|
Song Yingxing
Song Yingxing (Traditional Chinese: 宋應星; Simplified Chinese: 宋应星; Wade Giles: Sung Ying-Hsing; 1587–1666 AD) was a Chinese scientist and encyclopedist who lived during the late Ming Dynasty (1368–1644). He was the author of ''Tiangong Kaiwu'', an encyclopedia that covered a wide variety of technical subjects, including the use of gunpowder weapons.Needham, Volume 5, Part 7, 36. The British biochemist, sinologist, and historian Joseph Needham called Song Yingxing "The Diderot of China."Needham, Volume 5, Part 7, 102. Biography Song Yingxing was born in Yichun of Jiangxi in 1587 to a gentry family of reduced circumstances, he participated in the imperial examinations, and passed the provincial test in 1615, at the age of 28. He achieved only modest wealth and influence during his life. However, he was repeatedly unsuccessful in the metropolitan examination. Song sat for the test five times, the last being in 1631 at the age of 44. After this last failure, he h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Song (Chinese Name)
Song is the pinyin transliteration of the Chinese family name wiktionary:宋, 宋. It is transliterated as Sung in Wade-Giles, and Soong is also a common transliteration. In addition to being a common surname, it is also the name of a Chinese dynasty, the ''Song dynasty'', written with the same character. In 2019, it was the List of common Chinese surnames, 24th most common surname in Mainland China. Historical origin The first written record of the character wiktionary:宋, 宋 (Sòng) was found on the oracle bones of the Shang dynasty. State of Song In the written records of Chinese history, the first time the character Song was used as a surname appeared in the early stage of the Zhou dynasty. One of the children of the last emperor of the Shang dynasty, Weizi of Song, Weizi Qi (微子启), was a duke from the state named Song, who descended from his ancestor Xie of Shang, Xie (契) whose name was derived from the surname Zi (surname), Zi (子). Xie of Shang, Xie was born from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Literature
The history of Chinese literature extends thousands of years, and begins with the earliest recorded inscriptions, court archives, building to the major works of philosophy and history written during the Axial Age. The Han dynasty, Han (202 BC220 AD) and Tang dynasty, Tang (618–907 AD) dynasties were considered golden ages of poetry, while the Song dynasty, Song (960–1279) and Yuan dynasty, Yuan (1271–1368) were notable for their lyrics (''ci''), essays, dramas, and plays. During the Ming dynasty, Ming and Qing, mature novels were written in written vernacular Chinese, an evolution from the preeminence of Literary Chinese patterned off the language of the Chinese classics. The introduction of widespread woodblock printing during the Tang and the invention of movable type printing by Bi Sheng (990–1051) during the Song rapidly spread written knowledge throughout China. Around the turn of the 20th century, the author Lu Xun (1881–1936) is considered an influential voi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
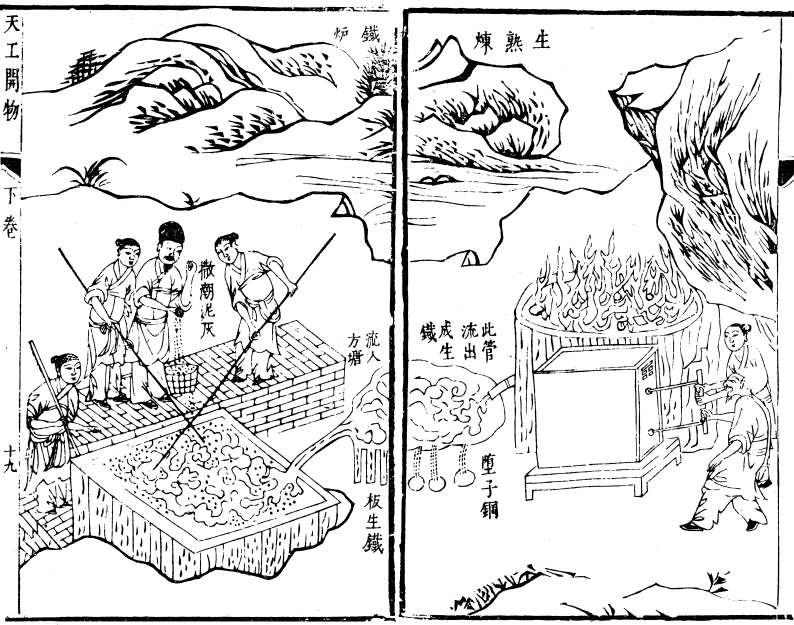
History Of Ferrous Metallurgy
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some theorists categorize history as a social science, while others see it as part of the humanities or consider it a hybrid discipline. Similar debates surround the purpose of history—for example, whether its main aim is theoretical, to uncover the truth, or practical, to learn lessons from the past. In a more general sense, the term ''history'' refers not to an academic field but to the past itself, times in the past, or to individual texts about the past. Historical research relies on primary and secondary sources to reconstruct past events and validate interpretations. Source criticism is used to evaluate these sources, assessing their authenticity, content, and reliability. Historians strive to integrate the perspectives of several sources to develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Agriculture
Agriculture began independently in different parts of the globe, and included a diverse range of Taxon, taxa. At least eleven separate regions of the Old World, Old and New World were involved as independent centers of origin. The development of agriculture about 12,000 years ago changed the way humans lived. They switched from nomadic hunter-gatherer lifestyles to permanent settlements and farming. Wild cereal, grains were collected and eaten from at least 104,000 years ago. However, domestication did not occur until much later. The earliest evidence of small-scale cultivation of edible grasses is from around 21,000 BC with the Ohalo II people on the shores of the Sea of Galilee. By around 9500 BC, the eight Neolithic founder crops – emmer wheat, einkorn wheat, barley, hulled barley, peas, lentils, Vicia ervilia, bitter vetch, chickpeas, and flax – were cultivated in the Levant. Rye may have been cultivated earlier, but this claim remains controversial. Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunpowder Warfare
Early modern warfare is the era of warfare during early modern period following medieval warfare. It is associated with the start of the widespread use of gunpowder and the development of suitable weapons to use the explosive, including artillery and firearms; for this reason the era is also referred to as the age of gunpowder warfare (a concept introduced by Michael Roberts in the 1950s). Fortification techniques evolved rapidly due to the development of artillery. Firearms revolutionized warfare, diminishing the role of aristocracies and heavy cavalry. Early firearms, like arquebuses and muskets, gradually replaced bows and crossbows, leading to the introduction and decline of plate armor as firearms became more effective. Flintlock muskets became dominant by the 1690s, and the invention of the bayonet combined pikes and muskets, transforming infantry into the most crucial military force. Warfare also saw a shift towards larger armies and more devastating conflicts. The r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Gunpowder
Gunpowder is the first explosive to have been developed. Popularly listed as one of the "Four Great Inventions" of China, it was invented during the late Tang dynasty (9th century) while the Wujing Zongyao, earliest recorded chemical formula for gunpowder dates to the Song dynasty (11th century). Knowledge of gunpowder spread rapidly throughout Asia and Europe, possibly as a result of the Mongol conquests during the 13th century, with written formulas for it appearing in the Middle East between 1240 and 1280 in a treatise by Hasan al-Rammah, and in Europe by 1267 in the by Roger Bacon. It was employed in warfare to some effect from at least the 10th century in weapons such as fire arrows, bombs, and the fire lance before the appearance of the gun in the 13th century. While the fire lance was eventually supplanted by the gun, other gunpowder weapons such as rockets and fire arrows continued to see use in China, Korea, India, and this eventually led to its use in the Middle East, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huolongjing
The ''Huolongjing'' (; Wade-Giles: ''Huo Lung Ching''; rendered in English as ''Fire Drake Manual'' or ''Fire Dragon Manual''), also known as ''Huoqitu'' (“Firearm Illustrations”), is a Chinese military treatise compiled and edited by Jiao Yu and Liu Bowen of the early Ming dynasty (1368–1683) during the 14th century. The ''Huolongjing'' is primarily based on the text known as ''Huolong Shenqi Tufa'' (''Illustrations of Divine Fire Dragon Engines''), which no longer exists. History The ''Huolongjings intended function was to serve as a guide to "fire weapons" involving gunpowder during the 1280s to 1350s. Its predecessor, the ''Huolong Shenqi Tufa'' (Fire-Drake Illustrated Technology of Magically (Efficacious) Weapons), has since been lost. The ''Huolongjing'' was one of three early Ming military treatises that were mentioned by Jiao Xu, but only the ''Huolongjing'' remains. Although the earliest edition of the ''Huolongjing'' was written by Jiao Yu, a Ming general, some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Science And Technology In China
Ancient Han Chinese, Chinese scientists and engineers made significant scientific innovations, findings and technological advances across various scientific disciplines including the natural sciences, engineering, medicine, military technology, mathematics, geology and astronomy. Among the earliest List of Chinese inventions, inventions were the abacus, the sundial, and the Kongming lantern. The ''Four Great Inventions'' – the compass, gunpowder, papermaking, and printing – were among the most important technological advances, only known to Europe by the end of the Middle Ages 1000 years later. The Tang dynasty (AD 618–906) in particular was a time of great innovation. A good deal of exchange occurred between Western and List of Chinese discoveries, Chinese discoveries up to the Qing dynasty. The Jesuit China missions of the 16th and 17th centuries introduced Western science and astronomy, while undergoing its own Scientific Revolution, scientific revolution, at the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea in the south. The Japanese archipelago consists of four major islands—Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu—and List of islands of Japan, thousands of smaller islands, covering . Japan has a population of over 123 million as of 2025, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh-most populous country. The capital of Japan and List of cities in Japan, its largest city is Tokyo; the Greater Tokyo Area is the List of largest cities, largest metropolitan area in the world, with more than 37 million inhabitants as of 2024. Japan is divided into 47 Prefectures of Japan, administrative prefectures and List of regions of Japan, eight traditional regions. About three-quarters of Geography of Japan, the countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monopolies
A monopoly (from Greek and ) is a market in which one person or company is the only supplier of a particular good or service. A monopoly is characterized by a lack of economic competition to produce a particular thing, a lack of viable substitute goods, and the possibility of a high monopoly price well above the seller's marginal cost that leads to a high monopoly profit. The verb ''monopolise'' or ''monopolize'' refers to the ''process'' by which a company gains the ability to raise prices or exclude competitors. In economics, a monopoly is a single seller. In law, a monopoly is a business entity that has significant market power, that is, the power to charge overly high prices, which is associated with unfair price raises. Although monopolies may be big businesses, size is not a characteristic of a monopoly. A small business may still have the power to raise prices in a small industry (or market). A monopoly may also have monopsony control of a sector of a market. A mono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China. At its height of power, the empire stretched from the Sea of Japan in the east to the Pamir Mountains in the west, and from the Mongolian Plateau in the north to the South China Sea in the south. Originally emerging from the Later Jin (1616–1636), Later Jin dynasty founded in 1616 and proclaimed in Shenyang in 1636, the dynasty seized control of the Ming capital Beijing and North China in 1644, traditionally considered the start of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty lasted until the Xinhai Revolution of October 1911 led to the abdication of the last emperor in February 1912. The multi-ethnic Qing dynasty Legacy of the Qing dynasty, assembled the territoria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |