|
Sokho
Sokho (alternate spellings: Sokhoh, Sochoh, Soco, Sokoh; he, שׂוֹכֹה ,שׂוֹכ֖וֹ ,שֹׂכֹ֖ה) is the name given to two ancient towns in the territorial domain of Judah as mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, west of the Judean hills. Both towns were given the name ''Shuweikah'' in Arabic, a diminutive of the Arabic ''shawk'', meaning "thorn". The remains of both have since been identified. One is located about southwest of Hebron and has been identified with the twin ruins known as ''Khirbet Shuwaikah Fauka'' and ''Tahta'' (Upper and Lower Shuwaikah), southwest of Eshtamoa in the Hebron Hills district (grid position 150/091 PAL)(). The other ruin is situated on a hilltop overlooking the Elah Valley between Adullam and Azekah (), in the lower stratum of the Judaean foothills (grid position 147/121 PAL). Today it is a popular tourist attraction better known as Givat HaTurmusim. The site, occupied as early as the Iron Age, was visited by Claude C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adullam
Adullam () is an ancient ruin, formerly known by the Arabic appellation ''ʿAīd el Mâ'' (or ''`Eîd el Mieh''), built upon a hilltop overlooking the Elah Valley, straddling the Green Line between Israel and the West Bank. In the late 19th century, the town was still in ruins. The hilltop ruin is also known by the name ''Khurbet esh-Sheikh Madkour'', named after Madkour, one of the sons of the Sultan Beder, for whom is built a shrine (''wely'') and formerly called by its inhabitants ''Wely Madkour''. The hilltop is mostly flat, with cisterns carved into the rock. The remains of stone structures which once stood there can still be seen. Sedimentary layers of ruins from the old Canaanite and Israelite eras, mostly potsherds, are noticeable everywhere, although olive groves now grow atop of this hill, enclosed within stone hedges. The villages of Aderet, Aviezer and Khirbet al-Deir are located nearby. The ruin lies about south of Moshav Neve Michael. The area around ancient Adu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigonus Of Sokho
Antigonus of Sokho ( he, אנטיגנוס איש סוכו) was the first scholar of whom Pharisee tradition has preserved not only the name but also an important theological doctrine. He flourished about the first half of the third century BCE. According to the Mishnah, he was the disciple of Simon the Just ( he, שמעון הצדיק). Antigonus is the first noted Jew to have a Greek language, Greek name, a fact commonly discussed by scholars regarding the extent of Hellenic influence on Judaism following the conquest of Judaea by Alexander the Great. A street in the Katamon, Katamonim neighborhood of Jerusalem is named after him. Sadducees and Boethusians Traditional Jewish sources connect Antigonus with the origin of the Sadducees and Boethusians. These sources argue that the Sadducee group originated ''in tandem'' with the Boethusians, Boethusian group during the Second Temple period, with their founders, Zadok and Boethus, both being individual students of Antigonus of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
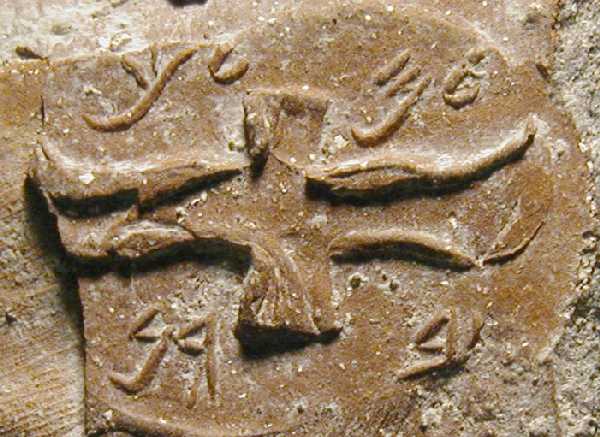
LMLK Seal
LMLK seals (with LMLK meaning 'of the king') are ancient Hebrew Stamp seal, seals stamped on the handles of large storage jars first issued in the reign of King Hezekiah (circa 700 BC) and discovered mostly in and around Jerusalem. Several complete jars were found ''in situ'' buried under a destruction layer caused by Sennacherib at Lachish. While none of the original seals have been found, some 2,000 impressions made by at least 21 seal types have been published. The iconography of the two and four winged symbols are representative of royal symbols whose meaning "was tailored in each kingdom to the local religion and ideology". Text LMLK stands for the Hebrew letters ''lamedh mem lamedh kaph'' (vocalized, ''lamelekh''; Phoenician language, Phoenician ''lāmed mēm lāmed kāp'' — 𐤋𐤌𐤋𐤊), which can be translated as: * "[belonging] to the king" (of Kingdom of Judah, Judah) * "[belonging] to King" (name of a person or deity) * "[belonging] to the government" (of Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valley Of Elah
The Valley of Elah or Ella Valley ("the valley of the terebinth"; from the he, עמק האלה ''Emek HaElah''), called in ar, وادي السنط, Wadi es-Sunt, is a long, shallow valley in Israel and the West Bank best known as the place described in the Hebrew Bible (or Old Testament of Christianity) where the Israelites were encamped when David fought Goliath (; ). It is home to several important archaeological sites, including those identified as the ancient towns of Azekah and Sokho, Socho (). Rising up from the valley on its extreme southeast end lies the hilltop ruin Adullam, and on its north lie the ruins of the ancient fortress city of Khirbet Qeiyafa, which is identified with the ancient town of Sha'araim (). The valley is named after the large and shady terebinth trees (''Pistacia atlantica'') which are indigenous to it. On the west side of the valley, near Socho, there is a very large and ancient tree of this kind, in height with a trunk in circumference and a ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azekah
Azekah ( he, עֲזֵקָה, ''ʿazēqā'') was an ancient town in the Shfela ("lowlands of Judea") guarding the upper reaches of the Valley of Elah, about 26 km (16 mi) northwest of Hebron. The current '' tell'' (ruin) by that name, also known as Tel Azeka ( he, תל עזקה, ''ʿtel azēqā'') or Tell Zakariya, has been identified with the biblical Azekah, dating back to the Canaanite period. Today, the site lies on the purlieu of Britannia Park. According to Epiphanius of Salamis, the name meant "white" in Hebrew. The ''tell'' is pear shaped with the tip pointing northward. Due to its location in the Elah Valley it functioned as one of the main Judahite border cities, sitting on the boundary between the lower and higher Shfela.Gadot, ''et al.'' (2012), pp. 196–206 Although listed in Joshua 15:35 as being a city in the plain, it is actually partly in the hill country, partly in the plain. Biblical history In the Bible, it is said to be one of the places where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goliath
Goliath ( ) ''Goləyāṯ''; ar, جُليات ''Ǧulyāt'' (Christian term) or (Quranic term). is a character in the Book of Samuel, described as a Philistine giant defeated by the young David in single combat. The story signified King Saul's unfitness to rule, as Saul himself should have fought for Israel. Scholars today believe that the original listed killer of Goliath was Elhanan, son of Jair, and that the authors of the Deuteronomic history changed the original text to credit the victory to the more famous character David. The phrase "David and Goliath" has taken on a more popular meaning denoting an underdog situation, a contest wherein a smaller, weaker opponent faces a much bigger, stronger adversary. "used to describe a situation in which a small or weak person or organization tries to defeat another much larger or stronger opponent: ''The game looks like it will be a David and Goliath contest.''" Biblical account The Goliath narrative in 1 Samuel 17 Saul and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". was, according to the Hebrew Bible, the third king of the United Kingdom of Israel. In the Books of Samuel, he is described as a young shepherd and harpist who gains fame by slaying Goliath, a champion of the Philistines, in southern Canaan. David becomes a favourite of Saul, the first king of Israel; he also forges a notably close friendship with Jonathan, a son of Saul. However, under the paranoia that David is seeking to usurp the throne, Saul attempts to kill David, forcing the latter to go into hiding and effectively operate as a fugitive for several years. After Saul and Jonathan are both killed in battle against the Philistines, a 30-year-old David is anointed king over all of Israel and Judah. Following his rise to power, D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rehoboam
Rehoboam (; , ; , ; la, Roboam, ) was, according to the Hebrew Bible, the last monarch of the United Kingdom of Israel and the first monarch of the Kingdom of Judah after the former's split. He was a son of and the successor to Solomon and a grandson of David. In the account of I Kings and II Chronicles, Rehoboam was initially a king of the United Monarchy, but later saw his rule limited to only the Kingdom of Judah in the south following a rebellion by the ten northern tribes of Israel in 932/931 BCE, which led to the formation of the independent Kingdom of Israel under the rule of Jeroboam in the north. Biblical background According to the ''Jewish Encyclopedia'', "Solomon's wisdom and power were not sufficient to prevent the rebellion of several of his border cities. Damascus under Rezon secured its independence romSolomon; and Jeroboam, a superintendent of works, his ambition stirred by the words of the prophet Ahijah (), fled to Egypt. Thus before the death of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahaz
Ahaz (; gr, Ἄχαζ, Ἀχάζ ''Akhaz''; la, Achaz) an abbreviation of Jehoahaz II (of Judah), " Yahweh has held" (; akk, 𒅀𒌑𒄩𒍣 ''Ya'úḫazi'' 'ia-ú-ḫa-zi'' Hayim Tadmor and Shigeo Yamada, ''The Royal Inscriptions of Tiglath-pileser III (744-727 BC) and Shalmaneser V (726-722 BC), Kings of Assyria''. (The Royal Inscriptions of the Neo-Assyrian Period 1; Winona Lake, IN: Eisenbrauns, 2011), Tiglath-Pileser III 47 r 11'. was the twelfth king of Judah, and the son and successor of Jotham. Ahaz was 20 when he became king of Judah and reigned for 16 years. Ahaz is portrayed as an evil king in the Second Book of Kings (2 Kings 16:2). In Edwin R. Thiele's opinion Ahaz was co-regent with Jotham from 736/735 BC, and his sole reign began in 732/731 and ended in 716/715 BC. However, William F. Albright has dated his reign to 744–728 BC. The Gospel of Matthew lists Ahaz of Judah in the genealogy of Jesus. He is also mentioned in Isaiah 7 and . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestine Grid
The Palestine grid was the geographic coordinate system used by the Survey Department of Palestine. The system was chosen by the Survey Department of the Government of Palestine in 1922. The projection used was the Cassini-Soldner projection. The central meridian (the line of longitude along which there is no local distortion) was chosen as that passing through a marker on the hill of Mar Elias Monastery south of Jerusalem. The false origin (zero point) of the grid was placed 100 km to the south and west of the Ali el-Muntar hill that overlooks Gaza city. The unit length for the grid was the kilometre; the British units were not even considered. At the time the grid was established, there was no intention of mapping the lower reaches of the Negev Desert, but this did not remain true. Those southern regions having a negative north-south coordinate then became a source of confusion, which was solved by adding 1000 to the northern coordinate in that case. For some military purpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bialik Institute
Bialik Institute ( he, מוסד ביאליק, ''Mosad Bialik'') is a research institution and publishing house, mostly dealing with the history and culture of the Hebrew language. It was established in 1935 by the World Zionist Executive and the Executive of the Jewish Agency and named after the Hebrew poet Hayim Nahman Bialik. Its works are mostly published in Hebrew and in English. Among the Bialik Institute's most notable publications are: * ''Encyclopaedia Biblica'' - an encyclopedia of the Hebrew Bible in eight volumes (1942−1982), and ''The Biblical Encyclopaedia Library''—a series of books on Semitic languages, Biblical criticism and history of the Middle East. * A complete collection of David Avidan's poems in four volumes (2008−2011) * A complete collection of Uri Zvi Grinberg Uri Zvi Greenberg ( he, אוּרִי צְבִי גְּרִינְבֵּרְג; September 22, 1896 – May 8, 1981; also spelled Uri Zvi Grinberg) was an acclaimed Israeli poet, journalis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; he, מִשְׁנָה, "study by repetition", from the verb ''shanah'' , or "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first major written collection of the Jewish oral traditions which is known as the Oral Torah. It is also the first major work of rabbinic literature. The Mishnah was redacted by Judah ha-Nasi probably in Beit Shearim or Sepphoris at the beginning of the 3rd century CE in a time when, according to the Talmud, the persecution of the Jews and the passage of time raised the possibility that the details of the oral traditions of the Pharisees from the Second Temple period (516 BCE – 70 CE) would be forgotten. Most of the Mishnah is written in Mishnaic Hebrew, but some parts are in Aramaic. The Mishnah consists of six orders (', singular ' ), each containing 7–12 tractates (', singular ' ; lit. "web"), 63 in total, and further subdivided into chapters and paragraphs. The word ''Mishnah'' can also indicate a single paragraph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)