|
Somogyszentpál
Somogyszentpál (until 1929 as ''Tótszentpál'', ) is a village in Somogy County, Hungary. Geography It lies southeast of Balatonkeresztúr and south of Balatonfenyves between Kéthely and Csömend. The village can be reached by car from Kéthely/Csömend, or by train from Balatonfenyves on the Balatonfenyves narrow-gauge railway. History Somogyszentpál was formed by the unification of the two villages of ''Varjaskér'' and ''Tótszentpál'' in 1929. At that time it had 1,750 residents. There were also other villages during the Middle Ages on the territory of today's ''Somogyszentpál'', but most of them disappeared during the Ottoman-Hungarian Wars like ''Thekeskér'', ''Nyír-falu'', ''Németi'', ''Zobafalva'', ''Gyulvez'', ''Szent-György falu'' and ''Muszt''. Varjaskér Varjaskér was first mentioned in 1226 as ''Ker'' and later as ''Keér'' between 1292 and 1321 in official documents. In the papal tithe register it was also mentioned between 1332 and 1337. The village had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balatonfenyves Narrow-gauge Railway
The Balatonfenyves narrow-gauge railway runs from Balatonfenyves on the South shore of Lake Balaton to Somogyszentpál over a distance of 13 km. It is the last remaining MÁV-operated narrow-gauge railroad of Hungary as of 2017. History The surroundings of the railroad were originally part of the Lake Balaton, but later it became an isolated moorland that was drained in the 1860s. After that, local landowners tried to connect their lands with the outside world, but they had difficulties with the muddy terrain. The first local line was a 4 km long, Track gauge, 600 mm gauge railroad that connected Balatonfenyves' normal gauge rail station with Imremajor. It used horses instead of locomotives, and there was no passenger traffic. During World War II, it was destroyed. The need for the railroad was still very strong (with no paved road in the area), therefore the construction of a new, Bosnian gauge, 760 mm gauge railway was started in 1950. It was one of the latest railroa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somogy County
Somogy (, ; ; , ) is an administrative county (Counties of Hungary, comitatus or ''vármegye'') in present Hungary, and also in the former Kingdom of Hungary. Somogy County lies in south-western Hungary, on the border with Croatia's Koprivnica-Križevci County, Koprivnica-Križevci and Virovitica-Podravina County, Virovitica-Podravina counties. It stretches between the river Dráva and the southern shore of Lake Balaton. It shares borders with the Hungarian counties of Zala County, Zala, Veszprém (county), Veszprém, Fejér, Tolna (county), Tolna, and Baranya (county), Baranya. Somogy is the most sparsely populated county in Hungary. The county capital is Kaposvár. Its area is 6,036 km2. History Somogy was also the name of a historic administrative county (Comitatus (Kingdom of Hungary), comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory, which was slightly larger than that of present Somogy County, is now in south-western Hungary. The capital of that county was also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcali District
Marcali () is a district in north-western part of Somogy County, in Hungary. ''Marcali'' is also the name of the town where the district seat is found. The district is located in the Southern Transdanubia Statistical Region. Geography Marcali District borders with Keszthely District ''(Zala County)'' to the north, Fonyód District and to the east, Kaposvár District to the southeast, Nagyatád District to the south, Csurgó District to the southwest, Nagykanizsa District ''(Zala County)'' to the west. The number of the inhabited places in Marcali District is 37. Municipalities The district has 1 town and 36 villages. (ordered by population, as of 1 January 2013) The bolded municipality is city. See also *List of cities and towns in Hungary Hungary has 3,152 Municipality, municipalities as of July 15, 2013: 346 towns (Hungarian term: , plural: ; the terminology does not distinguish between city, cities and towns – the term town is used in official translations) and 2, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balatonfenyves
Balatonfenyves is a village at Lake Balaton in Somogy county, Hungary. The name comes from the lake and the Hungarian word for pine tree: ''fenyves''. Formerly part of Fonyód, the village was granted independence as a result of a referendum held on 12 May 1991. The area between the railroad and lake is a holiday destination that attracts mainly families staying in holiday houses. The summer weekends can be busy as people come for the day by train or car. The pedestrian Vachott Sándor street has the shops and is the main link between the station and the beach. The train station is a stop on the Székesfehérvár-Gyékényes line and has a smaller side station from which a (touristic) Balatonfenyves narrow-gauge railway can be taken land inward connecting the Imremajor and Pálmajor outskirts of the village. The beach, the longest on the lake (about ) and freely accessible, is a grass area with many lángos and gyros Gyros, sometimes anglicized as a gyro (; , ), is meat c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balatonkeresztúr
Balatonkeresztúr is a village in Somogy county, Hungary. The settlement is part of the Balatonboglár wine region. Etymology According to the local tradition, the village's name comes from the crossing of roads (). However, the more well-accepted theory states that, like many other villages in Somogy County, Balatonkeresztúr was named after the patron of its church, in this case, ''Szent Kereszt'' (). History According to ''László Szita,'' the settlement was completely Hungarian in the 18th century. Culture The Hungarian folk song Szép a huszár, ha felül a lovára was collected in 1923 in Balatonkeresztúr by Lajos Bárdos Lajos Bárdos (1 October 1899 – 18 November 1986) was a composer, conductor, music theorist, and professor of music at the Franz Liszt Academy of Music, in Budapest, Hungary, where he had previously studied under Albert Siklós and Zoltán Ko .... External links Street map (Hungarian) References Populated places in Somogy Coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prekmurje
Prekmurje (; Prekmurje Slovene: ''Prèkmürsko'' or ''Prèkmüre''; ) is a geographically, linguistically, culturally, and ethnically defined region of Slovenia, settled by Slovenes and a Hungarians in Slovenia, Hungarian minority, lying between the Mur River in Slovenia and the Rába Valley (the Drainage basin, watershed of the Rába (river), Rába; ) in the westernmost part of Hungary. It covers an area of and has a population of 78,000 people. Its largest town and urban center is Murska Sobota, the other urban center being Lendava. Name It is named after the Mur (river), Mur River, which separates it from the rest of Slovenia. The name ''Prekmurje'' literally means 'area beyond the Mur' (''prek'' 'beyond, on the other side' + ''Mura'' 'Mur River' + ''je'', a collective suffix). In Hungarian language, Hungarian, the region is known as ''Muravidék'', and in German language, German as ''Übermurgebiet''. The name Prekmurje was introduced in the twentieth century, although it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Papal Tithes From 1332–1337 In The Kingdom Of Hungary
The List of Papal Tithes from 1332–1337 () is the most important historical source for the ecclesiastical topography of medieval Kingdom of Hungary, containing the names of parishes and of their priests paying the yearly tithes, a tenth of their income. Background The papal register has survived in Rome, together with the register of the diocese of Zagreb (1334), which also covering the Lower Slavonian counties, contains altogether 4066 parishes. This list also gives the most comprehensive picture of the settlement network of the late Árpád and Anjou periods in the Kingdom of Hungary. However, the source is far from complete, some of the gaps can be filled on the basis of other sources. The Hungarian parish system was similar to the Western European, and it seems that the parish/population ratio was close to the number known from similar French and English sources (c. 520–530 persons/parish). Comparing the three papal registers (English, French and Hungarian), there were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunyadi Family
The House of Hunyadi was one of the most powerful noble families in the Kingdom of Hungary during the 15th century. A member of the family, Matthias Corvinus, was King of Hungary from 1458 until 1490, King of Bohemia (ruling in Moravia, Lower Lusatia, Upper Lusatia, and Silesia) from 1469 until 1490, and Duke of Austria from 1487 until 1490. His illegitimate son, John Corvinus, ruled the Duchy of Troppau from 1485 until 1501, and five further Silesian duchies, including Bytom, Głubczyce, Loslau, Racibórz, and Tost, from 1485 until 1490. The Hunyadi coat-of-arms depicted a raven with a golden ring in its beak. The founder of the family, Voyk, received the eponymous Hunyad Castle (in present-day Hunedoara, Romania) from Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, Sigismund, King of Hungary, in 1409. His ethnicity is the subject of scholarly debate. Some modern historians describe him as a Vlach, or Romanians, Romanian, Knez (Vlach leader), knez or Boyars of Wallachia and Moldavia, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harrach
The House of Harrach is the name of an old and influential German nobility, Austro-German noble family, which was also part of the Bohemian nobility. The ''Grafen'' (Counts) of Harrach were among the most prominent families in the Habsburg Empire. As one of a small number of Mediatised Houses, mediatized houses, the family belongs to the ''Uradel, High nobility'' (ancient nobility). History The family first appeared in 1195 in the documents found in :File:Ranshofen-6.JPG, Ranshofen Abbey, Duchy of Bavaria. There are two main family branches — the Rohrau, Austria, Rohrau branch in Austria (until 1886) and the Jilemnice branch in Bohemia. They were formed by two sons of Count Karl von Harrach (1570–1628). Two branches were later founded by grandsons of Friedrich August von Harrach-Rohrau — Ernest Christopher Joseph (d. 1838) and Ferdinand Joseph (d. 1841). * 1195 — first mention of the family in Ranshofen monastery. * 14th century — owned lands in Austria, Carinthia (pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bálint Török
Bálint Török de Enying (25 September 1502 in Szigetvár – 1551 in Istanbul) was a Hungarian aristocrat, Ban of Nándorfehérvár (Belgrade), and between 1527–1542 the Lord of Csesznek. He led a rebellion against the Ottoman Empire until he was captured by the Ottomans and taken to Istanbul Istanbul is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, constituting the country's economic, cultural, and historical heart. With Demographics of Istanbul, a population over , it is home to 18% of the Demographics ... where he was executed for rebellion against the state. Sources *Bessenyei József: ''A Héttorony foglya'' *(MTA) ''Magyarország történeti kronológiája'' (II. kötet) *Bethlen Farkas: ''Erdély története'' *Nagy Iván: ''Magyarország családai czímerekkel és nemzedékrendi táblákkal'' *Hóman Bálint-Szekfű Gyula: ''Magyar történet'' (III. kötet) 1502 births 1551 deaths 16th-century rebels Hungarian nobility Voivo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gutkeled
The coat-of-arms of the Hungarian Gutkeled clan Gutkeled (spelling variants: Gut-Keled, Guthkeled, Guth-Keled) was the name of a ''gens'' (Latin for "clan"; ''nemzetség'' in Hungarian) in the Kingdom of Hungary, to which a number of Hungarian noble families belong. History The primary source of their origins is the Gesta Hungarorum of Simon of Kéza, in which the author writes: :''Sed postea, tempore Petri regis Kelad et Gut intrant tres frateres ex gente Svevorum procreati. De castello Stof sunt nativi.'' :''″But afterwards, during the reign of king Peter, Kelad and Gut three brothers of Swabian descent immigrated. They were born at the castle of Stof.″'' The castle "Stof" is assumed to be a corruption of ''Stauf'', meaning either the Staufen Castle in Staufen im Breisgau or the Hohenstaufen Castle in Göppingen. The king mentioned is Péter Orseolo, placing the arrival of the Gutkeleds to Hungary sometime around the 1040s.Simon Kezai, Lázló Veszprémy, Frank Schaer (e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
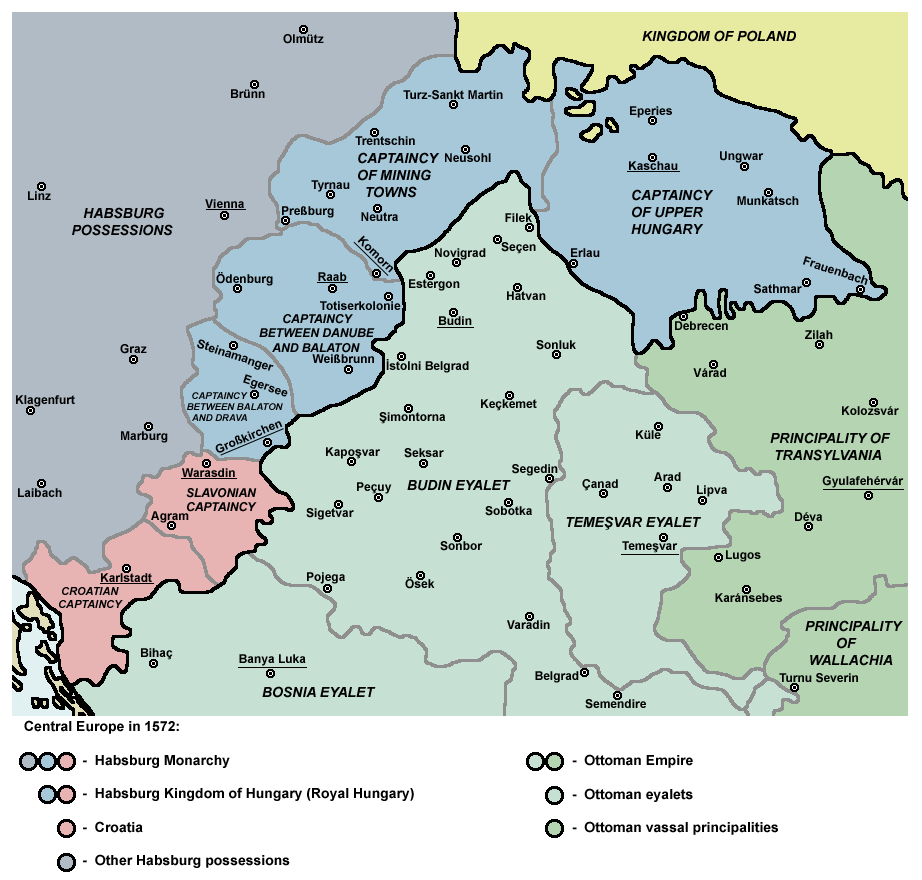
Ottoman Hungary
Ottoman Hungary () encompassed the parts of the Kingdom of Hungary which were under the rule of the Ottoman Empire from the occupation of Buda in 1541 until the Treaty of Karlowitz in 1699. The territory was incorporated into the empire, under the name ''Macaristan.'' For most of its duration, Ottoman Hungary covered Southern Transdanubia and almost the entire region of the Great Hungarian Plain. Ottoman Hungary was divided for administrative purposes into Eyalets (provinces), which were further divided into Sanjaks. Ownership of much of the land was distributed to Ottoman soldiers and officials with the remaining territory being retained by the Ottoman state. As a border territory, much of Ottoman Hungary was heavily fortified with troop garrisons. Remaining economically under-developed, it became a drain on Ottoman resources. During the centuries long three-way Hungarian–Habsburg–Ottoman wars the Hungarian population was highly decimated. Although there was some immigr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |