|
St Paul Island, Alaska
St. Paul ( or , ) is a city in the Aleutians West Census Area, Alaska, United States. It is the main settlement of Saint Paul Island in the Pribilofs, a small island group in the Bering Sea. The population was 413 at the 2020 census, down from 479 in 2010. Saint Paul Island is known as a birdwatching haven. The three closest islands to Saint Paul Island are Otter Island to the southwest, Saint George slightly to the south, and Walrus Island to the east. St. Paul Island's land area is . St. Paul Island in 2008 had one school (K-12, 76 students), one post office, one bar, one small store, and one church (the Russian Orthodox Sts. Peter and Paul Church), which is listed on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places. The island was one of the last places where woolly mammoths survived, until around 5,600 years ago. Geography and geology St. Paul is located at (57.133806, −170.266614). Saint Paul is the largest of the Pribilof Islands and lies the farthest north. With a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City (Alaska)
Alaska ( ) is a Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the northernmost, westernmost, and easternmost (the Aleutian Islands cross the 180th meridian into the eastern hemisphere) state in the United States. It borders the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian territory of Yukon and the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of British Columbia to the east. It shares a western maritime border, in the Bering Strait, with Russia's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. The Chukchi Sea, Chukchi and Beaufort Sea, Beaufort Seas of the Arctic Ocean lie to the north, and the Pacific Ocean lies to the south. Technically, it is a enclave and exclave, semi-exclave of the U.S., and is the largest exclave in the world. Alaska is the list of U.S. states and territories by area, largest U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
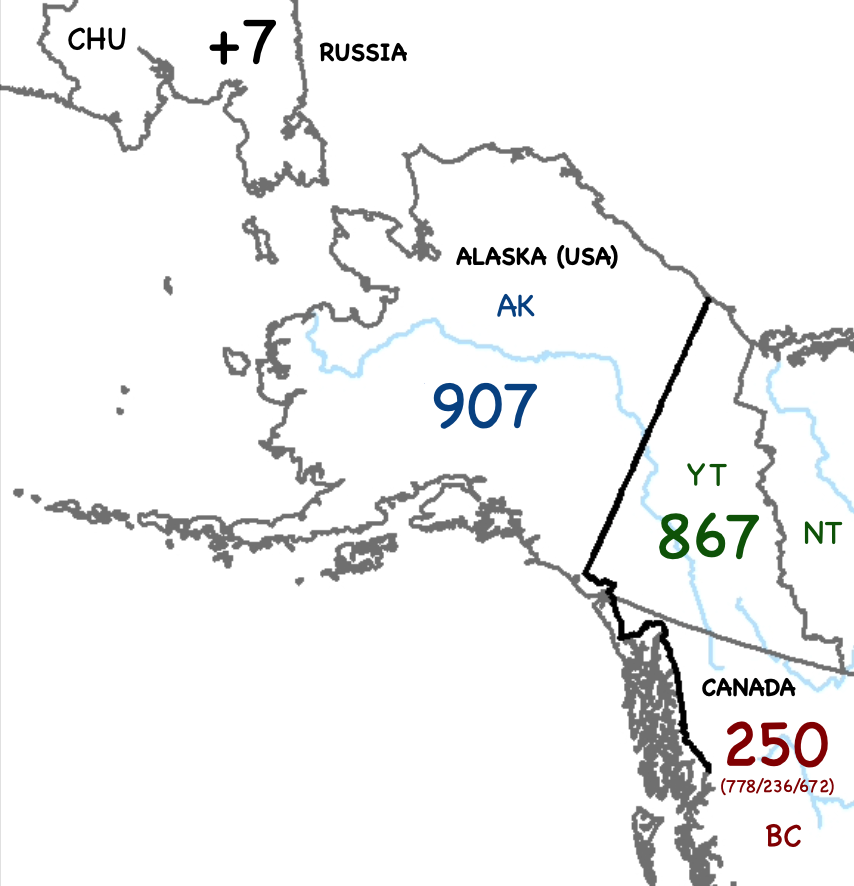
Area Code 907
Area code 907 is a telephone area code in the North American Numbering Plan (NANP) for the U.S. state of Alaska, with the exception of the small southeastern community of Hyder, which is served by the Canadian overlay complex 236/250/257/672/778 from the Stewart, British Columbia rate center. Despite having telephone service to the contiguous United States via a terrestrial line via the town of Juneau since 1937,AT&T (1974) ''Events in Telephone History'' Alaska was not assigned an area code until after the Alaska submarine cable was opened for traffic in 1956. The Alaska numbering plan area (NPA) was assigned the area code 907 and entered service in 1957. The Alaska numbering plan area is geographically the largest of any in the United States. It is the second-largest in the NANP, and on the entire North American continent behind 867, which serves Canada Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three terr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinder Cone
A cinder cone or scoria cone is a steep, volcanic cone, conical landform of loose pyroclastic rock, pyroclastic fragments, such as volcanic ash, clinkers, or scoria that has been built around a volcanic vent. The pyroclastic fragments are formed by explosive eruptions or lava fountains from a single, typically cylindrical, vent. As the gas-charged lava is blown violently into the air, it breaks into small fragments that solidify and fall as either cinders, clinkers, or scoria around the vent to form a cone that is often symmetrical, with slopes between 30° and 40° and a nearly circular base. Most cinder cones have a bowl-shaped volcanic crater, crater at the summit. Mechanics of eruption Cinder cones range in size from tens to hundreds of meters tall. They are composed of loose pyroclastic material (Scoria, cinder or scoria), which distinguishes them from ''spatter cones'', which are composed of agglomerated volcanic bombs. The pyroclastic material making up a cinder cone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the Federal statistical system, U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and American economy, economy. The U.S. Census Bureau is part of the United States Department of Commerce, U.S. Department of Commerce and its Director of the United States Census Bureau, director is appointed by the president of the United States. Currently, Ron S. Jarmin is the acting director of the U.S. Census Bureau. The Census Bureau's primary mission is conducting the United States census, U.S. census every ten years, which allocates the seats of the United States House of Representatives, U.S. House of Representatives to the U.S. state, states based on their population. The bureau's various censuses and surveys help allocate over $675 billion in federal funds every year and it assists states, local communities, and businesses in making informed decisions. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woolly Mammoth
The woolly mammoth (''Mammuthus primigenius'') is an extinct species of mammoth that lived from the Middle Pleistocene until its extinction in the Holocene epoch. It was one of the last in a line of mammoth species, beginning with the African ''Mammuthus subplanifrons'' in the early Pliocene. The woolly mammoth began to diverge from the steppe mammoth about 800,000 years ago in Siberia. Its closest extant relative is the Asian elephant. The Columbian mammoth (''Mammuthus columbi'') lived alongside the woolly mammoth in North America, and DNA studies show that the two Hybrid (biology), hybridised with each other. Mammoth remains were long known in Asia before they became known to Europeans. The origin of these remains was long debated and often explained as the remains of legendary creatures. The mammoth was identified as an extinct elephant species by Georges Cuvier in 1796. The appearance and behaviour of the woolly mammoth are among the best studied of any Prehistory, prehi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Register Of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government's official United States National Register of Historic Places listings, list of sites, buildings, structures, Historic districts in the United States, districts, and objects deemed worthy of Historic preservation, preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic value". The enactment of the National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA) in 1966 established the National Register and the process for adding properties to it. Of the more than one and a half million properties on the National Register, 95,000 are listed individually. The remainder are contributing property, contributing resources within historic district (United States), historic districts. For the most of its history, the National Register has been administered by the National Park Service (NPS), an agency within the United States Department of the Interior. Its goals are to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walrus Island, Pribilof Islands
Walrus Island () is a small islet located 15 km east of Saint Paul Island, Alaska in the Bering Sea. It is part of the Pribilof Islands group. Its length is and its area is 50.3 acres (0.2036 km2). There is no resident population. The name of this island is a translation from the Russian "Ostrov Morzhovoy" meaning "Walrus Island," published by Capt. Lt. Vasiliev of the Imperial Russian Navy (IRN) in 1829 (map 3). This islet should not be confused with the Walrus Islands in the Walrus Islands State Game Sanctuary, located close to Hagemeister Island (in the Dillingham Census Area), nor with Walrus Island located in the southeastern shores of the Bristol Bay Bristol Bay (, ) is the easternmost arm of the Bering Sea, at 57° to 59° North 157° to 162° West in Southwest Alaska. Bristol Bay is 400 km (250 mi) long and 290 km (180 mi) wide at its mouth. A number of rivers flow in ... (in the Aleutians East Borough). ReferencesWalrus Island ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otter Island, Alaska
Otter Island is a small island located southwest of Saint Paul Island, Alaska, in the Bering Sea. It is a member of the Pribilof Islands The Pribilof Islands (formerly the Northern Fur Seal Islands; , ) are a group of four volcanic islands off the coast of mainland Alaska, in the Bering Sea, about north of Unalaska and 200 miles (320 km) southwest of Cape Newenham. The .... Its land area is and there is no resident population. The highest point on the island is above sea level. The island is closed to hunting. The island is long and wide. ReferencesOtter Island: Block 1042, Census Tract 1, Aleutians West Census Area, AlaskaUnited States Census Bureau Pribilof Islands Islands of the Aleutian Islands Uninhabited islands of Alaska Islands of Alaska Islands of Unorganized Borough, Alaska {{AleutiansWestAK-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birdwatching
Birdwatching, or birding, is the observing of birds, either as a recreational activity or as a form of citizen science. A birdwatcher may observe by using their naked eye, by using a visual enhancement device such as binoculars or a telescope, by listening for bird sounds, watching public webcams, or by viewing smart bird feeder cameras. Most birdwatchers pursue this activity for recreational or social reasons, unlike ornithologists, who engage in the study of birds using formal scientific methods. Birding, birdwatching, and twitching The first recorded use of the term ''birdwatcher'' was in 1712 by William Oldsworth. The term ''birding'' was also used for the practice of ''fowling'' or hunting with firearms as in Shakespeare's '' The Merry Wives of Windsor'' (1602): "She laments sir... her husband goes this morning a-birding." The terms ''birding'' and ''birdwatching'' are today used by some interchangeably, although some participants prefer ''birding'', partly because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bering Sea
The Bering Sea ( , ; rus, Бе́рингово мо́ре, r=Béringovo móre, p=ˈbʲerʲɪnɡəvə ˈmorʲe) is a marginal sea of the Northern Pacific Ocean. It forms, along with the Bering Strait, the divide between the two largest landmasses on Earth: Eurasia and the Americas. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelf, continental shelves. The Bering Sea is named after Vitus Bering, a Denmark, Danish-born Russia, Russian navigator, who, in 1728, was the first European to systematically explore it, sailing from the Pacific Ocean northward to the Arctic Ocean. The Bering Sea is separated from the Gulf of Alaska by the Alaska Peninsula. It covers over and is bordered on the east and northeast by Alaska, on the west by the Russian Far East and the Kamchatka Peninsula, on the south by the Alaska Peninsula and the Aleutian Islands and on the far north by the Bering Strait, which connects the Berin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pribilof Islands
The Pribilof Islands (formerly the Northern Fur Seal Islands; , ) are a group of four volcanic islands off the coast of mainland Alaska, in the Bering Sea, about north of Unalaska and 200 miles (320 km) southwest of Cape Newenham. The islands are part of the Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuge. The Siberian coast is roughly northwest. About in total area, they are mostly rocky and are covered with tundra, with a population of 572 as of the 2010 census. Principal islands The principal islands are Saint Paul and Saint George. The former was named for the Feast of Saints Peter and Paul, on the day of which the island was first encountered by the Russian explorer Gavriil Pribylov; the latter was probably named for the ship sailed by Pribylov. The Otter and Walrus islets are near St. Paul. The total land area of all the islands is . The islands are part of the Bering Sea unit of the Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuge. Fur trade While oral traditions of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Paul Island Figb0218
In Christian belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and denomination. In Anglican, Oriental Orthodox, and Lutheran doctrine, all of their faithful deceased in Heaven are considered to be saints, but a selected few are considered worthy of greater honor or emulation. Official ecclesiastical recognition, and veneration, is conferred on some denominational saints through the process of canonization in the Catholic Church or glorification in the Eastern Orthodox Church after their approval. In many Protestant denominations, and following from Pauline usage, ''saint'' refers broadly to any holy Christian, without special recognition or selection. While the English word ''saint'' (deriving from the Latin ) originated in Christianity, historians of religion tend to use the appellation "in a more general way to refer to the state of special h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |