|
Solar Tracking
A solar tracker is a device that orients a payload toward the Sun. Payloads are usually solar panels, parabolic troughs, Fresnel reflectors, lenses, or the mirrors of a heliostat. For flat-panel photovoltaic systems, trackers are used to minimize the angle of incidence between the incoming sunlight and a photovoltaic panel, sometimes known as the cosine error. Reducing this angle increases the amount of energy produced from a fixed amount of installed power-generating capacity. In standard photovoltaic applications, it was predicted in 2008–2009 that trackers could be used in at least 85% of commercial installations greater than one megawatt from 2009 to 2012. As the pricing, reliability, and performance of single-axis trackers have improved, the systems have been installed in an increasing percentage of utility-scale projects. According to data from WoodMackenzie/GTM Research, global solar tracker shipments hit a record 14.5 gigawatts in 2017. This represents growth of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Solar Trackers
Solar may refer to: Astronomy * Of or relating to the Sun ** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun ** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels") ** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate the position of the Earth on its revolution around the Sun ** Solar eclipse, an eclipse of a sun in which it is obstructed by the moon ** Solar System, the planetary system made up by the Sun and the objects orbiting it * Solar Maximum Mission, a satellite * SOLAR (ISS), an observatory on International Space Station Music * "Solar" (composition), attributed to Miles Davis * ''Solar'' (Red Garland album), 1962 * ''Solar'' (Taeyang album), 2010 * ''Solar'', a 2011 album by Rubik * "Solar", a song by Northlane from ''Mesmer'', 2017 * "Solar", a song by Sault from ''Air'', 2022 * ”Solar”, a song by Stam1na from '' Taival'', 2018 * SOLAR Records, a record label Geography * Solar (Spanish term), a type of urban site * Solar, County ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Polarization (waves)
, or , is a property of transverse waves which specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. One example of a polarized transverse wave is vibrations traveling along a taut string, for example, in a musical instrument like a guitar string. Depending on how the string is plucked, the vibrations can be in a vertical direction, horizontal direction, or at any angle perpendicular to the string. In contrast, in longitudinal waves, such as sound waves in a liquid or gas, the displacement of the particles in the oscillation is always in the direction of propagation, so these waves do not exhibit polarization. Transverse waves that exhibit polarization include electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves, gravitational waves, and transverse sound waves ( shear waves) in solids. An electromagnetic wave such as light consists of a coupled oscillating el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Polar
Polar may refer to: Geography * Geographical pole, either of the two points on Earth where its axis of rotation intersects its surface ** Polar climate, the climate common in polar regions ** Polar regions of Earth, locations within the polar circles, referred to as the Arctic and Antarctic Places * Polar, Wisconsin, town in Langlade County, Wisconsin, United States ** Polar (community), Wisconsin, unincorporated community in Langlade County, Wisconsin, United States Arts, entertainment and media * ''Polar'' (webcomic), a webcomic and series of graphic novels by Víctor Santos * ''Polar'' (film), a 2019 Netflix film adaption of the above comic series * ''Polar'', a 2002 novel by T. R. Pearson Music * Polar Music, a record label * Polar Studios, music studio of ABBA in Sweden * ''Polar'' (album), second album by the High Water Marks * ''Polars'' (album), an album by the Dutch metal band, Textures Brands and enterprises * Polar Air Cargo, an American airline * Polar Airline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
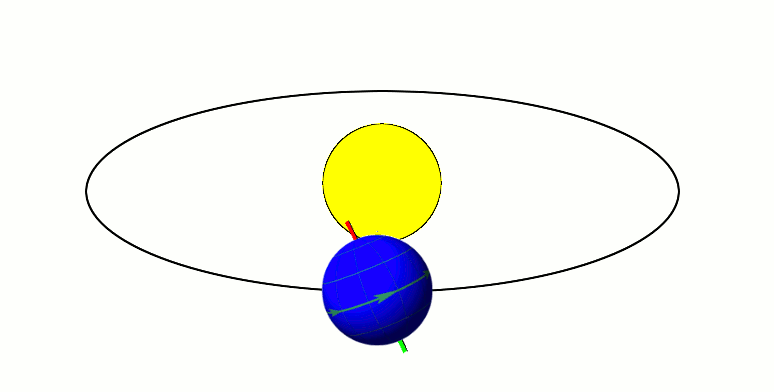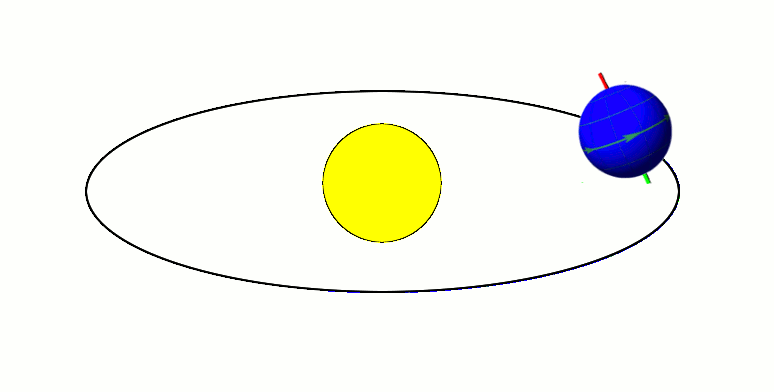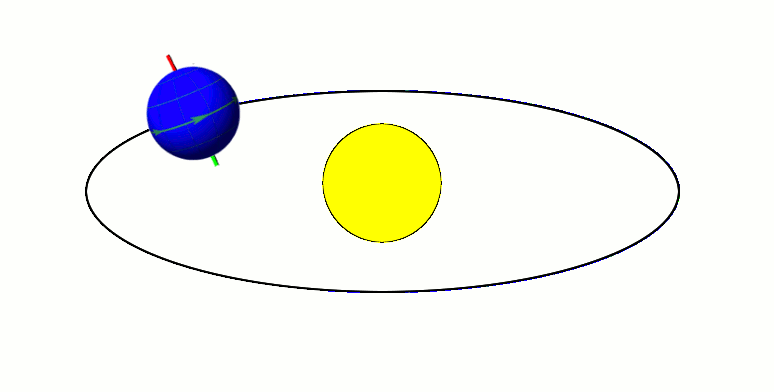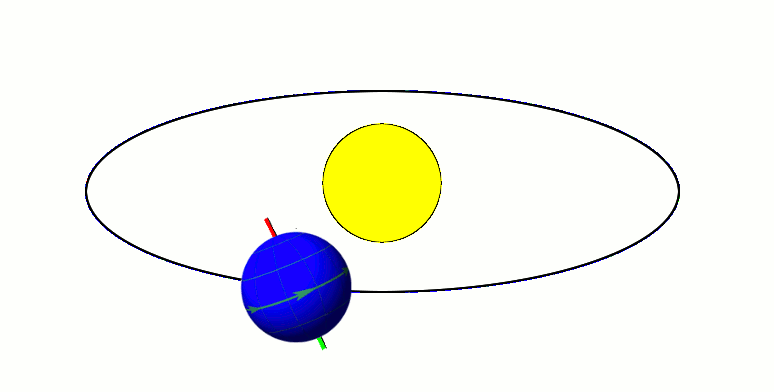
Axial Tilt
In astronomy, axial tilt, also known as obliquity, is the angle between an object's rotational axis and its orbital axis, which is the line perpendicular to its orbital plane; equivalently, it is the angle between its equatorial plane and orbital plane. It differs from orbital inclination. At an obliquity of 0 degrees, the two axes point in the same direction; that is, the rotational axis is perpendicular to the orbital plane. The rotational axis of Earth, for example, is the imaginary line that passes through both the North Pole and South Pole, whereas the Earth's orbital axis is the line perpendicular to the imaginary plane through which the Earth moves as it revolves around the Sun; the Earth's obliquity or axial tilt is the angle between these two lines. Over the course of an orbital period, the obliquity usually does not change considerably, and the orientation of the axis remains the same relative to the background of stars. This causes one pole to be pointed mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Destructive Interference
In physics, interference is a phenomenon in which two coherent waves are combined by adding their intensities or displacements with due consideration for their phase difference. The resultant wave may have greater amplitude (constructive interference) or lower amplitude (destructive interference) if the two waves are in phase or out of phase, respectively. Interference effects can be observed with all types of waves, for example, light, radio, acoustic, surface water waves, gravity waves, or matter waves as well as in loudspeakers as electrical waves. Etymology The word ''interference'' is derived from the Latin words ''inter'' which means "between" and ''fere'' which means "hit or strike", and was used in the context of wave superposition by Thomas Young in 1801. Mechanisms The principle of superposition of waves states that when two or more propagating waves of the same type are incident on the same point, the resultant amplitude at that point is equal to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Anti-reflective Coating
An antireflective, antiglare or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lens (optics), lenses, other optical elements, and photovoltaic cells to reduce reflection (physics), reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost due to reflection. In complex systems such as cameras, binoculars, telescopes, and optical microscope, microscopes the reduction in reflections also improves the Contrast (vision), contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on glasses, eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight. Many coatings consist of transparent thin-film optics, thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fresnel Equations
The Fresnel equations (or Fresnel coefficients) describe the reflection and transmission of light (or electromagnetic radiation in general) when incident on an interface between different optical media. They were deduced by French engineer and physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel () who was the first to understand that light is a transverse wave, when no one realized that the waves were electric and magnetic fields. For the first time, polarization could be understood quantitatively, as Fresnel's equations correctly predicted the differing behaviour of waves of the ''s'' and ''p'' polarizations incident upon a material interface. Overview When light strikes the interface between a medium with refractive index and a second medium with refractive index , both reflection and refraction of the light may occur. The Fresnel equations give the ratio of the ''reflected'' wave's electric field to the incident wave's electric field, and the ratio of the ''transmitted'' wave's electric f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Refractive Index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refraction, refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, , where and are the angle of incidence (optics), angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices and . The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflectivity, reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity (Fresnel equations) and Brewster's angle. The refractive index, n, can be seen as the factor by which the speed and the wavelength of the radiation are reduced with respect to their vacuum values: the speed of light in a medium is , and similarly the wavelength in that me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Reflection (physics)
Reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two different media so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated. Common examples include the reflection of light, sound and water waves. The ''law of reflection'' says that for specular reflection (for example at a mirror) the angle at which the wave is incident on the surface equals the angle at which it is reflected. In acoustics, reflection causes echoes and is used in sonar. In geology, it is important in the study of seismic waves. Reflection is observed with surface waves in bodies of water. Reflection is observed with many types of electromagnetic wave, besides visible light. Reflection of VHF and higher frequencies is important for radio transmission and for radar. Even hard X-rays and gamma rays can be reflected at shallow angles with special "grazing" mirrors. Reflection of light Reflection of light is either '' specular'' (mirror-like) or '' diffuse'' (retai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fresnel Reflection
The Fresnel equations (or Fresnel coefficients) describe the reflection and transmission of light (or electromagnetic radiation in general) when incident on an interface between different optical media. They were deduced by French engineer and physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel () who was the first to understand that light is a transverse wave, when no one realized that the waves were electric and magnetic fields. For the first time, polarization could be understood quantitatively, as Fresnel's equations correctly predicted the differing behaviour of waves of the ''s'' and ''p'' polarizations incident upon a material interface. Overview When light strikes the interface between a medium with refractive index and a second medium with refractive index , both reflection and refraction of the light may occur. The Fresnel equations give the ratio of the ''reflected'' wave's electric field to the incident wave's electric field, and the ratio of the ''transmitted'' wave's electric fie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lambert's Cosine Law
In optics, Lambert's cosine law says that the observed radiant intensity or luminous intensity from an ideal diffusely reflecting surface or ideal diffuse radiator is directly proportional to the cosine of the angle ''θ'' between the observer's line of sight and the surface normal; .RCA Electro-Optics Handbook, p.18 ffModern Optical Engineering, Warren J. Smith, McGraw-Hill, p. 228, 256 The law is also known as the cosine emission law or Lambert's emission law. It is named after Johann Heinrich Lambert, from his '' Photometria'', published in 1760. A surface which obeys Lambert's law is said to be ''Lambertian'', and exhibits Lambertian reflectance. Such a surface has a constant radiance/luminance, regardless of the angle from which it is observed; a single human eye perceives such a surface as having a constant brightness, regardless of the angle from which the eye observes the surface. It has the same radiance because, although the emitted power from a given area ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sun Path
Sun path, sometimes also called day arc, refers to the diurnal motion, daily (sunrise to sunset) and seasonal arc (geometry), arc-like path that the Sun appears to follow across the sky as the Earth Earth's rotation, rotates and Earth's orbit, orbits the Sun. The Sun's path affects the length of daytime experienced and amount of daylight received along a certain latitude during a given season. The relative position of the Sun is a major factor in the solar gain, heat gain of buildings and in the performance of solar energy systems. Accurate location-specific knowledge of sun path and climatic conditions is essential for economic decisions about solar thermal collector, solar collector area, orientation, landscaping, summer shading, and the cost-effective use of solar trackers. Angles Effect of the Earth's axial tilt Sun paths at any latitude and any time of the year can be determined from basic geometry. The Earth's axis of Earth's rotation, rotation tilts about Axial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |