|
Soldering Iron
A soldering iron is a hand tool used in soldering. It supplies heat to melt solder so that it can flow into the joint between two workpieces. A soldering iron is composed of a heated metal tip (the ''bit'') and an insulated handle. Heating is often achieved electrically, by passing an electric current (supplied through an electrical cord or battery cables) through a resistive heating element. Cordless irons can be heated by combustion of gas stored in a small tank, often using a catalytic heater rather than a flame. Simple irons, less commonly used today than in the past, were simply a large copper ''bit'' on a handle, heated in a flame. Solder melts at approximately . Soldering irons are designed to reach a temperature range of . Soldering irons are most often used for installation, repairs, and limited production work in electronics assembly. High-volume production lines use other soldering methods.Bralla, James G. ''Handbook of Manufacturing Processes - How Products, Compon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soldering Gun
A soldering gun is an approximately pistol-shaped, electrically powered tool for soldering metals using tin-based solder to achieve a strong mechanical bond with good electrical contact. The tool has a trigger-style switch so it can be easily operated with one hand. The body of the tool contains a transformer with a primary winding connected to mains electricity when the trigger is pressed, and a single-turn secondary winding of thick copper with very low resistance. A soldering tip, made of a loop of thinner copper wire, is secured to the end of the transformer secondary by screws, completing the secondary circuit. When the primary of the transformer is energized, several hundred amperes of current flow through the secondary and very rapidly heat the copper tip. Since the tip has a much higher resistance than the rest of the tubular copper winding, the tip gets very hot while the remainder of the secondary warms at a much slower rate. An additional secondary winding is often us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheet Metal
Sheet metal is metal formed into thin, flat pieces, usually by an industrial process. Thicknesses can vary significantly; extremely thin sheets are considered foil (metal), foil or Metal leaf, leaf, and pieces thicker than 6 mm (0.25 in) are considered plate, such as plate steel, a class of structural steel. Sheet metal is available in flat pieces or coiled strips. The coils are formed by running a continuous sheet of metal through a roll slitting, roll slitter. In most of the world, sheet metal thickness is consistently specified in millimeters. In the U.S., the thickness of sheet metal is commonly specified by a traditional, non-linear measure known as its Sheet metal gauge, gauge. The larger the gauge number, the thinner the metal. Commonly used steel sheet metal ranges from 30 gauge (0.40 mm) to about 7 gauge (4.55 mm). Gauge differs between ferrous (Iron, iron-based) metals and nonferrous metals such as aluminum or copper. Copper thickness, for example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butane
Butane () is an alkane with the formula C4H10. Butane exists as two isomers, ''n''-butane with connectivity and iso-butane with the formula . Both isomers are highly flammable, colorless, easily liquefied gases that quickly vaporize at room temperature and pressure. Butanes are a trace components of natural gases (NG gases). The other hydrocarbons in NG include propane, ethane, and especially methane, which are more abundant. Liquefied petroleum gas is a mixture of propane and some butanes. The name butane comes from the root but- (from butyric acid, named after the Greek word for butter) and the suffix -ane (for organic compounds). History The first synthesis of butane was accidentally achieved by British chemist Edward Frankland in 1849 from ethyl iodide and zinc, but he had not realized that the ethyl radical dimerized and misidentified the substance. It was discovered in crude petroleum in 1864 by Edmund Ronalds, who was the first to describe its proper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scope Soldering Iron
The "Scope" soldering iron is a tool for soldering with lead-tin alloys, made in Australia since 1950, and intended for occasional or intermittent use. It has the virtue of quickly coming up to soldering temperature (~300C) and delivering considerable heat to a small area, but requires care to avoid overheating. It operates on low voltage (3–6V) and high current (tens of amps) from a battery or suitable transformer, so is by design electrically safe, and as it cools down rapidly when it leaves the operator's hand, should not constitute a fire risk. Principle of operation The soldering iron's " element" is a small carbon tip at the end of a pushrod connected to one terminal of the power supply, inside the stainless-steel barrel of the tool, but insulated from it. The barrel and its copper tip (the "bit"), is connected to the other terminal. When the user operates the pushrod, the carbon element bears against the back of the "bit", resulting in electric heating of the resistive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
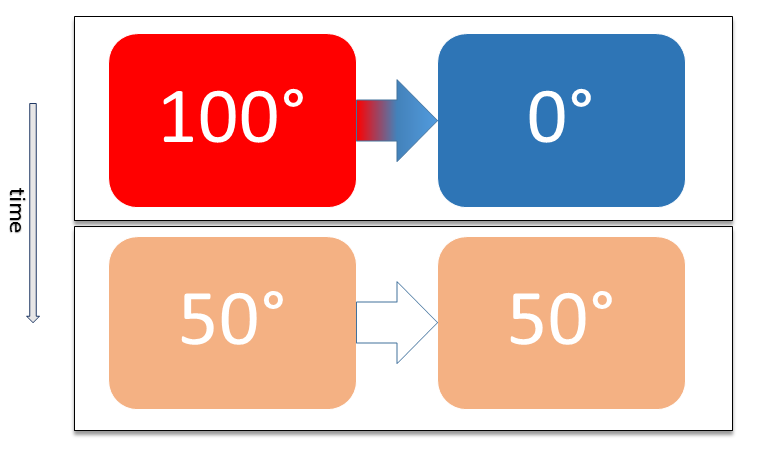
Thermal Equilibrium
Two physical systems are in thermal equilibrium if there is no net flow of thermal energy between them when they are connected by a path permeable to heat. Thermal equilibrium obeys the zeroth law of thermodynamics. A system is said to be in thermal equilibrium with itself if the temperature within the system is spatially uniform and temporally constant. Systems in thermodynamic equilibrium are always in thermal equilibrium, but the converse is not always true. If the connection between the systems allows transfer of energy as 'change in internal energy' but does not allow transfer of matter or transfer of energy as work, the two systems may reach thermal equilibrium without reaching thermodynamic equilibrium. Two varieties of thermal equilibrium Relation of thermal equilibrium between two thermally connected bodies The relation of thermal equilibrium is an instance of equilibrium between two bodies, which means that it refers to transfer through a selectively permeable par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of Power (physics), power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantification (science), quantify the rate of Work (physics), energy transfer. The watt is named in honor of James Watt (1736–1819), an 18th-century Scottish people, Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved the Newcomen engine with his own Watt steam engine, steam engine in 1776, which became fundamental for the Industrial Revolution. Overview When an object's velocity is held constant at one meter per second against a constant opposing force of one Newton (unit), newton, the rate at which Work (physics), work is done is one watt. \mathrm. In terms of electromagnetism, one watt is the rate at which electrical work is performed when a current of one ampere (A) flows across an electrical potential difference of one volt (V), meaning the watt is equivalent to the vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
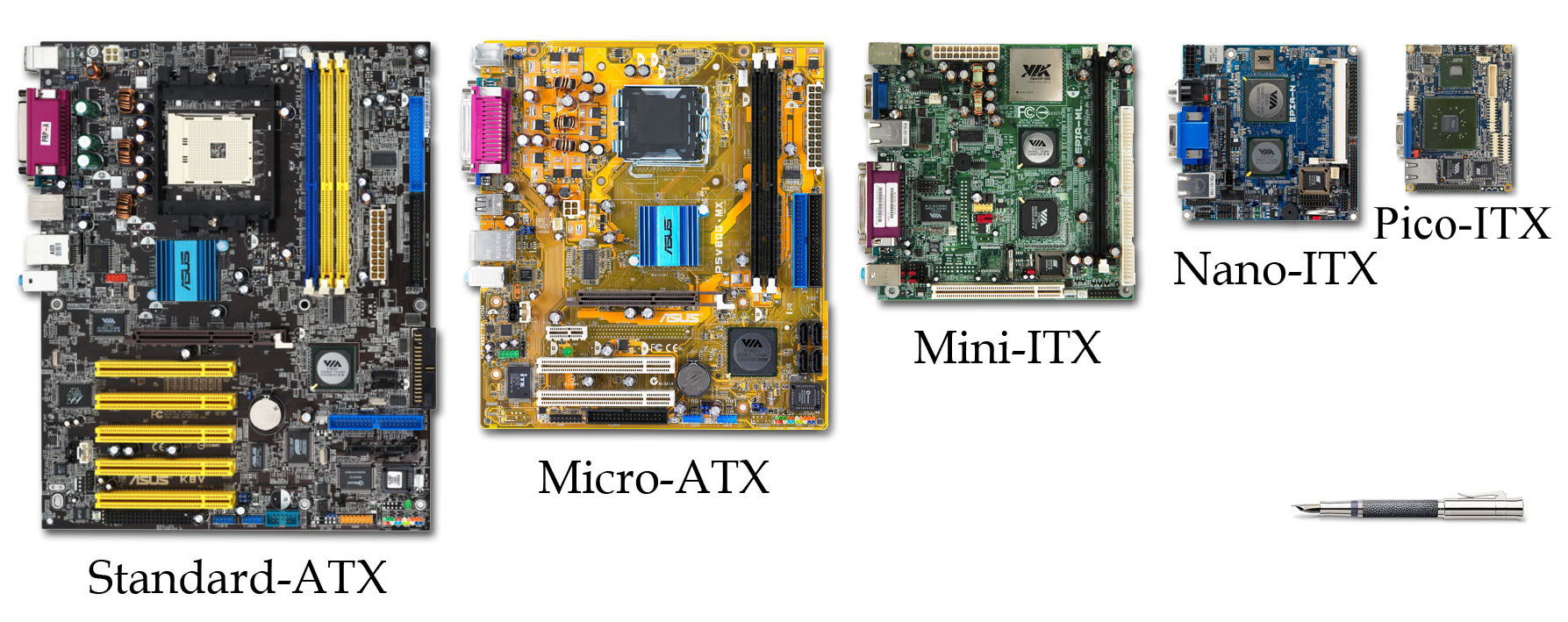
Form Factor (design)
Form factor is a hardware design aspect that defines and prescribes the size, shape, and other physical specifications of components, particularly in electronics. A form factor may represent a broad class of similarly sized components, or it may prescribe a specific standard. It may also define an entire system, as in a computer form factor. Evolution and standardization As electronic hardware has become smaller following Moore's law and related patterns, ever-smaller form factors have become feasible. Specific technological advances, such as PCI Express, have had a significant design impact, though form factors have historically evolved slower than individual components. Standardization of form factors is vital for hardware compatibility between different manufacturers. Trade-offs Smaller form factors may offer more efficient use of limited space, greater flexibility in the placement of components within a larger assembly, reduced use of material, and greater ease of transportat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Soldering Iron
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations. Common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others. The presence of either a positive or negative electric charge produces an electric field. The motion of electric charges is an electric current and produces a magnetic field. In most applications, Coulomb's law determines the force acting on an electric charge. Electric potential is the work done to move an electric charge from one point to another within an electric field, typically measured in volts. Electricity plays a central role in many modern technologies, serving in electric power where electric current is used to energise equipment, and in electronics dealing with electrical c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of the secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high-tech, but it is most commonly applied to industrial design, in which raw materials from the primary sector are transformed into finished goods on a large scale. Such goods may be sold to other manufacturers for the production of other more complex products (such as aircraft, household appliances, furniture, sports equipment or automobiles), or distributed via the tertiary industry to end users and consumers (usually through wholesalers, who in turn sell to retailers, who then sell them to individual customers). Manufacturing engineering is the field of engineering that designs and optimizes the manufacturing process, or the steps through which raw materials are transformed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resistance Wire
Resistance wire is wire intended for making electrical resistors (which are used to control the amount of current in a circuit). It is better if the alloy used has a high resistivity, since a shorter wire can then be used. In many situations, the stability of the resistor is of primary importance, and thus the alloy's temperature coefficient of resistivity and corrosion resistance play a large part in material selection. When resistance wire is used for heating elements (in electric heaters, toasters, and the like), high resistivity and oxidation resistance is important. Sometimes resistance wire is insulated by ceramic powder and sheathed in a tube of another alloy. Such heating elements are used in electric ovens and water heaters, and in specialized forms for cooktops. __TOC__ Types Nichrome, a non-magnetic 80/20 alloy of nickel and chromium, is the most common resistance wire for heating purposes because it has a high resistivity and resistance to oxidation at high tempe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |