|
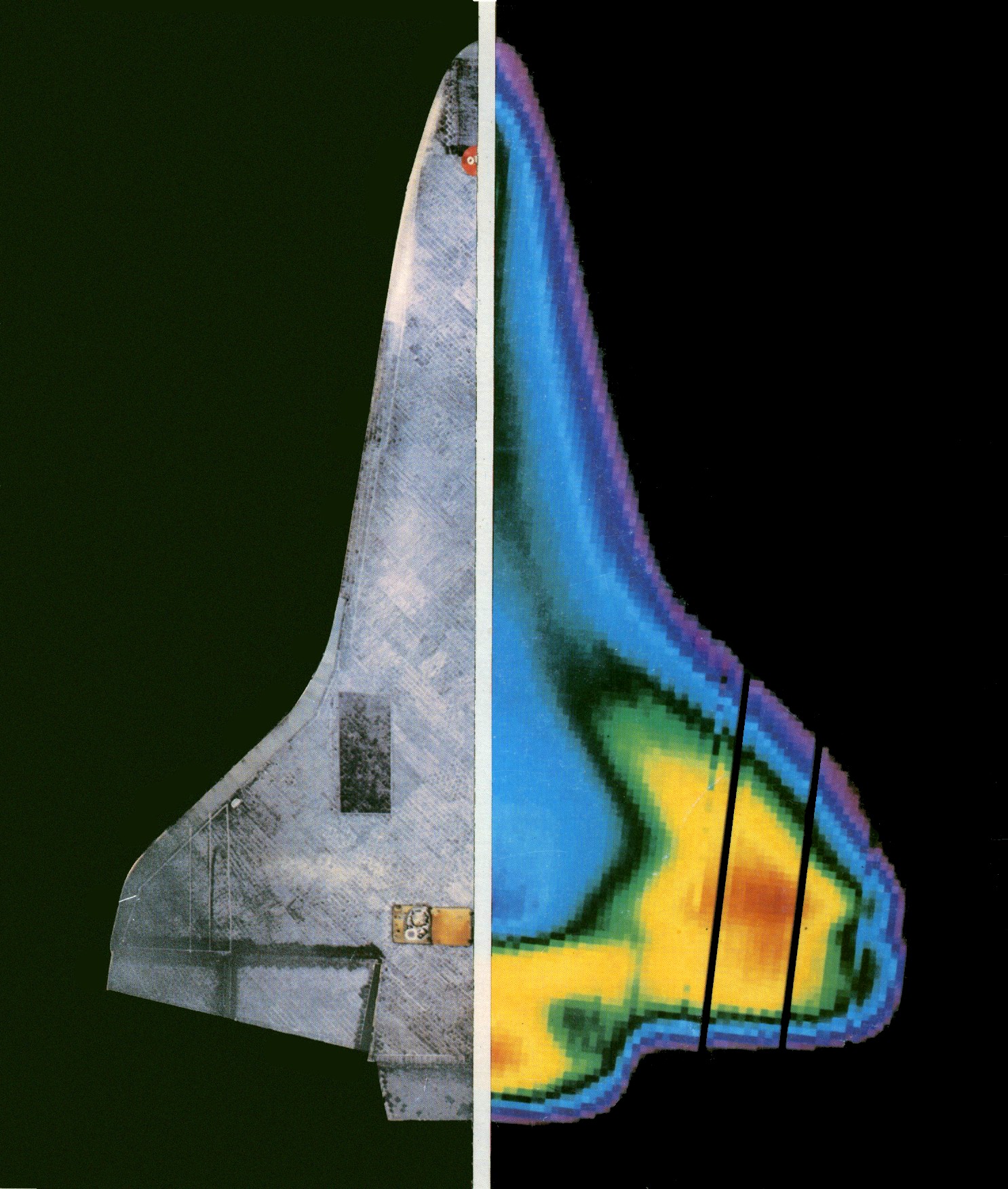
Space Shuttle Columbia Disaster
On Saturday, February 1, 2003, Space Shuttle Columbia, Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disintegrated as it Atmospheric entry, re-entered the atmosphere over Texas and Louisiana, killing all seven astronauts on board. It was the second List of Space Shuttle missions, Space Shuttle mission to end in disaster, after the Space Shuttle Challenger disaster, loss of ''Challenger'' and crew in 1986. The mission, designated STS-107, was the twenty-eighth flight for the orbiter, the 113th flight of the Space Shuttle fleet and the 88th after the ''Challenger'' disaster. It was dedicated to research in various fields, mainly on board the SpaceHab module inside the shuttle's payload bay. During launch, a piece of the Polyurethane foam, insulating foam broke off from the Space Shuttle external tank and struck the Space Shuttle thermal protection system, thermal protection system tiles on the Space Shuttle orbiter, orbiter's left wing. Similar foam shedding had occurred during previous Space Shu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
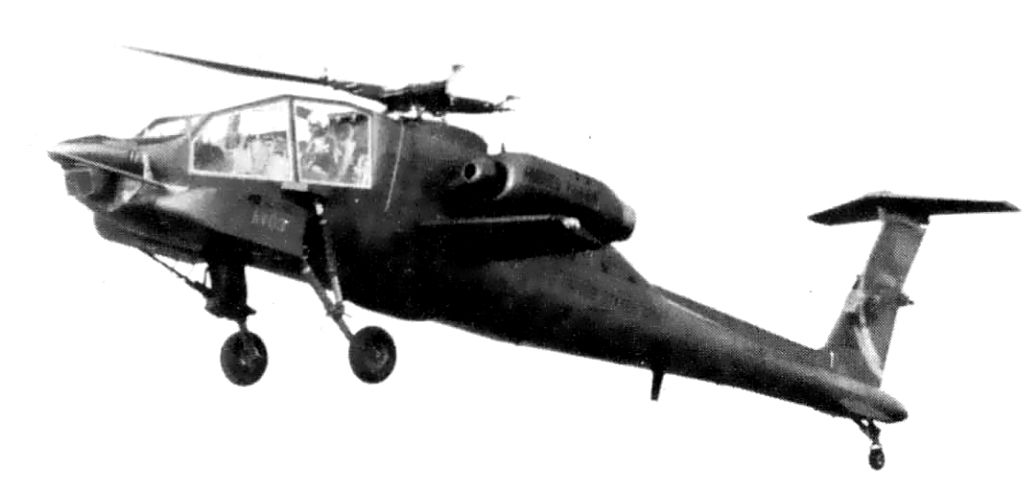
Boeing AH-64 Apache
The Hughes/McDonnell Douglas/Boeing AH-64 Apache ( ) is an American twin-turboshaft attack helicopter with a tailwheel-type landing gear and a tandem cockpit for a crew of two. Nose-mounted sensors help target acquisition, acquire targets and provide night vision device, night vision. It carries a 30 mm caliber, M230 chain gun under its forward fuselage and four hardpoints on stub-wing pylons for armament and stores, typically AGM-114 Hellfire missiles and Hydra 70 rocket pods. redundancy (engineering), Redundant systems help it survive combat damage. The Apache began as the ''Model 77'' developed by Hughes Helicopters for the United States Army's Advanced Attack Helicopter program to replace the Bell AH-1 Cobra, AH-1 Cobra. The prototype YAH-64 first flew on 30 September 1975. The U.S. Army selected the YAH-64 over the Bell YAH-63 in 1976, and later approved full production in 1982. After acquiring Hughes Helicopters in 1984, McDonnell Douglas continued AH-64 production and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Entry
Atmospheric entry (sometimes listed as Vimpact or Ventry) is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. Atmospheric entry may be ''uncontrolled entry,'' as in the entry of astronomical objects, space debris, or bolides. It may be ''controlled entry'' (or ''reentry'') of a spacecraft that can be navigated or follow a predetermined course. Methods for controlled atmospheric ''entry, descent, and landing'' of spacecraft are collectively termed as ''EDL''. Objects entering an atmosphere experience atmospheric drag, which puts mechanical stress on the object, and aerodynamic heating—caused mostly by compression of the air in front of the object, but also by drag. These forces can cause loss of mass ( ablation) or even complete disintegration of smaller objects, and objects with lower compressive strength can explode. Objects have reentered with speeds ranging from 7.8 km/s for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-3xx
Space Shuttle missions designated STS-3xx (officially called Launch On Need (LON) missions) were rescue missions which would have been mounted to rescue the crew of a Space Shuttle if their vehicle was damaged and deemed unable to make a successful reentry. Such a mission would have been flown if Mission Control determined that the heat shielding tiles and reinforced carbon-carbon panels of a currently flying orbiter were damaged beyond the repair capabilities of the available on-orbit repair methods. These missions were also referred to as Launch on Demand (LOD) and Contingency Shuttle Crew Support. The program was initiated following loss of Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' in 2003. No mission of this type was launched before the Space Shuttle program ended in 2011. Procedure The orbiter and four of the crew which were due to fly the next planned mission would be retasked to the rescue mission. The planning and training processes for a rescue flight would allow NASA to launch the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-114
STS-114 was the first "Return to Flight" Space Shuttle mission following the Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster. ''Discovery'' launched at 10:39 EDT (14:39 UTC) on her 31st flight on July 26, 2005. The launch, 907 days (approx. 29 months) after the loss of ''Columbia'', was approved despite unresolved fuel sensor anomalies in the external tank that had prevented the shuttle from launching on July 13, its originally scheduled date. The mission ended on August 9, 2005, when ''Discovery'' landed at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Poor weather over the Kennedy Space Center in Florida hampered the shuttle from using its primary landing site. Analysis of the launch footage showed debris separating from the external tank during ascent; this was of particular concern because it was the issue that had set off the ''Columbia'' disaster. As a result, NASA decided on July 27 to postpone future shuttle flights pending additional modifications to the flight hardware. Shuttle fligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Shield
In engineering, a heat shield is a component designed to protect an object or a human operator from being burnt or overheated by dissipating, reflecting, and/or absorbing heat. The term is most often used in reference to exhaust heat management and to systems for dissipating frictional heat. Heat shields are used most commonly in the automotive and aerospace industries. Principles of operation Heat shields protect structures from extreme temperatures and thermal gradients by two primary mechanisms. Thermal insulation and radiative cooling, respectively isolate the underlying structure from high external surface temperatures, while emitting heat outwards through thermal radiation. To achieve good functionality the three attributes required of a heat shield are low thermal conductivity (high thermal resistance), high emissivity, and good thermal stability (refractoriness). Porous ceramics with high emissivity coatings (HECs) are often employed to address these three characteristic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere Of Earth
The atmosphere of Earth is composed of a layer of gas mixture that surrounds the Earth's planetary surface (both lands and oceans), known collectively as air, with variable quantities of suspended aerosols and particulates (which create weather features such as clouds and hazes), all retained by gravity of Earth, Earth's gravity. The atmosphere serves as a protective buffer between the Earth's surface and outer space, shields the surface from most meteoroids and ultraviolet solar irradiance, solar radiation, keeps it warm and reduces diurnal temperature variation (temperature extremes between daytime, day and night) through heat retention (greenhouse effect), redistributes heat and moisture among different regions via air currents, and provides the atmospheric chemistry, chemical and climate conditions allowing life to exist and evolution, evolve on Earth. By mole fraction (i.e., by quantity of molecules), dry air contains 78.08% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.04% carbon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Shuttle Orbiter
The Space Shuttle orbiter is the spaceplane component of the Space Shuttle, a partially reusable launch system, reusable orbital spaceflight, orbital spacecraft system that was part of the discontinued Space Shuttle program. Operated from 1981 to 2011 by NASA, the U.S. space agency, this vehicle could carry astronauts and payloads into low Earth orbit, perform in-space operations, then atmospheric entry, re-enter the atmosphere and land as a glider aircraft, glider, returning its crew and any on-board payload to the Earth. Six orbiters were built for flight: ''Space Shuttle Enterprise, Enterprise'', ''Space Shuttle Columbia, Columbia'', ''Space Shuttle Challenger, Challenger'', ''Space Shuttle Discovery, Discovery'', ''Space Shuttle Atlantis, Atlantis'', and ''Space Shuttle Endeavour, Endeavour''. All were built in Palmdale, California, by the Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania-based Rockwell International company's North American Aircraft Operations branch. The first orbiter, ''Enterpris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Shuttle Thermal Protection System
The Space Shuttle thermal protection system (TPS) is the barrier that protected the Space Shuttle Orbiter during the extreme heat of atmospheric reentry. A secondary goal was to protect from the heat and cold of space while in orbit. Materials The TPS covered essentially the entire orbiter surface, and consisted of seven different materials in varying locations based on amount of required heat protection: * Reinforced carbon–carbon (RCC), used in the nose cap, the chin area between the nose cap and nose landing gear doors, the arrowhead aft of the nose landing gear door, and the wing leading edges. Used where reentry temperature exceeded . * High-temperature reusable surface insulation (HRSI) tiles, used on the orbiter underside. Made of coated LI-900 silica ceramics. Used where reentry temperature was below 1,260 °C. * Fibrous refractory composite insulation (FRCI) tiles, used to provide improved strength, durability, resistance to coating cracking and weight reduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
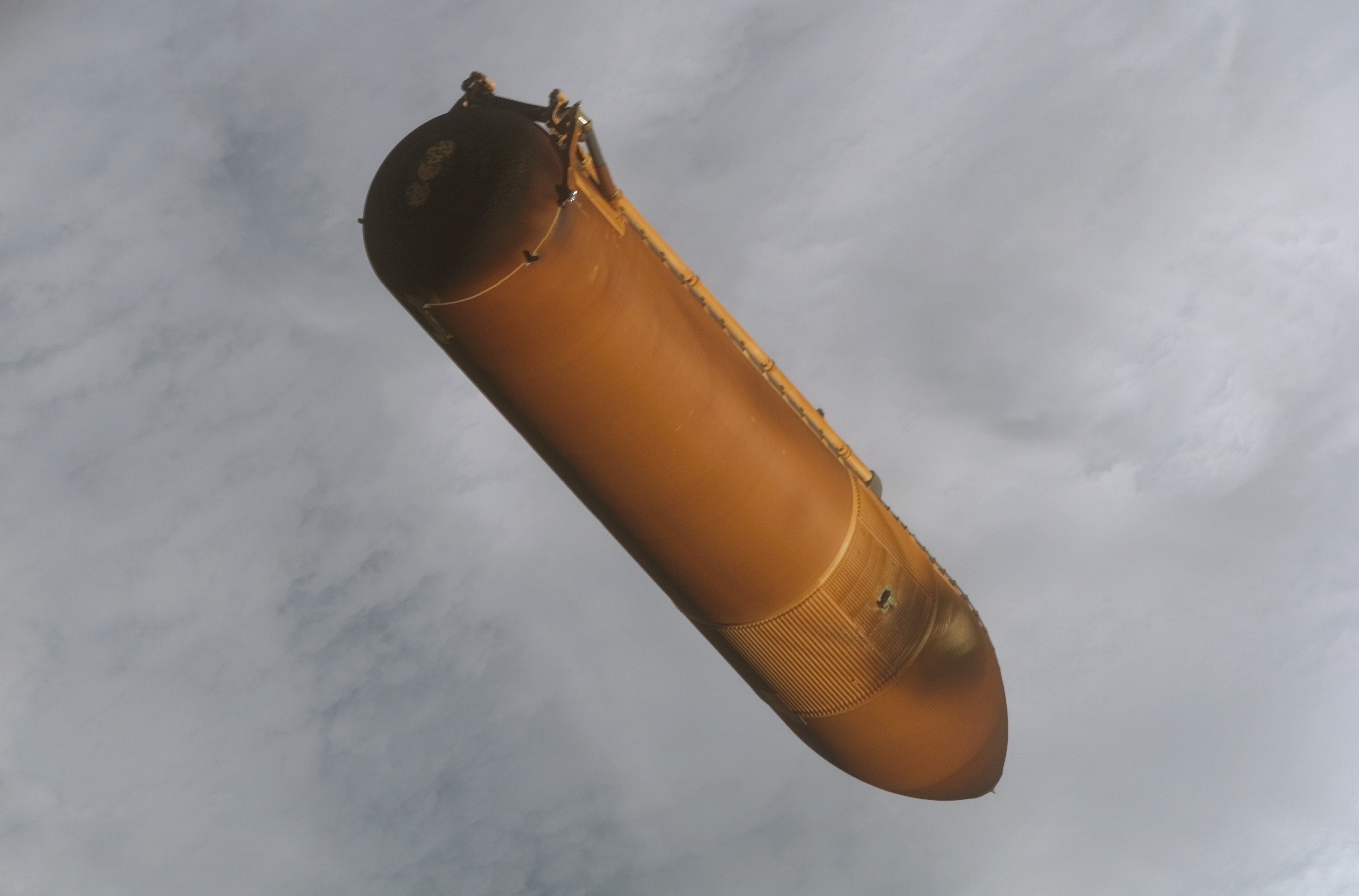
Space Shuttle External Tank
The Space Shuttle external tank (ET) was the component of the Space Shuttle launch vehicle that contained the liquid hydrogen fuel and liquid oxygen oxidizer. During lift-off and ascent it supplied the fuel and oxidizer under pressure to the three RS-25 main engines in the orbiter. The ET was jettisoned just over 10 seconds after main engine cut-off (MECO) and it re-entered the Earth's atmosphere. Unlike the Solid Rocket Boosters, external tanks were not re-used. They broke up before impact in the Indian Ocean (or Pacific Ocean in the case of direct-insertion launch trajectories), away from shipping lanes and were not recovered. Overview The ET was the largest element of the Space Shuttle, and when loaded, it was also the heaviest. It consisted of three major components: * the forward liquid oxygen (LOX) tank * an unpressurized intertank that contains most of the electrical components * the aft liquid hydrogen (LH2) tank; this was the largest part, but it was relatively l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
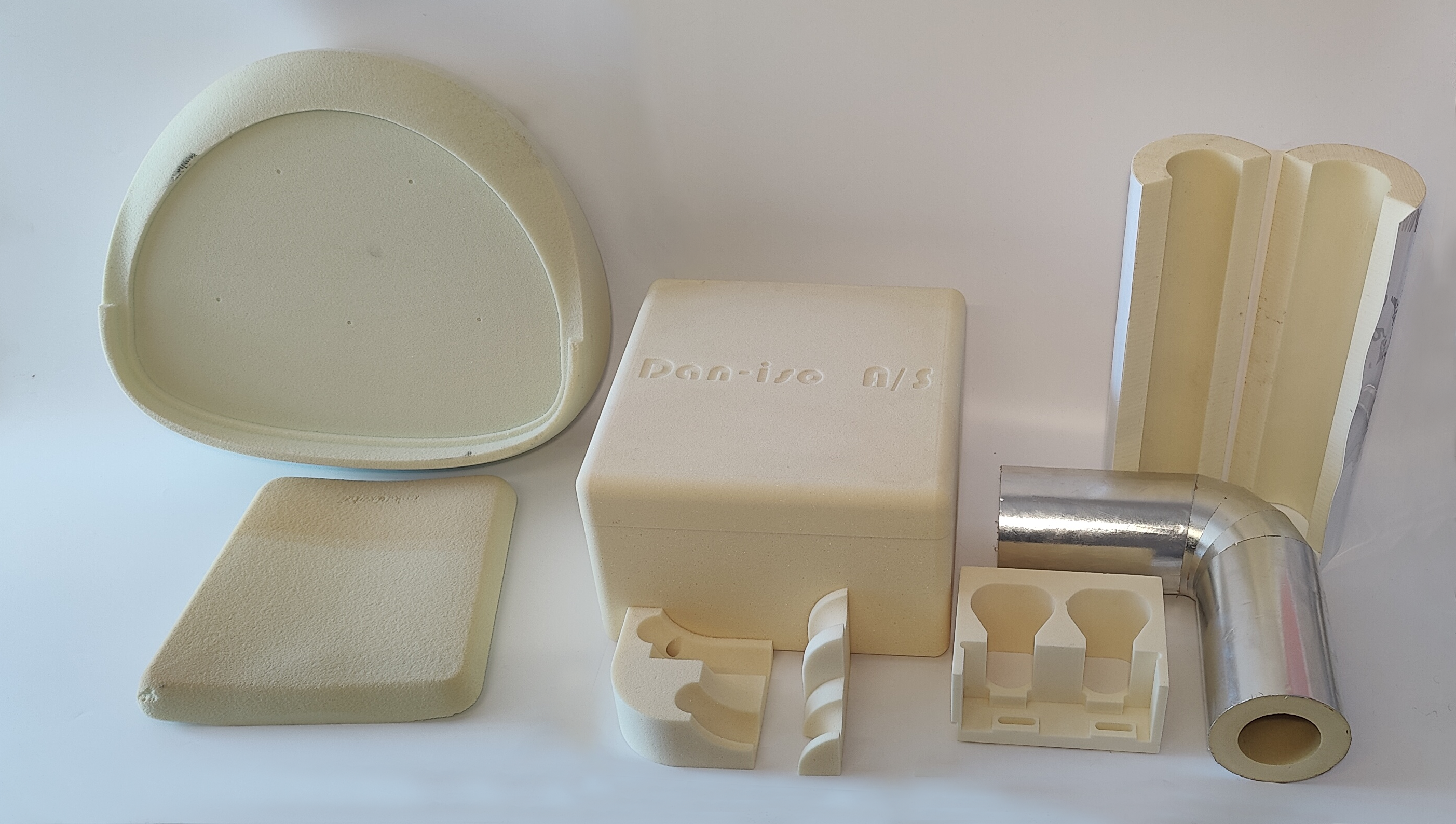
Polyurethane Foam
Polyurethane foam is a solid polymeric foam based on polyurethane chemistry. As a specialist synthetic fibre, synthetic material with highly diverse applications, polyurethane foams are primarily used for thermal insulation and as a cushioning material in mattresses, upholstered furniture or as seating in vehicles. Its low density and thermal conductivity combined with its mechanical properties make them excellent thermal and sound insulators, as well as structural and comfort materials. Polyurethane foams are Thermosetting polymer, thermosetting polymers. They cannot be melted and reshaped after initially formed, because the chemical bonds between the molecules in the material are very strong and are not broken down by heating. Once cured and cooled, the material maintains its shape and properties.EURO-MOULDERS (2023) 'What is polyurethane foam' https://euromoulders.org/polyurethane-in-automobiles/what-is-polyurethane-foam/ Classification of polyurethane foams Polyurethane foa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SpaceHab
Astrotech Corporation, formerly Spacehab Inc., is a technology incubator headquartered in Austin, Texas. Astrotech uses technology sourced internally and from research institutions, government laboratories, and universities to fund, manage and sell start-up companies. Astrotech Corporation's subsidiaries provide commercial products and services to NASA, the U.S. Department of Defense, national space agencies, and global commercial customers. History Astrotech Corporation Astrotech Corporation was established in 1984. Prior to 2009, it was known as SPACEHAB, Inc., a company that provided space habitat microgravity experimentation equipment and services to NASA during the Space Shuttle era. As the Shuttle program came to an end, the company put more focus on its spacecraft processing business, Astrotech Space Operations, Inc. (ASO), its mass spectrometer instrumentation business, 1st Detect, Inc. and its microgravity vaccine development company, Astrogenetix, Inc. In August 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |