|
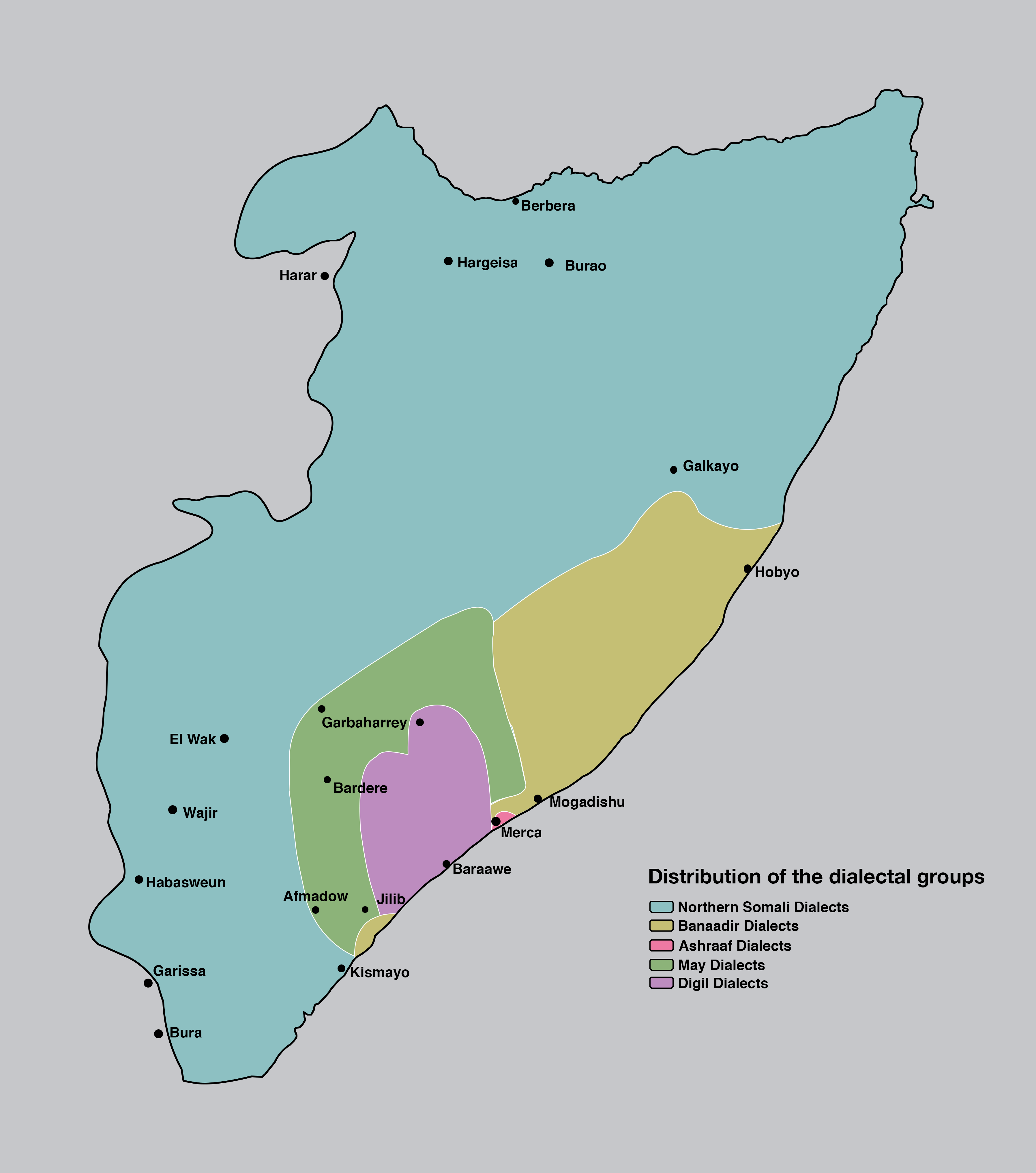
Somali Languages
The Somali languages form a group that are part of the Afro-Asiatic language family. They are spoken as a mother tongue by ethnic Somalis in Horn of Africa and the Somali diaspora. Even with linguistic differences, Somalis collectively view themselves as speaking dialects of a common language. Some neighboring populations and individuals have also adopted the languages. Somali is for instance used as a second language by speakers of Girirra. Overview Somali variations form a group of East Cushitic languages that are part of the Afroasiatic language family. Their closest relatives are the Aweer and Garre languages, followed by Rendille; this group is sometimes known as Sam or Eastern Omo-Tana. Together with Bayso and the Arboroid languages such as Daasanach, these are known as the Omo-Tana languages. A term "Somaloid" is ambiguous and has been used for either all of Omo-Tana, for the Sam group, or for a group comprising Sam and Baiso. * Afroasiatic ** Semitic languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somalia
Somalia, officially the Federal Republic of Somalia, is the easternmost country in continental Africa. The country is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti to the northwest, Kenya to the southwest, the Gulf of Aden to the north, and the Indian Ocean to the east. Somalia has the longest coastline on Africa's mainland. Somalia has an estimated population of 18.1 million, of which 2.7 million live in the capital and largest city, Mogadishu. Around 85% of Somalia's residents are ethnic Somali people, Somalis. The official languages of the country are Somali language, Somali and Arabic, though Somali is the Languages of Somalia, primary language. Somalia has historic and religious ties to the Arab world. The people in Somalia are mainly Muslims, following the Sunni Islam, Sunni branch.. In antiquity, Somalia was an important commercial center. During the Middle Ages, several powerful Somali empires dominated the regional trade, including th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Cushitic Languages
The East Cushitic languages are a branch of Cushitic within the Afroasiatic phylum. Prominent East Cushitic languages include Oromo, Somali, and Sidama. The unity of East Cushitic has been contested: Robert Hetzron suggested combining the Highland East Cushitic languages with the Agaw languages into a "Highland Cushitic" branch, while most other scholars follow in seeing Highland and Lowland as two branches of East Cushitic. Classification Clearly distinct subgroups within East Cushitic are Highland East Cushitic (including Sidama and Hadiyya), Oromoid (including Oromo and Konso), Omo-Tana (including Somali and Arbore), Dullay, and Saho-Afar. A number of tree models of how these relate to each other have been put forward. Highland East Cushitic is commonly seen as a primary branch, also in the "traditional" or "classical" view which groups Yaaku with Dullay and groups the rest as Lowland East Cushitic. With the addition of Dahalo, formerly considered to belong to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highland East Cushitic
Highland East Cushitic or Burji-Sidamo is a branch of the Afroasiatic language family spoken in south-central Ethiopia. They are often grouped with Lowland East Cushitic, Dullay, and Yaaku as East Cushitic. The most popular language is Sidama, with close to two million speakers. The languages are: ** Burji (divergent) **Sidamoid (also Sidamic) *** Sidama *** Gedeo *** Hadiyya–Libido In psychology, libido (; ) is psychic drive or energy, usually conceived of as sexual in nature, but sometimes conceived of as including other forms of desire. The term ''libido'' was originally developed by Sigmund Freud, the pioneering origin ... *** Kambaata– Alaba The four to six Sidamoid languages are all closely related. Hadiyya and Libido are especially close, as are Kambaata and Alaba. Their relationship with Burji is more distant and was first proposed in 1940; it has been accepted widely but not universally. Language contact The Highland East Cushitic languages show para ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agaw Languages
The Agaw or Central Cushitic languages are Afro-Asiatic languages spoken by several groups in Ethiopia and, in one case, Eritrea. They form the main substratum influence on Amharic and other Ethiopian Semitic languages. Classification The Central Cushitic languages are classified as follows (after Appleyard): * Awngi (South Agaw) spoken southwest of Lake Tana, much the largest, with over 350,000 speakers :( Kunfäl, spoken west of Lake Tana, is poorly recorded but most likely a dialect of Awngi) * Northern Agaw: :*Bilen–Xamtanga: ::* Bilen (North) spoken (70,000 speakers) in Eritrea around the town of Keren and eastern Sudan around the town of Kassala ::* Xamtanga (Central Agaw; also called Khamir, Khamta) 143,000 speakers in the North Amhara Region :* Qimant (Western Agaw) nearly extinct, spoken by the Qemant in Semien Gondar Zone ::(dialects Qwara – nearly extinct, spoken by Beta Israel formerly living in Qwara, now in Israel; Kayla – extinct, formerly spok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beja Language
Beja ( or ) is an Afroasiatic language of the Cushitic branch spoken on the western coast of the Red Sea by the Beja people. Its speakers inhabit parts of Egypt, Sudan and Eritrea. In 2022 there were 2,550,000 Beja speakers in Sudan, and 121,000 Beja speakers in Eritrea according to Ethnologue. As of 2023 there are an estimated 88,000 Beja speakers in Egypt. The total number of speakers in all three countries is 2,759,000. Name The name ''Beja'', derived from , is most common in English-language literature. Native speakers use the term (indefinite) or (definite). Classification Beja is held by most linguists to be part of the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic family, constituting the only member of the Northern Cushitic subgroup. As such, Beja contains a number of linguistic innovations that are unique to it, as is also the situation with the other subgroups of Cushitic (e.g. idiosyncratic features in Agaw or Central Cushitic). The characteristics of Beja that differ fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian Language
The Egyptian language, or Ancient Egyptian (; ), is an extinct branch of the Afro-Asiatic languages that was spoken in ancient Egypt. It is known today from a large corpus of surviving texts, which were made accessible to the modern world following the decipherment of the ancient Egyptian scripts in the early 19th century. Egyptian is one of the earliest known written languages, first recorded in the hieroglyphic script in the late 4th millennium BC. It is also the longest-attested human language, with a written record spanning over 4,000 years. Its classical form, known as " Middle Egyptian," served as the vernacular of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt and remained the literary language of Egypt until the Roman period. By the time of classical antiquity, the spoken language had evolved into Demotic, and by the Roman era, diversified into various Coptic dialects. These were eventually supplanted by Arabic after the Muslim conquest of Egypt, although Bohairic Coptic rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semitic Languages
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. They include Arabic, Amharic, Tigrinya language, Tigrinya, Aramaic, Hebrew language, Hebrew, Maltese language, Maltese, Modern South Arabian languages and numerous other ancient and modern languages. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of Western Asia, West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, Malta, and in large Immigration, immigrant and Expatriate, expatriate communities in North America, Europe, and Australasia. The terminology was first used in the 1780s by members of the Göttingen school of history, who derived the name from Shem, one of the three Generations of Noah, sons of Noah in the Book of Genesis. Semitic languages List of languages by first written account, occur in written form from a very early historical date in West Asia, with East Semitic languages, East Semitic Akkadian language, Akkadian (also known as Ancient Assyrian language, Assyrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daasanach Language
Daasanach (also known as Dasenech, Daasanech, Dathanaik, Dathanaic, Dathanik, Dhaasanac, Gheleba, Geleba, Geleb, Gelebinya, Gallab, Galuba, Gelab, Gelubba, Dama, Marille, Merile, Merille, Morille, Reshiat, Russia) is a Cushitic language spoken by the Daasanach in Ethiopia, South Sudan and Kenya whose homeland is along the Lower Omo River and on the shores of Lake Turkana.Raymond G. Gordon Jr., ed. 2005. ''Ethnologue: Languages of the World''. 15th edition. Dallas: Summer Institute of Linguistics. Phonology Consonants * A glottal may also occur in word-initial position, when preceding vowels in various positions * /ð/ may freely alternate with an alveolar among speakers. * /w/ may be heard as a fricative when before front vowels. * Sounds /t̪, k/ can be heard as spiranted �, ɣin intervocalic positions. /k/ can also be heard as uvular �when in between back vowel sounds. * /k/ can be heard as a uvular when before back vowel sounds. * /ɗ̠/ in intervocalic po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayso Language
Baiso or Bayso is a Lowland East Cushitic language belonging to the Omo–Tana subgroup, and is spoken in Ethiopia, in the region around Lake Abaya. Alternative names for Baiso are Giddicho, named after an island on Lake Abaya, and Alkali. According to the Baiso people, however, Giddicho is primarily the name given to the Baiso people by the Guji Oromo, a neighbor clan with close relationship to them. The Baiso term for ''Giddicho'' apparently is ''maman''. As the Baiso people are a minority ethnic group in Ethiopia, their language is endangered. Today, there are between 3 500 and 5 000 mother tongue speakers of Baiso. This number, however, is decreasing. About 95% of the Baiso are multilingual in at least four languages, the most prominent Amharic, which is also the language most young Baiso speakers today primarily use throughout their day. Only recently, the writing system of the Latin alphabet was adapted to the Baiso language. Hence, it does not yet have any literary trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rendille Language
Rendille (also known as Rendile, Randile) is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken by the Rendille people inhabiting northern Kenya. It is part of the family's Cushitic branch. The Ariaal sub-group of the Rendille, who are of mixed Nilotic and Cushitic descent, speak the Nilo-Saharan Samburu language Samburu is a Maa language dialect spoken by Samburu pastoralists in northern Kenya Kenya, officially the Republic of Kenya, is a country located in East Africa. With an estimated population of more than 52.4 million as of mid-2024, Kenya ... of the Samburu Nilotes, near whom they live. Phonology Consonants * /tɕ/ can be heard as �by some speakers. * Some speakers always pronounce /x/ as a uvular stop * �can be heard as a free variant of /ħ/, or when /ħ/ is heard in intervocalic position. * Voiced sounds become voiceless when in word-final position. * /b/ can be pronounced as when preceding /ħ/, or as a fricative �in intervocalic position. * /r/ can also freely be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |