|
Solar Spicule
In solar physics, a spicule, also known as a fibril or mottle, is a dynamic jet of plasma in the Sun's chromosphere about 300 km in diameter.Quantifying Spicules, Tiago M. D. Pereira, Bart De Pontieu, and Mats Carlsson, ''The Astrophysical Journal'' 759, #1 (October 2012), pp. 18-34, , . They move upwards with speeds between 15 and 110 km/s from the photosphere and last a few minutes each before falling back to the solar atmosphere. They were discovered in 1877 by Angelo Secchi, but the physical mechanism that generates them is still hotly debated. Description Spicules last for about 15 minutes; at the solar limb they appear elongated (if seen on the disk, they are known as "mottles" or "fibrils"). They are usually associated with regions of high magnetic flux; their mass flux is about 100 times that of the solar wind. They rise at a rate of 20 km/s (or 72,000 km/h) and can reach several thousand kilometers in height before collapsing and fading away. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halpha %2B700 Limb Spicules 08Aug2007 SST
Hydrogen-alpha, typically shortened to H-alpha or Hα, is a deep-red visible spectral line of the hydrogen atom with a wavelength of 656.28 nanometre, nm in air and 656.46 nm in vacuum. It is the first spectral line in the Balmer series and is emitted when an electron falls from a hydrogen atom's third- to second-lowest energy level. H-alpha has applications in astronomy where its emission can be observed from emission nebulae and from features in the Sun's Sun#Atmosphere, atmosphere, including solar prominences and the chromosphere. Balmer series According to the Bohr model of the atom, electrons exist in Quantum, quantized energy levels surrounding the atom's atomic nucleus, nucleus. These energy levels are described by the principal quantum number ''n'' = 1, 2, 3, ... . Electrons may only exist in these states, and may only transit between these states. The set of transitions from ''n'' ≥ 3 to ''n'' = 2 is called the Balmer series and its members are named sequenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Physics
Solar physics is the branch of astrophysics that specializes in the study of the Sun. It intersects with many disciplines of pure physics and astrophysics. Because the Sun is uniquely situated for close-range observing (other stars cannot be resolved with anything like the spatial or temporal resolution that the Sun can), there is a split between the related discipline of observational astrophysics (of distant stars) and observational solar physics. The study of solar physics is also important as it provides a "physical laboratory" for the study of plasma physics. History Ancient times Babylonians were keeping a record of solar eclipses, with the oldest record originating from the ancient city of Ugarit, in modern-day Syria. This record dates to about 1300 BC. Ancient Chinese astronomers were also observing solar phenomena (such as solar eclipses and visible sunspots) with the purpose of keeping track of calendars, which were based on lunar and solar cycles. Unfortunately, rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosphere
A chromosphere ("sphere of color", from the Ancient Greek words χρῶμα (''khrôma'') 'color' and σφαῖρα (''sphaîra'') 'sphere') is the second layer of a Stellar atmosphere, star's atmosphere, located above the photosphere and below the solar transition region and Stellar corona, corona. The term usually refers to the Sun's chromosphere, but not exclusively, since it also refers to the corresponding layer of a stellar atmosphere. The name was suggested by the English astronomer Norman Lockyer after conducting systematic solar observations in order to distinguish the layer from the white-light emitting photosphere. In the solar atmosphere, Sun's atmosphere, the chromosphere is roughly in height, or slightly more than 1% of the Sun's radius at maximum thickness. It possesses a homogeneous layer at the boundary with the photosphere. Narrow jets of Plasma (physics), plasma, called Solar spicule, spicules, rise from this homogeneous region and through the chromosphere, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosphere
The photosphere is a star's outer shell from which light is radiated. It extends into a star's surface until the plasma becomes opaque, equivalent to an optical depth of approximately , or equivalently, a depth from which 50% of light will escape without being scattered. A photosphere is the region of a luminous object, usually a star, that is transparent to photons of certain wavelengths. Stars, except neutron stars, have no solid or liquid surface. Therefore, the photosphere is typically used to describe the Sun's or another star's visual surface. Etymology The term ''photosphere'' is derived from Ancient Greek roots, φῶς, φωτός/''phos'', ''photos'' meaning "light" and σφαῖρα/''sphaira'' meaning "sphere", in reference to it being a spherical surface that is perceived to emit light. Temperature The surface of a star is defined to have a temperature given by the effective temperature in the Stefan–Boltzmann law. Various stars have photospheres of vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angelo Secchi
Angelo Secchi (; 28 June 1818 – 26 February 1878) was an Italians, Italian Priesthood in the Catholic Church, Catholic priest and astronomer from the Regions of Italy, Italian region of Emilia-Romagna, Emilia. He was director of the observatory at the Pontifical Gregorian University (then called the Roman College) for 28 years. He was a pioneer in astronomical spectroscopy, and was one of the first scientists to state authoritatively that the Sun is a star. Biography Secchi was born in Reggio Emilia, where he studied at the Jesuit Gymnasium (school), gymnasium. At the age of 16, he entered the Society of Jesus, Jesuit Order in Rome. He continued his studies at the Roman College, and demonstrated great scientific ability. In 1839, he was appointed tutor of mathematics and physics at the college. In 1841, he became professor of physics at the Jesuit College in Loreto (AN), Loreto. In 1844, he began theology, theological studies in Rome, and was Holy Orders, ordained a priest o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Limb
Limb darkening is an optical effect seen in stars (including the Sun) and planets, where the central part of the disk appears brighter than the edge, or ''limb''. Its understanding offered early solar astronomers an opportunity to construct models with such gradients. This encouraged the development of the theory of radiative transfer. Basic theory Optical depth, a measure of the opacity of an object or part of an object, combines with effective temperature gradients inside the star to produce limb darkening. The light seen is approximately the integral of all emission along the line of sight modulated by the optical depth to the viewer (i.e. 1/e times the emission at 1 optical depth, 1/e2 times the emission at 2 optical depths, etc.). Near the center of the star, optical depth is effectively infinite, causing approximately constant brightness. However, the effective optical depth decreases with increasing radius due to lower gas density and a shorter line of sight distance t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Flux
In physics, specifically electromagnetism, the magnetic flux through a surface is the surface integral of the normal component of the magnetic field B over that surface. It is usually denoted or . The SI unit of magnetic flux is the weber (Wb; in derived units, volt–seconds or V⋅s), and the CGS unit is the maxwell. Magnetic flux is usually measured with a fluxmeter, which contains measuring coils, and it calculates the magnetic flux from the change of voltage on the coils. Description The magnetic interaction is described in terms of a vector field, where each point in space is associated with a vector that determines what force a moving charge would experience at that point (see Lorentz force). Since a vector field is quite difficult to visualize, introductory physics instruction often uses field lines to visualize this field. The magnetic flux, through some surface, in this simplified picture, is proportional to the number of field lines passing through that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Flux
In physics and engineering, mass flux is the rate of mass flow per unit of area. Its SI units are kgs−1m−2. The common symbols are ''j'', ''J'', ''q'', ''Q'', ''φ'', or Φ (Greek lowercase or capital Phi), sometimes with subscript ''m'' to indicate mass is the flowing quantity. This flux quantity is also known simply as "mass flow". "Mass flux" can also refer to an alternate form of flux in Fick's law that includes the molecular mass, or in Darcy's law that includes the mass density. Less commonly the defining equation for mass flux in this article is used interchangeably with the defining equation in mass flow rate. Definition Mathematically, mass flux is defined as the limit j_m = \lim_ \frac, where I_m = \lim_ \frac = \frac is the mass current (flow of mass per unit time ) and is the area through which the mass flows. For mass flux as a vector , the surface integral of it over a surface ''S'', followed by an integral over the time duration to , gives the total a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
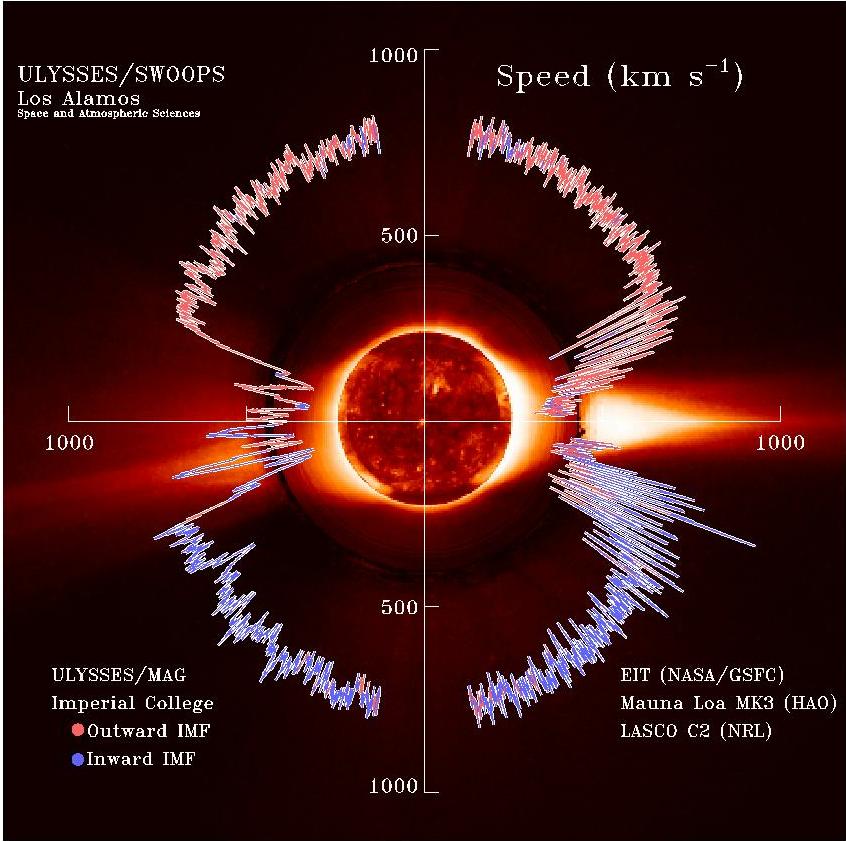
Solar Wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the Stellar corona, corona. This Plasma (physics), plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of particle species found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei of Chemical element, elements such as carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, neon, magnesium, silicon, sulfur, and iron. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as phosphorus, titanium, chromium, and nickel's isotopes 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superimposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over Solar coordinate systems#Heliographic, solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bart De Pontieu
Bart De Pontieu is a solar physicist who works at Lockheed Martin's Solar & Astrophysics Laboratory. He is known for his work on the dynamics and heating of the solar chromosphere, transition region and corona, via both wave mechanisms and nanoflares. De Pontieu has had a major role in multiple solar scientific space missions, including TRACE, Hinode, the Solar Dynamics Observatory, and IRIS. He is the Principal Investigator of the in-development Multi-slit Solar Explorer selected by NASA in February 2022. De Pontieu is a member of the American Astronomical Society and its Solar Physics Division, as well as the American Geophysical Union and the Belgian Astronomical Society (''Vereniging voor Sterrenkunde''). He was elected to the Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters in 2018. Education * M.Sc., Physics/Electrotechnical Engineering, University of Ghent, Belgium, 1992 * Ph.D., Physics, Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics The Max Planck Institute for Extr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed Martin Solar And Astrophysics Laboratory
The Lockheed Martin Solar and Astrophysics Laboratory (LMSAL) is part of the Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center (ATC) that is known primarily for its scientific work in the field of solar physics, astronomy and space weather. The LMSAL team is part of Lockheed Martin Space Systems and has close affiliations with NASA and the solar physics group at Stanford University. Located in Palo Alto, California, LMSAL is involved in many ground- and space-based missions that study the Sun, with a sharp focus on basic research into understanding and predicting space weather and the behavior of the Sun, including its impacts on Earth and climate. Space weather Enormous storms on the Sun driven by electromagnetic activity generate space weather that propagates outward across the Solar System and can cause severe disturbances of Earth's upper atmosphere and of the near-Earth space environment, with potential catastrophic impacts on ground- and space-based technological infrastructure. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palo Alto, California
Palo Alto ( ; Spanish language, Spanish for ) is a charter city in northwestern Santa Clara County, California, United States, in the San Francisco Bay Area, named after a Sequoia sempervirens, coastal redwood tree known as El Palo Alto. The city of Palo Alto was incorporated in 1894 by the American industrialist Leland Stanford and his wife, Jane Stanford, when they founded Stanford University in memory of their only child, Leland Stanford Jr. Palo Alto later expanded and now borders East Palo Alto, California, East Palo Alto, Mountain View, California, Mountain View, Los Altos, California, Los Altos, Los Altos Hills, California, Los Altos Hills, Stanford, California, Stanford, Portola Valley, California, Portola Valley, and Menlo Park, California, Menlo Park. As of the 2020 United States census, the population was 68,572. Palo Alto has one of the highest costs of living in the United States, and its residents are among the most educated in the country. However, it has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |