|
St Kilda, Scotland
St Kilda () is a remote archipelago situated west-northwest of North Uist in the North Atlantic Ocean. It contains the westernmost islands of the Outer Hebrides of Scotland. The largest island is Hirta, whose sea cliffs are the highest in the United Kingdom; three other islands (Dùn, St Kilda, Dùn, Soay, St Kilda, Soay and Boreray, St Kilda, Boreray) were also used for grazing and seabird hunting. The islands are administratively a part of the Comhairle nan Eilean Siar local authority area. The origin of the name ''St Kilda'' is a matter of conjecture. The islands' human heritage includes unique architectural features from the historic and prehistoric periods, although the earliest written records of island life date from the Scotland in the Late Middle Ages, Late Middle Ages. The medieval village on Hirta was rebuilt in the 19th century, but illnesses brought by increased external contacts through tourism, and the upheaval of the First World War, contributed to the island's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comhairle Nan Eilean Siar
for, gd, Comhairle nan Eilean Siar, italic=no, Council of the Western Isles, paren=left; ) is the Local government in Scotland, local authority for ''Na h-Eileanan an Iar'' (the Western Isles, also known as the Outer Hebrides), one of the 32 council areas of Scotland. It is based in Stornoway on the Isle of Lewis. Name Comhairle nan Eilean Siar is the only local council in Scotland to have a Scottish Gaelic, Gaelic-only name. When first created in 1975 the council's English language name was 'Western Isles Islands Council', which was changed to 'Western Isles Council' in 1996. In 1998, following the Local Government (Gaelic Names) (Scotland) Act 1997, the Western Isles Council changed the English language version of the area's name from Western Isles to ''Na h-Eileanan an Iar'' (Gaelic for 'the Western Isles'), and the name of the council to ''Comhairle nan Eilean Siar'' ('Council of the Western Isles'), to be used in both English and Gaelic contexts. History In 1975, the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boreray (sheep)
The Boreray, also known as the Boreray Blackface or Hebridean Blackface, is a breed of sheep originating on the St Kilda archipelago off the west coast of Scotland and surviving as a feral animal on one of the islands, Boreray. The breed was once reared for meat and wool, but is now used mainly for conservation grazing. The Boreray is one of the Northern European short-tailed sheep group of breeds. It is one of the rarest breeds of sheep in the United Kingdom. The breed is classed as "Category 3: Vulnerable" by the Rare Breeds Survival Trust, because 500–900 breeding ewes are known to exist. It had previously been the only breed classed in "Category 2: Critical" but by 2017 the population had grown. St Kilda sheep St Kilda is a remote archipelago, west of the Outer Hebrides. Several types of sheep have been associated with St Kilda. In addition to the Boreray, these include the Soay sheep, a feral type from Soay (one of the other islands in the St Kilda archipelago), a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Burt Taylor
Alexander Burt Taylor, (6 June 1904 – 13 March 1972) was a Scottish civil servant and author who served as the Registrar General for Scotland. Life Alexander Burt Taylor was born 6 June 1904 at Earlston, Berwickshire, Scotland, the son of Rev A. B. Taylor of the United Free Church of Scotland. Following schooling at the Hamilton Academy his father moved to the Paterson United Free Church in Kirkwall on Orkney in 1919, so he completed his schooling at Kirkwall Grammar School. Taylor matriculated at the University of Edinburgh and graduated MA in 1925. He taught at schools in Stirling and Falkirk in Scotland, then at Columbia University, New York.Archives Hub, University of Manchester. Papers of Dr. Alexander Burt Taylor . Retrieved 2011-04-16 In 1933, he bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
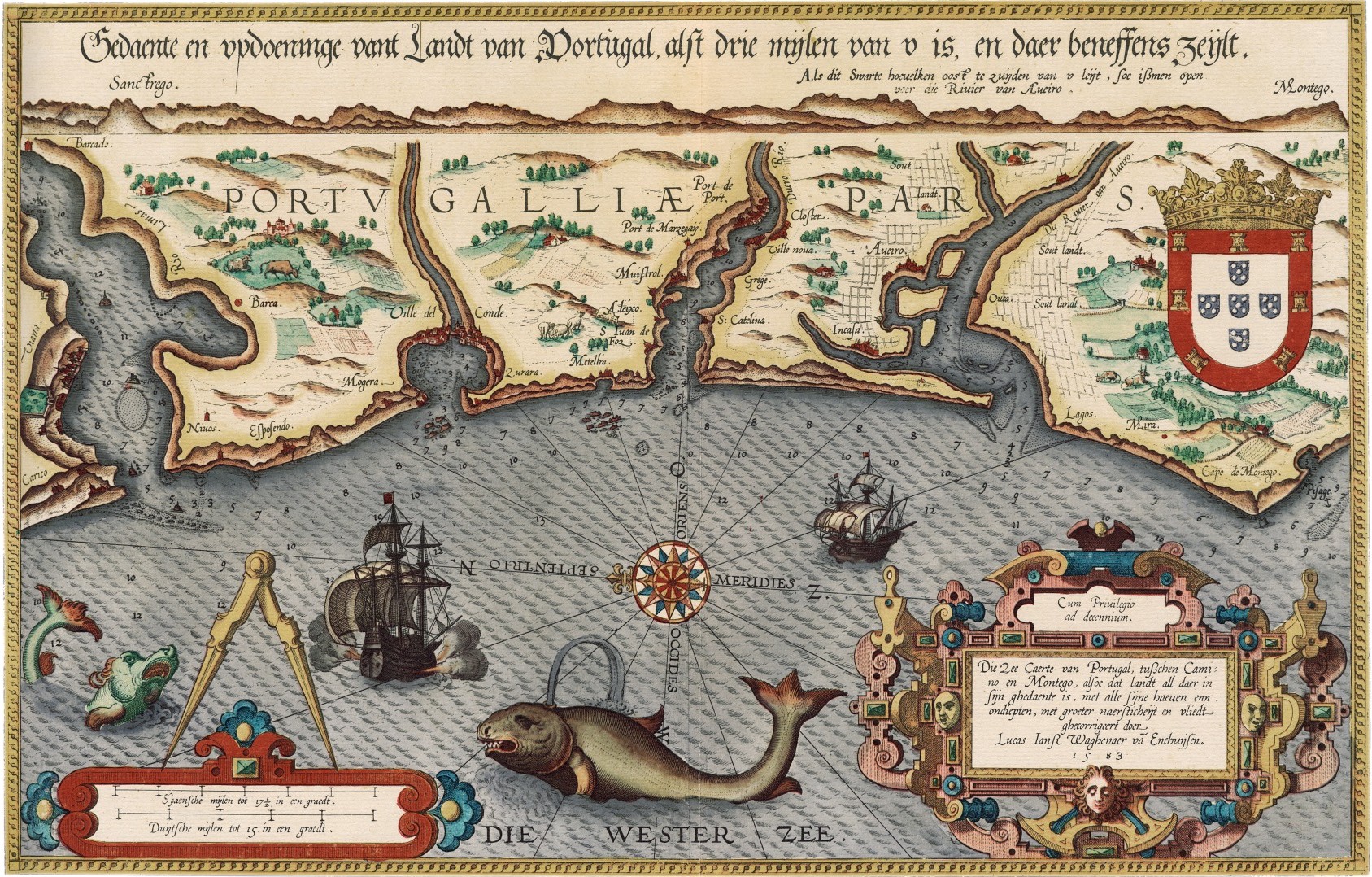
Lucas Waghenaer
Lucas Janszoon Waghenaer (–) was a Dutch cartographer and a notable figure of the Golden Age of Netherlandish cartography, known for his pioneering contributions on the subject of nautical cartography. Career Seafaring Waghenaer is one of the founding fathers and most famous members of the North Holland school, which played a major role in the early development of Dutch nautical chart-making. Between 1550 and 1579, Waghenaer sailed the seas as a chief officer. During these years he must have been in contact with Portuguese, Spanish, and Italian seafarers. The knowledge of maritime charts and sailing instructions Waghenaer gained from these contacts were of great influence on his later work. After his seafaring career he worked in the port of Enkhuizen, as collector of maritime dues. Cartography His first publication, ''Spieghel der zeevaerdt'' ("Mariner's mirror"), appeared in 1584. This chart-book combined an atlas An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural heritage around the world considered to be of outstanding value to humanity". To be selected, a World Heritage Site is nominated by its host country and determined by the UNESCO's World Heritage Committee to be a unique landmark which is geographically and historically identifiable, having a special cultural or physical significance, and to be under a sufficient system of legal protection. World Heritage Sites might be ancient ruins or historical structures, buildings, cities, deserts, forests, islands, lakes, monuments, mountains or wilderness areas, and others. A World Heritage Site may signify a remarkable accomplishment of humankind and serve as evidence of humanity's intellectual history on the planet, or it might be a place of grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Heritage Sites In Scotland
World Heritage Sites in Scotland are locations that have been included in the UNESCO World Heritage Programme list of sites of outstanding cultural or natural importance to the common heritage of humankind. Historic Environment Scotland is responsible for 'cultural' sites as part of their wider responsibility towards the historic environment. The Environment Directorate is responsible for natural sites. There are currently seven sites in Scotland, with one further site undergoing a process of formal evaluation. Informal discussion of a site for " Þings" ( Norse parliaments) has taken place. Existing sites The seven existing sites are mapped to the right and described in detail below. They are: # St. Kilda # Edinburgh Old Town and New Town # The Heart of Neolithic Orkney # New Lanark # The Antonine Wall # The Forth Bridge # The Flow Country St. Kilda is a small, out-lying archipelago of Hebridean islands which was inscribed as a "natural" site in 1986. In 2004, the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subspecies
In Taxonomy (biology), biological classification, subspecies (: subspecies) is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (Morphology (biology), morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species have subspecies, but for those that do there must be at least two. Subspecies is abbreviated as subsp. or ssp. and the singular and plural forms are the same ("the subspecies is" or "the subspecies are"). In zoology, under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, the subspecies is the only taxonomic rank below that of species that can receive a name. In botany and mycology, under the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, other infraspecific name, infraspecific ranks, such as variety (botany), variety, may be named. In bacteriology and virology, under standard International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes, bacterial nomenclature and virus clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Kilda Field Mouse
The St Kilda field mouse (''Apodemus sylvaticus hirtensis'') is a subspecies of the wood mouse that is endemic to the Scottish archipelago of St Kilda, the island west of Benbecula in the Outer Hebrides, and from mainland Scotland. Unique to the islands, the mouse is believed to have arrived on the boats of Viking settlers more than a millennium ago. It is not to be confused with the St Kilda house mouse (''Mus musculus muralis''), a subspecies of the house mouse which is now extinct. The last remaining human inhabitants of St Kilda abandoned the islands on 29 August 1930. Thereafter the mice that survived, even those occupying houses abandoned by the St Kildans, were field mice that had moved into the houses from the hills. The islands' house mice could not survive the harsh conditions for more than two years after the archipelago was abandoned by its human population. The islands currently have temporary human habitations. While field mice are widespread on Hirta, their co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Kilda Wren
The St Kilda wren (''Troglodytes troglodytes hirtensis'') is a small passerine bird in the wren family. It is a distinctive subspecies of the Eurasian wren endemic to the islands of the isolated St Kilda archipelago, in the Atlantic Ocean west of the Outer Hebrides, Scotland. Description The St Kilda wren is distinguished from the mainland form by its larger size and heavier barring, as well as its generally greyer and less rufous colouration. It differs from other Scottish island sub-species by its heavy barring, long and strong bill, and its greyer and paler plumage. The voice is somewhat louder than the mainland subspecies. Distribution and habitat This wren is known only from St Kilda in the Outer Hebrides, where it is present on all islands in the group. In the breeding season it is largely found on the cliffs and steep rocky slopes with thick vegetation, but also around old buildings. Outside the breeding season it is more widely dispersed around the islands. Ecology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Fulmar
The northern fulmar (''Fulmarus glacialis''), fulmar, or Arctic fulmar is an abundant seabird found primarily in subarctic regions of the North Atlantic and North Pacific oceans. There has been one confirmed sighting in the Southern Hemisphere, with a single bird seen south of New Zealand. Fulmars come in one of two colour morphs; a light one in temperate populations, with white head and body and grey wings and tail, and a dark one in arctic populations, which is uniformly grey; intermediate birds are common. Svensson, L., Mullarney, K., & Zetterström, D. (2009) '' Collins Bird Guide'', ed. 2. Though similar in appearance to gulls, fulmars are in fact members of the family Procellariidae, which includes petrels and shearwaters. The northern fulmar and its sister species, the southern fulmar (), are the only extant members of the genus . The fulmars are in turn a member of the order Procellariiformes, and they all share certain identifying features. First, they have nasal pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Puffin
The Atlantic puffin ('), also known as the common puffin, is a species of seabird in the auk family (biology), family. It is the only puffin native to the Atlantic Ocean; two related species, the tufted puffin and the horned puffin being found in the northeastern Pacific. The Atlantic puffin breeds in Russia, Iceland, Ireland, Great Britain, Britain, Norway, Greenland, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, and the Faroe Islands, and as far south as Maine in the west and France in the east. It is most commonly found in the Westman Islands, Iceland. Although it has a large population and a wide range, the species has declined rapidly, at least in parts of its range, resulting in it being rated as Vulnerable species, vulnerable by the IUCN. On land, it has the typical upright stance of an auk. At sea, it swims on the surface and feeds on zooplankton, small fish, and crabs, which it catches by diving underwater, using its wings for propulsion. This puffin has a black crown and bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |