|
Sodium Selenide
Sodium selenide is an inorganic compound of sodium and selenium with the chemical formula Na2Se. Preparation This colourless solid is prepared by the reaction of selenium with a solution of sodium in liquid ammonia at −40 °C.Brauer, G. ed. (1963) ''Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry'', 2nd Ed., Academic Press, NY., Vol. 1. p. 421. Alternatively, sodium selenide can be prepared by the reaction of gaseous hydrogen selenide with metallic sodium at 100 °C. Reactions Like other alkali metal chalcogenides, this material is highly sensitive to water, easily undergoing hydrolysis to give mixtures of sodium biselenide (NaSeH) and hydroxide. This hydrolysis occurs because of the extreme basicity of the Se2− ion. :Na2Se + H2O → NaHSe + NaOH Similarly, sodium selenide is readily oxidized to polyselenides, a conversion signaled by off-white samples. Sodium selenide reacts with acids to produce toxic hydrogen selenide gas. :Na2Se + 2 HCl → H2Se + 2 NaCl The compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRC Press
The CRC Press, LLC is an American publishing group that specializes in producing technical books. Many of their books relate to engineering, science and mathematics. Their scope also includes books on business, forensics and information technology. CRC Press is now a division of Taylor & Francis, itself a subsidiary of Informa. History The CRC Press was founded as the Chemical Rubber Company (CRC) in 1903 by brothers Arthur, Leo and Emanuel Friedman in Cleveland, Ohio, based on an earlier enterprise by Arthur, who had begun selling rubber laboratory aprons in 1900. The company gradually expanded to include sales of laboratory equipment to chemist A chemist (from Greek ''chēm(ía)'' alchemy; replacing ''chymist'' from Medieval Latin ''alchemist'') is a graduated scientist trained in the study of chemistry, or an officially enrolled student in the field. Chemists study the composition of ...s. In 1913 the CRC offered a short (116-page) manual called the ''Rubber Handboo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compound
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bondsthat is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep Mantle (geology), mantle remain active areas of investigation. All allotropes (structurally different pure forms of an element) and some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, graphene, etc.), carbon monoxide , carbon dioxide , carbides, and salt (chemistry), salts of inorganic anions such as carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, thiocyanates, isothiocyanates, etc. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it cannot occur within life, living things. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Compounds
Sodium atoms have 11 electrons, one more than the stable configuration of the noble gas neon. As a result, sodium usually forms ionic compounds involving the Na+ cation. Sodium is a reactive alkali metal and is much more stable in ionic compounds. It can also form intermetallic compounds and organosodium compounds. Sodium compounds are often soluble in water. Metallic sodium Metallic sodium is generally less reactive than potassium and more reactive than lithium. Sodium metal is highly reducing, with the standard reduction potential for the Na+/Na couple being −2.71 volts, though potassium and lithium have even more negative potentials. The thermal, fluidic, chemical, and nuclear properties of molten sodium metal have caused it to be one of the main coolants of choice for the fast breeder reactor. Such nuclear reactors are seen as a crucial step for the production of clean energy. Salts and oxides Sodium compounds are of immense commercial importance, being particularly centr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
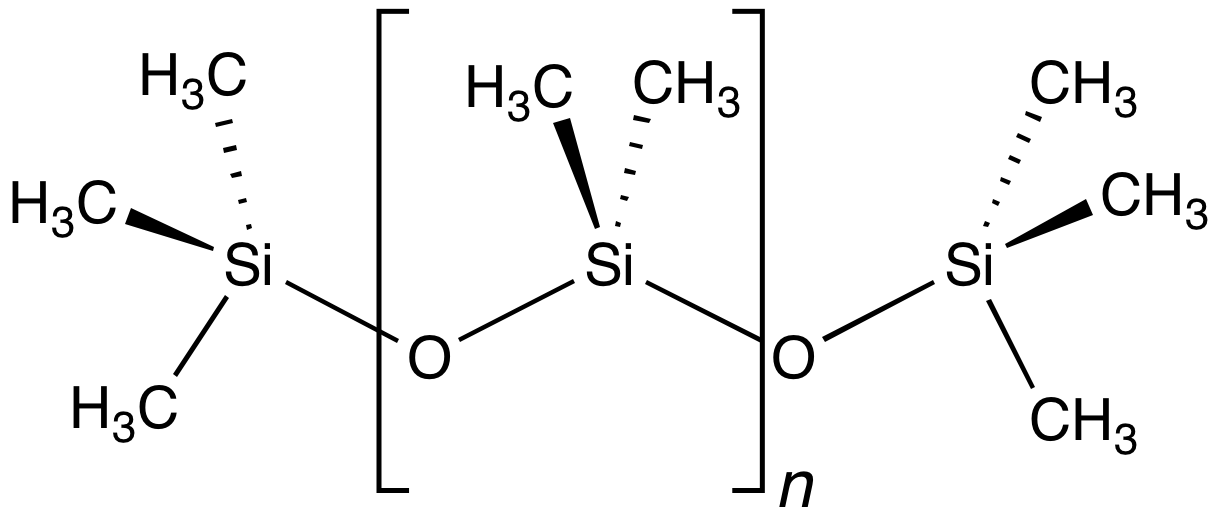
Organosilicon
Organosilicon chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds containing carbon–silicon bonds, to which they are called organosilicon compounds. Most organosilicon compounds are similar to the ordinary organic compounds, being colourless, flammable, hydrophobic, and stable to air. Silicon carbide is an ''inorganic'' compound. History In 1863, Charles Friedel and James Crafts made the first organochlorosilane compound. The same year, they also described a "polysilicic acid ether" in the preparation of ethyl- and methyl-o-silicic acid. Extensive research in the field of organosilicon compounds was pioneered in the beginning of 20th century by Frederic S. Kipping. He also had coined the term "silicone" (resembling ''ketones'', though this is erroneous) in relation to these materials in 1904. In recognition of Kipping's achievements, the Dow Chemical Company had established an award in the 1960s that is given for significant contributions to the field of silicon chemistry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organotin
Organotin chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organotin compounds or stannanes, which are organometallic compounds containing tin–carbon bonds. The first organotin compound was diethyltin diiodide (), discovered by Edward Frankland in 1849. The area grew rapidly in the 1900s, especially after the discovery of the Grignard reagents, which are useful for producing Sn–C bonds. The area remains rich with many applications in industry and continuing activity in the research laboratory. Structure Organotin compounds are generally classified according to their oxidation states. Tin(IV) compounds are much more common and more useful. Organic derivatives of tin(IV) The tetraorgano derivatives are invariably tetrahedral. Compounds of the type SnRR'R''R have been resolved into individual enantiomers. Organotin halides Organotin chlorides have the formula for values of ''n'' up to 3. Bromides, iodides, and fluorides are also known, but are less imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organoselenium Compound
Organoselenium chemistry is the science exploring the properties and reactivity of organoselenium compounds, chemical compounds containing carbon-to-selenium chemical bonds. Selenium belongs with oxygen and sulfur to the group 16 elements or chalcogens, and similarities in chemistry are to be expected. Organoselenium compounds are found at trace levels in ambient waters, soils and sediments. Selenium can exist with oxidation state −2, +2, +4, +6. Se(II) is the dominant form in organoselenium chemistry. Down the group 16 column, the bond strength becomes increasingly weaker (234 kilojoule, kJ/mole (unit), mol for the bond and 272 kJ/mol for the bond) and the bond lengths longer ( 198 pm, 181 pm and 141 pm). Selenium compounds are more nucleophilic than the corresponding sulfur compounds and also more acidic. The pKa, p''K''a values of are 16 for oxygen, 7 for sulfur and 3.8 for selenium. In contrast to sulfoxides, the corresponding selenoxides are unstable in the presence of � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid. The first category of acids are the proton donors, or Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acids. In the special case of aqueous solutions, proton donors form the hydronium ion H3O+ and are known as Acid–base reaction#Arrhenius theory, Arrhenius acids. Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted, Brønsted and Martin Lowry, Lowry generalized the Arrhenius theory to include non-aqueous solvents. A Brønsted–Lowry or Arrhenius acid usually contains a hydrogen atom bonded to a chemical structure that is still energetically favorable after loss of H+. Aqueous Arrhenius acids have characteristic properties that provide a practical description of an acid. Acids form aqueous solutions with a sour taste, can turn blue litmus red, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyselenide
In chemistry, a polyselenide usually refers to anions of the formula (Sen)2−, where Se is the Chemical symbol, atomic symbol for the element selenium. Many main group and transition metals form complexes with polyselenide anions. Preparation Conceptually, polyselenides are derived by deprotonation polyselenanes H2Sen, but compounds with Se-H bonds are rare or labile. Instead, analogous to the preparation of many Zintl ions, polyselenides can produced by reduction of elemental Se with alkali metals. Such reactions can be conducted by heating a mixture of the solids or by dissolving Se metal in amine solutions of alkali metals. Synthesis can also be conducted in high-boiling, polar, aprotic solvents such as DMF, HMPA, and NMP. These reactions appear to proceed by initial formation of the alkali metal selenide, followed by the reaction of the latter with additional selenium: :2 Na + Se → Na2Se :Na2Se + ''n'' Se → Na2Se''n''+1 Once generated, alkali metal poly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Biselenide
Sodium hydroselenide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a salt of hydrogen selenide. It consists of sodium cations and hydroselenide anions . Each unit consists of one sodium, one selenium, and one hydrogen atom. Sodium hydroselenide is a selenium analog of sodium hydroxide NaOH. Production Sodium hydroselenide can be made by reducing selenium with sodium borohydride: : Alternatively it can be made from sodium ethoxide exposed to hydrogen selenide: : Sodium hydroselenide is not made for storage, instead it is used immediately after production in a fume hood thanks to the appalling odour of hydrogen selenide. Properties Sodium hydroselenide dissolves in water or ethanol. In humid air sodium hydroselenide is changed to sodium polyselenide In chemistry, a polyselenide usually refers to anions of the formula (Sen)2−, where Se is the Chemical symbol, atomic symbol for the element selenium. Many main group and transition metals form complexes with polyse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcogenide
: 220px, Cadmium sulfide, a prototypical metal chalcogenide, is used as a yellow pigment. A chalcogenide is a chemical compound consisting of at least one chalcogen anion and at least one more electropositive element. Although all group 16 elements of the periodic table are defined as chalcogens, the term chalcogenide is more commonly reserved for sulfides, selenides, tellurides, and polonides, rather than oxides. Many metal ores exist as chalcogenides. Photoconductive chalcogenide glasses are used in xerography. Some pigments and catalysts are also based on chalcogenides. The metal dichalcogenide MoS2 is a common solid lubricant. Alkali metal and alkaline earth chalcogenides Alkali metal and alkaline earth monochalcogenides are salt-like, being colourless and often water-soluble. The sulfides tend to undergo hydrolysis to form derivatives containing bisulfide (SH−) anions. The alkali metal chalcogenides often crystallize with the antifluorite structure and the alkal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Selenide
Hydrogen selenide is an inorganic compound with the formula H2Se. This hydrogen chalcogenide is the simplest and most commonly encountered hydride of selenium. H2Se is a colorless, flammable gas under standard conditions. It is the most toxic selenium compoundhttp://www.epa.gov/ttnatw01/hlthef/selenium.html, US Environmental Protection Agency, Air Toxins website with an exposure limit of 0.05 ppm over an 8-hour period.https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/81-123/pdfs/0336.pdf Occupational Health Guideline for Hydrogen Selenide, The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, 1978 Even at extremely low concentrations, this compound has a very irritating smell resembling that of decayed horseradish or "leaking gas", but smells of rotten eggs at higher concentrations. Structure and properties H2Se adopts a bent structure with a H−Se−H bond angle of 91°. Consistent with this structure, three IR-active vibrational bands are observed: 2358, 2345, and 1034 cm−1. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Formula
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name since it does not contain any words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae. The simplest types of chemical formulae are called '' empirical formulae'', which use letters and numbers indicating the numerical ''proportions'' of atoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |