|
Sound Localization In Owls
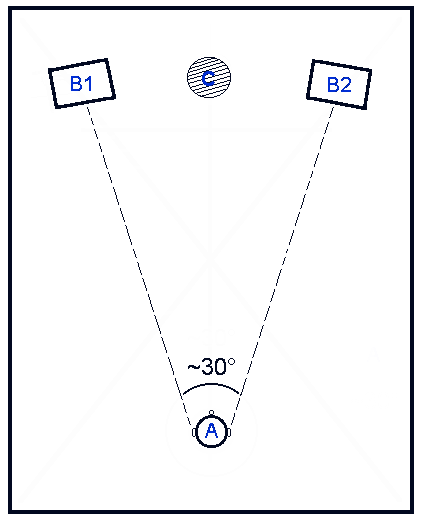
Most owls are nocturnal or crepuscular birds of prey. Because they hunt at night, they must rely on non-visual senses. Experiments by Roger Payne have shown that owls are sensitive to the sounds made by their prey, not the heat or the smell. In fact, the sound cues are both necessary and sufficient for localization of mice from a distant location where they are perched. For this to work, the owls must be able to accurately localize both the azimuth and the elevation of the sound source. Introduction to sound localization Owls are very adept nocturnal predators, hunting prey that includes small mammals, reptiles, and insects. They are able to rotate their head up to 270 degrees, lock onto prey, and launch a silent attack. Owls lock onto prey by using sound localization. Sound localization is an animal’s ability to identify the origin of a sound in distance and direction. Several owl species have ears that are asymmetrical in size and location, which enhances this ability. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bubo Bubo Winter 1
A bubo (Greek βουβών, ''boubṓn'', 'groin') is adenitis or inflammation of the lymph nodes and is an example of reactive infectious lymphadenopathy. Classification Buboes are a symptom of bubonic plague and occur as painful swellings in the thighs, neck, groin or armpits. They are caused by ''Yersinia pestis'' bacteria spreading from flea bites through the bloodstream to the lymph nodes, where the bacteria replicate, causing the nodes to swell. Plague buboes may turn black and necrotic, rotting away the surrounding tissue, or they may rupture, discharging large amounts of pus. Infection can spread from buboes around the body, resulting in other forms of the disease such as pneumonic plague. Management Plague patients whose buboes swell to such a size that they burst tend to survive the disease. Before the discovery of antibiotics, doctors often drained buboes with leeches or heated rods to save patients. Buboes are also symptoms of other diseases, such as chancroid a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectorial Membrane
The tectoria membrane (TM) is one of two acellular membranes in the cochlea of the inner ear, the other being the basilar membrane (BM). "Tectorial" in anatomy means forming a cover. The TM is located above the spiral limbus and the spiral organ of Corti and extends along the longitudinal length of the cochlea parallel to the BM. Radially the TM is divided into three zones, the limbal, middle and marginal zones. Of these the limbal zone is the thinnest (transversally) and overlies the auditory teeth of Huschke with its inside edge attached to the spiral limbus. The marginal zone is the thickest (transversally) and is divided from the middle zone by Hensen's Stripe. It overlies the sensory inner hair cells and electrically-motile outer hair cells of the organ of Corti and during acoustic stimulation stimulates the inner hair cells through fluid coupling, and the outer hair cells via direct connection to their tallest stereocilia. Structure The TM is a gel-like structure conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Colliculus
The inferior colliculus (IC) (Latin for ''lower hill'') is the principal midbrain nucleus of the Auditory system, auditory pathway and receives input from several peripheral brainstem nuclei in the auditory pathway, as well as inputs from the auditory cortex.Shore, S. E.: ''Auditory/Somatosensory Interactions''. In: Squire (Ed.): ''Encyclopedia of Neuroscience'', Academic Press, 2009, pp. 691–695 The inferior colliculus has three subdivisions: the central nucleus, a dorsal cortex by which it is surrounded, and an external cortex which is located laterally. Its bimodal neurons are implicated in auditory-Somatosensory system, somatosensory interaction, receiving projections from Somatosensory system, somatosensory nuclei. This multisensory integration may underlie a filtering of self-effected sounds from vocalization, chewing, or respiration activities. The inferior colliculi together with the superior colliculi form the eminences of the corpora quadrigemina, and also part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochlear Nuclei
The cochlear nucleus (CN) or cochlear nuclear complex comprises two cranial nerve nuclei in the human brainstem, the ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN) and the dorsal cochlear nucleus (DCN). The ventral cochlear nucleus is unlayered whereas the dorsal cochlear nucleus is layered. Auditory nerve fibers, fibers that travel through the auditory nerve (also known as the cochlear nerve or eighth cranial nerve) carry information from the inner ear, the cochlea, on the same side of the head, to the nerve root in the ventral cochlear nucleus. At the nerve root the fibers branch to innervate the ventral cochlear nucleus and the deep layer of the dorsal cochlear nucleus. All acoustic information thus enters the brain through the cochlear nuclei, where the processing of acoustic information begins. The outputs from the cochlear nuclei are received in higher regions of the auditory brainstem. Structure The cochlear nuclei (CN) are located at the dorso-lateral side of the brainstem, span ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Locking
In mathematics, particularly in dynamical systems, Arnold tongues (named after Vladimir Arnold) Section 12 in page 78 has a figure showing Arnold tongues. are a pictorial phenomenon that occur when visualizing how the rotation number of a dynamical system, or other related invariant property thereof, changes according to two or more of its parameters. The regions of constant rotation number have been observed, for some dynamical systems, to form geometric shapes that resemble tongues, in which case they are called Arnold tongues. Arnold tongues are observed in a large variety of natural phenomena that involve oscillating quantities, such as concentration of enzymes and substrates in biological processes and cardiac electric waves. Sometimes the frequency of oscillation depends on, or is constrained (i.e., ''phase-locked'' or ''mode-locked'', in some contexts) based on some quantity, and it is often of interest to study this relation. For instance, the outset of a tumor triggers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axons
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis) or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences) is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the nerve cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. In certain sensory neurons ( pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the axons are called afferent nerve fibers and the electrical impulse travels along these from the periphery to the cell body and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction can be the cause of many inherited and acquired neurological disorders that affect both the peripheral and central neurons. Nerve fibers are classed into three types group A nerve fibers, group B nerve fibers, and group C nerve fibers. Groups A and B are myelinated, and group C are unmyelina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interaural Time Difference
The interaural time difference (or ITD) when concerning humans or animals, is the difference in arrival time of a sound between two ears. It is important in the Sound localization, localization of sounds, as it provides a cue to the direction or angle of the sound source from the head. If a signal arrives at the head from one side, the signal has further to travel to reach the far ear than the near ear. This pathlength difference results in a time difference between the sound's arrivals at the ears, which is detected and aids the process of identifying the direction of sound source. When a signal is produced in the horizontal plane, its angle in relation to the head is referred to as its azimuth, with 0 degrees (0°) azimuth being directly in front of the listener, 90° to the right, and 180° being directly behind. Different methods for measuring ITDs * For an abrupt stimulus such as a click, onset ITDs are measured. An onset ITD is the time difference between the onset of the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Localization
Sound localization is a listener's ability to identify the location or origin of a detected sound in direction and distance. The sound localization mechanisms of the mammalian auditory system have been extensively studied. The auditory system uses several cues for sound source localization, including time difference and level difference (or intensity difference) between the ears, and spectral information. Other animals, such as birds and reptiles, also use them but they may use them differently, and some also have localization cues which are absent in the human auditory system, such as the effects of ear movements. Animals with the ability to localize sound have a clear evolutionary advantage. How sound reaches the brain Sound is the perceptual result of mechanical vibrations traveling through a medium such as air or water. Through the mechanisms of compression and rarefaction, sound waves travel through the air, bounce off the Pinna (anatomy), pinna and concha of the exter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eccentricity (mathematics)
In mathematics, the eccentricity of a Conic section#Eccentricity, conic section is a non-negative real number that uniquely characterizes its shape. One can think of the eccentricity as a measure of how much a conic section deviates from being circular. In particular: * The eccentricity of a circle is 0. * The eccentricity of a non-circular ellipse is between 0 and 1. * The eccentricity of a parabola is 1. * The eccentricity of a hyperbola is greater than 1. * The eccentricity of a pair of Line (geometry), lines is \infty. Two conic sections with the same eccentricity are similarity (geometry), similar. Definitions Any conic section can be defined as the Locus (mathematics), locus of points whose distances to a point (the focus) and a line (the directrix) are in a constant ratio. That ratio is called the ''eccentricity'', commonly denoted as . The eccentricity can also be defined in terms of the intersection of a plane and a Cone (geometry), double-napped cone associated with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipsoid
An ellipsoid is a surface that can be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional Scaling (geometry), scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation. An ellipsoid is a quadric surface; that is, a Surface (mathematics), surface that may be defined as the zero set of a polynomial of degree two in three variables. Among quadric surfaces, an ellipsoid is characterized by either of the two following properties. Every planar Cross section (geometry), cross section is either an ellipse, or is empty, or is reduced to a single point (this explains the name, meaning "ellipse-like"). It is Bounded set, bounded, which means that it may be enclosed in a sufficiently large sphere. An ellipsoid has three pairwise perpendicular Rotational symmetry, axes of symmetry which intersect at a Central symmetry, center of symmetry, called the center of the ellipsoid. The line segments that are delimited on the axes of symmetry by the ellipsoid are called the ''principal ax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
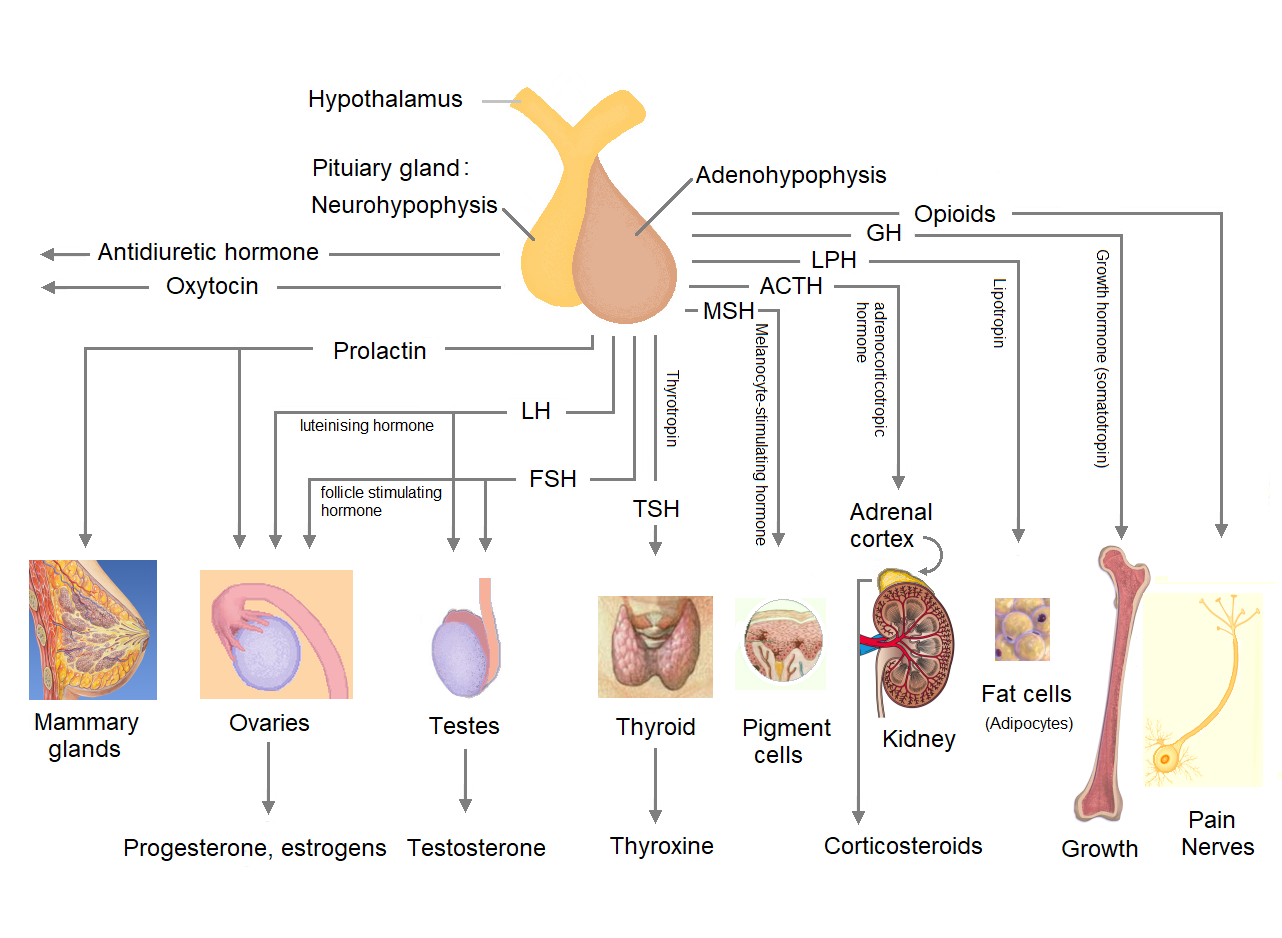
Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the human brain, brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus control much of the body's endocrine system. It is seated in part of the sella turcica a fossa (anatomy), depression in the sphenoid bone, known as the hypophyseal fossa. The human pituitary gland is ovoid, oval shaped, about 1 cm in diameter, in weight on average, and about the size of a kidney bean. Digital version. There are two main lobes of the pituitary, an anterior pituitary, anterior lobe, and a posterior pituitary, posterior lobe joined and separated by a small intermediate lobe. The anterior lobe (adenohypophysis) is the glandular part that produces and secretes several hormones. The posterior lobe (neurohypophysis) secretes neurohypophysial hormones produced in the hypothalamus. Both lobes have different origins and they are both co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammals has been usually termed as the incisive bone. Other terms used for this structure include premaxillary bone or ''os premaxillare'', intermaxillary bone or ''os intermaxillare'', and Goethe's bone. Human anatomy In human anatomy, the premaxilla is referred to as the incisive bone (') and is the part of the maxilla which bears the incisor teeth, and encompasses the anterior nasal spine and alar region. In the nasal cavity, the premaxillary element projects higher than the maxillary element behind. The palatal portion of the premaxilla is a bony plate with a generally transverse orientation. The incisive foramen is bound anteriorly and laterally by the premaxilla and posteriorly by the palatine process of the maxilla. It is formed from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |