union (EMU). Based primarily on :s:Consolidated version of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union/Title VIII: Economic and Monetary Policy#Article 121, Articles 121 and :s:Consolidated version of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union/Title VIII: Economic and Monetary Policy#Article 126, 126 of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union, it consists of fiscal monitoring of member states by the European Commission and the Council of the European Union, and the issuing of a yearly The European Semester#May, Country-Specific Recommendation for fiscal policy actions to ensure a full compliance with the SGP also in the medium-term. If a member state breaches the SGP's outlined maximum limit for government deficit and debt, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fiscal Compliance 2014-debt
Fiscal usually refers to government finance. In this context, it may refer to: Economics * Fiscal policy, use of government expenditure to influence economic development * Fiscal policy debate * Fiscal adjustment, a reduction in the government primary budget deficit * Fiscal agent, a proxy that manages fiscal matters on behalf of another party * Fiscal illusion, a public choice theory of government expenditure * Fiscal space, the flexibility of a government in its spending choices * Fiscal sponsorship, when non-profit organizations offer their legal and tax-exempt status to groups * Fiscal sustainability, the ability of a government to sustain its current spending * Fiscal transparency, publication of information on how governments manage public resources * Fiscal year, reporting periods for firms and other agencies Places * Fiscal Parish, in Portugal * Fiscal, Spain municipality in Huesca, Spain Other * ''Fiscal Studies'', a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal * Fiscal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Russian Invasion Of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, , starting the largest and deadliest war in Europe since World War II, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, conflict between the two countries which began in 2014. The fighting has caused hundreds of thousands of Casualties of the Russo-Ukrainian War, military casualties and tens of thousands of Ukrainian Attacks on civilians in the Russian invasion of Ukraine, civilian casualties. As of 2025, Russian troops Russian-occupied territories of Ukraine, occupy about 20% of Ukraine. From a population of 41 million, about 8 million Ukrainians had been internally displaced and more than 8.2 million Ukrainian refugee crisis, had fled the country by April 2023, creating Europe's List of largest refugee crises, largest refugee crisis since World War II. In late 2021, Russia Prelude to the Russian invasion of Ukraine, massed troops near Ukraine's borders and December 2021 Russian ultimatum to NATO, issued demands to the Western world, West i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
European Union Law
European Union law is a system of Supranational union, supranational Law, laws operating within the 27 member states of the European Union (EU). It has grown over time since the 1952 founding of the European Coal and Steel Community, to promote peace, social justice, a social market economy with full employment, and environmental protection. The Treaties of the European Union agreed to by member states form its constitutional structure. EU law is interpreted by, and EU case law is created by, the judicial branch, known collectively as the Court of Justice of the European Union. Legal Act of the European Union, Legal Acts of the EU are created by a variety of European Union legislative procedure, EU legislative procedures involving the popularly elected European Parliament, the Council of the European Union (which represents member governments), the European Commission (a cabinet which is elected jointly by the Council and Parliament) and sometimes the European Council (composed o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Enhanced Cooperation
In the European Union (EU), enhanced cooperation (previously known as closer cooperation) is a procedure where a minimum of nine EU member states are allowed to establish advanced integration or cooperation in an area within EU structures but without the other member states being involved. As of October 2017, this procedure is being used in the fields of the Schengen acquis, divorce law, patents, property regimes of international couples, and European Public Prosecutor and is approved for the field of a financial transaction tax. This is distinct from the EU opt-out, that is a form of cooperation between EU member states within EU structures, where it is allowed for a limited number of states to refrain from participation (e.g. EMU, Schengen Area). It is further distinct from Mechanism for Cooperation and Verification and permanent acquis suspensions, whose lifting is conditional on meeting certain benchmarks by the affected member states. History Enhanced cooperation, at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Member State Of The European Union
The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of Lists of member states of the European Union, 27 member states that are party to the EU's Treaties of the European Union, founding treaties, and thereby subject to the privileges and obligations of membership. They have agreed by the treaties to share their own sovereignty through the institutions of the European Union in certain aspects of government. State governments must agree unanimously in the Council of the European Union, Council for the union to adopt some policies; for others, collective decisions are made by qualified majority voting. These obligations and sharing of sovereignty within the EU (sometimes referred to as Supranational union, supranational) make it unique among international organisations, as it has established its own legal order which by the provisions of the founding treaties is Primacy of European Union law, both legally binding and supreme on all the member states (after Costa v ENEL, a land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
European Fiscal Compact
The Treaty on Stability, Coordination and Governance in the Economic and Monetary Union; also referred to as TSCG, or more plainly the Fiscal Stability Treaty is an intergovernmental treaty introduced as a new stricter version of the Stability and Growth Pact, signed on 2 March 2012 by all member states of the European Union (EU), except the Czech Republic and the United Kingdom. The treaty entered into force on 1 January 2013 for the 16 states which completed ratification prior to this date. As of 3 April 2019, it had been ratified and entered into force for all 25 signatories plus Croatia, which acceded to the EU in July 2013, and the Czech Republic. The Fiscal Compact is the fiscal chapter of the Treaty (Title III). It binds 23 member states: the 20 member states of the eurozone, plus Bulgaria, Denmark and Romania, who have chosen to opt in. It is accompanied by a set of common principles. Member states bound by the Fiscal Compact have to transpose int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Euro Area Crisis
The euro area crisis, often also referred to as the eurozone crisis, European debt crisis, or European sovereign debt crisis, was a multi-year debt crisis and financial crisis in the European Union (EU) from 2009 until, in Greece, 2018. The eurozone member states of Greece, Portugal, Ireland, and Cyprus were unable to repay or refinance their government debt or to bailout fragile banks under their national supervision and needed assistance from other eurozone countries, the European Central Bank (ECB), and the International Monetary Fund (IMF). The crisis included the Greek government-debt crisis, the 2008–2014 Spanish financial crisis, the 2010–2014 Portuguese financial crisis, the post-2008 Irish banking crisis and the post-2008 Irish economic downturn, as well as the 2012–2013 Cypriot financial crisis. The crisis contributed to changes in leadership in Greece, Ireland, France, Italy, Portugal, Spain, Slovenia, Slovakia, Belgium, and the Netherlands as well as in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pension Scheme
A pension (; ) is a fund into which amounts are paid regularly during an individual's working career, and from which periodic payments are made to support the person's retirement from work. A pension may be either a "Defined benefit pension plan, defined benefit plan", where defined periodic payments are made in retirement and the sponsor of the scheme (e.g. the employer) must make further payments into the fund if necessary to support these defined retirement payments, or a "defined contribution plan", under which defined amounts are paid in during working life, and the retirement payments are whatever can be afforded from the fund. Pensions should not be confused with severance pay; the former is usually paid in regular amounts for life after retirement, while the latter is typically paid as a fixed amount after involuntary termination of employment before retirement. The terms "Retirement plans in the United States, retirement plan" and "Superannuation in Australia, superann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Exchange Rate Mechanism
The European Exchange Rate Mechanism (ERM II) is a system introduced by the European Economic Community on 1 January 1999 alongside the introduction of a single currency, the euro (replacing ERM 1 and the euro's predecessor, the ECU) as part of the European Monetary System (EMS), to reduce exchange rate variability and achieve monetary stability in Europe. After the adoption of the euro, policy changed to linking currencies of EU countries outside the eurozone to the euro (having the common currency as a central point). The goal was to improve the stability of those currencies, as well as to gain an evaluation mechanism for potential eurozone members. As of January 2025, two currencies participate in ERM II: the Danish krone and the Bulgarian lev. Intent and operation The ERM is based on the concept of fixed currency exchange rate margins, but with exchange rates variable within those margins. This is also known as a semi-pegged system. Before the introduction of the eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fiscal Sustainability
Fiscal sustainability, or public finance sustainability, is the ability of a government to sustain its current spending, tax and other policies in the long run without threatening government solvency or defaulting on some of its liabilities or promised expenditures. There is no consensus among economists on a precise operational definition for fiscal sustainability, rather different studies use their own, often similar, definitions. However, the European Commission defines public finance sustainability as: the ability of a government to sustain its current spending, tax and other policies in the long run without threatening the government's solvency or without defaulting on some of the government's liabilities or promised expenditures. Many countries and research institutes have published reports which assess the sustainability of fiscal policies based on long-run projections of country's public finances (see for example, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Potential GDP
In economics, potential output (also referred to as "natural gross domestic product") refers to the highest level of real gross domestic product (potential output) that can be sustained over the long term. Actual output happens in real life while potential output shows the level that could be achieved. Limits to output Natural (physical, etc) and institutional constraints impose limits to growth. If actual GDP rises and stays above potential output, then, in a free market economy (i.e. in the absence of wage and price controls), inflation tends to increase as demand for factors of production exceeds supply. This is because of the finite supply of workers and their time, of capital equipment, and of natural resources, along with the limits of our technology and our management skills. Graphically, the expansion of output beyond the natural limit can be seen as a shift of production volume above the optimum quantity on the average cost curve. Likewise, if GDP persists below natural G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
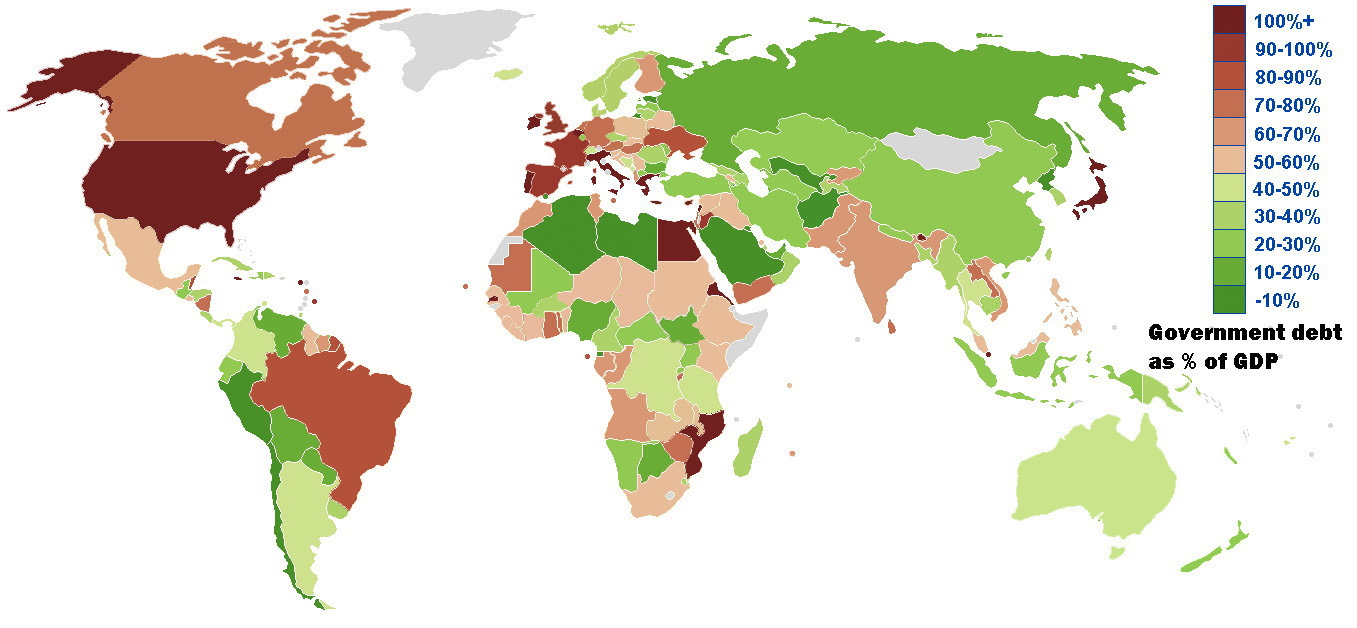
Debt-to-GDP Ratio
In economics, the debt-to-GDP ratio is the ratio of a country's accumulation of government debt (measured in units of currency) to its gross domestic product (GDP) (measured in units of currency per year). A low debt-to-GDP ratio indicates that an economy produces goods and services sufficient to pay back debts without incurring further debt. Geopolitical and economic considerations – including interest rates, war, recessions, and other variables – influence the borrowing practices of a nation and the choice to incur further debt. It should not be confused with a deficit-to-GDP ratio, which, for countries running budget deficits, measures a country's annual net fiscal loss in a given year ( government budget balance, or the net change in debt per annum) as a percentage share of that country's GDP; for countries running budget surpluses, a ''surplus-to-GDP ratio'' measures a country's annual net fiscal ''gain'' as a share of that country's GDP. Particularly in macroeconomics, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |