|
Snore
Snoring is an abnormal respiratory sounds, breath sound caused by partially obstructed, turbulent airflow and vibration of tissues in the upper respiratory tract (e.g., uvula, soft palate, base of tongue) which occurs during sleep. It usually happens during inhalations (breathing in). Primary snoring is snoring without any associated sleep disorders and usually without any serious health effects. It is usually defined as apnea–hypopnea index score or respiratory disturbance index score less than 5 events per hour (as diagnosed with polysomnography or home sleep apnea test) and lack of Excessive daytime sleepiness, daytime sleepiness. Snoring may also be a symptom of upper airway resistance syndrome or obstructive sleep apnea (apneic snoring). In obstructive sleep apnea, snoring occurs in combination with breath holding, gasping, or choking. Classification In the International Classification of Sleep Disorders third edition (ICSD-3), snoring is listed under "Isolated symp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sleep Disorder
A sleep disorder, or somnipathy, is a medical disorder affecting an individual's sleep patterns, sometimes impacting physical, mental, social, and emotional functioning. Polysomnography and actigraphy are tests commonly ordered for diagnosing sleep disorders. Sleep disorders are broadly classified into dyssomnias, parasomnias, circadian rhythm sleep disorders involving the timing of sleep, and other disorders, including those caused by medical or psychological conditions. When a person struggles to fall asleep or stay asleep without any obvious cause, it is referred to as insomnia, which is the most common sleep disorder. Other sleep disorders include sleep apnea, narcolepsy, hypersomnia (excessive sleepiness at inappropriate times), sleeping sickness (disruption of the sleep cycle due to infection), sleepwalking, and night terrors. Sleep disruptions can be caused by various issues, including teeth grinding (bruxism) and night terrors. Managing sleep disturbances that are seconda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common sleep-related breathing disorder and is characterized by recurrent episodes of complete or partial airway obstruction, obstruction of the respiratory tract#Upper respiratory tract, upper airway leading to reduced or absent breathing during sleep. These episodes are termed "apneas" with complete or near-complete cessation of breathing, or "hypopneas" when the reduction in breathing is partial. In either case, a fall in oxygen saturation (medicine), blood oxygen saturation, a disruption in sleep, or both, may result. A high frequency of apneas or hypopneas during sleep may interfere with the quality of sleep, whichin combination with disturbances in blood oxygenationis thought to contribute to negative consequences to health and quality of life. The terms obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) or obstructive sleep apnea–hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS) may be used to refer to OSA when it is associated with symptoms during the daytime (e.g. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
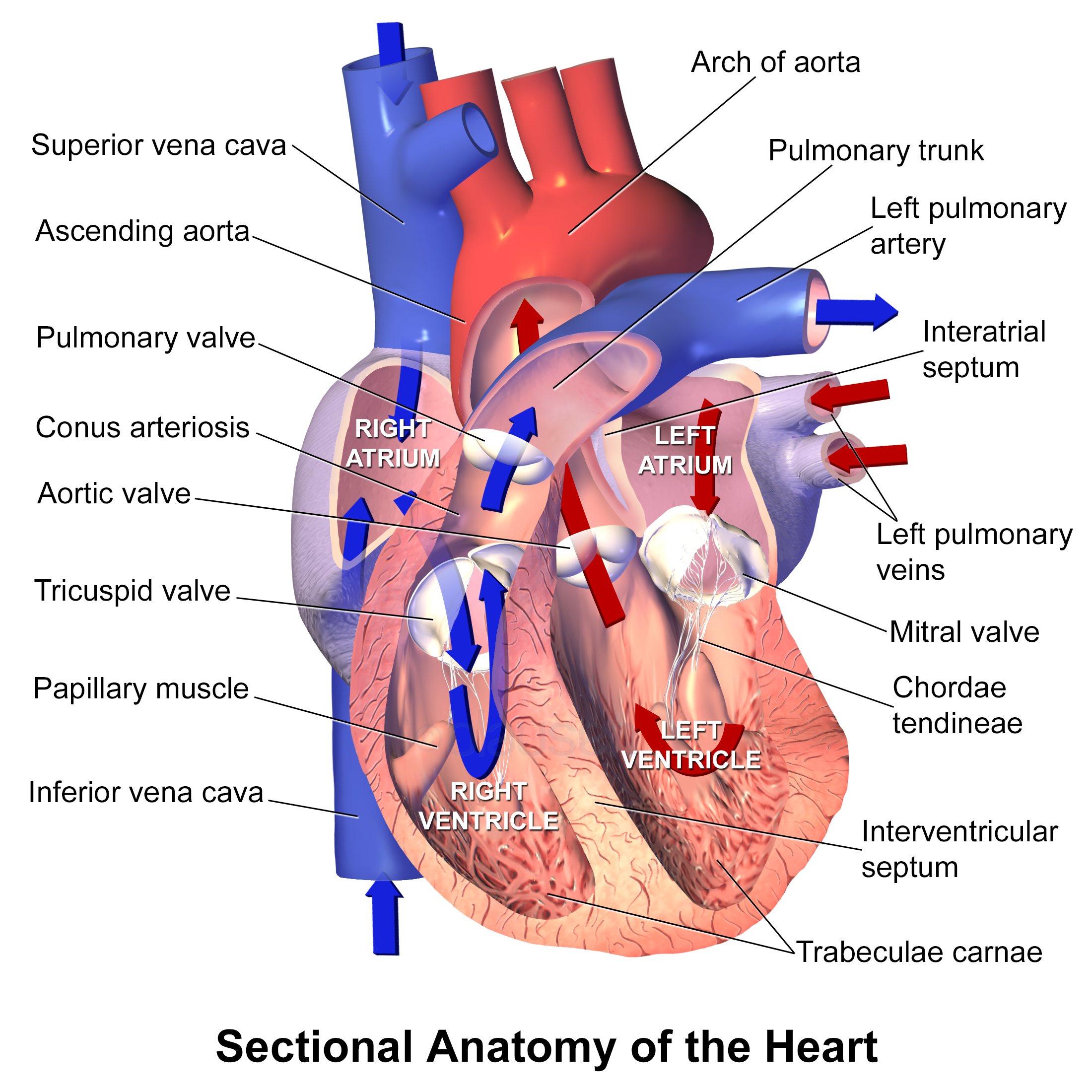
Sleep And Breathing
When we sleep, our breathing changes due to normal biological processes that affect both our respiratory and muscular systems. Physiology Sleep Onset Breathing changes as we transition from wakefulness to sleep. These changes arise due to biological changes in the processes that regulate our breathing. When we fall asleep, minute ventilation (the amount of air that we breathe per minute) reduces due to decreased metabolism. Non-REM (NREM) Sleep During NREM sleep, we move through three sleep stages, with each progressively deeper than the last. As our sleep deepens, our minute ventilation continues to decrease, reducing by 13% in the second NREM stage and by 15% in the third. For example, a study of 19 healthy adults revealed that the minute ventilation in NREM sleep was 7.18 liters/minute compared to 7.66 liters/minute when awake. Ribcage & Abdominal Muscle Contributions Rib cage contribution to ventilation increases during NREM sleep, mostly by lateral movement, and is detected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airway Resistance
In respiratory physiology, airway resistance is the resistance of the respiratory tract to airflow during inhalation and exhalation. Airway resistance can be measured using plethysmography. Definition Analogously to Ohm's law: :R_ = \frac Where: : = P_ - P_A So: :R_ = \frac Where: *R_ = Airway Resistance *P = Pressure Difference driving airflow *P_ = Atmospheric Pressure *P_A = Alveolar Pressure *\dot V = Volumetric Airflow (not minute ventilation which, confusingly, may be represented by the same symbol) N.B. PA and \dot V change constantly during the respiratory cycle. Determinants of airway resistance There are several important determinants of airway resistance including: *The diameter of the airways *Whether airflow is laminar or turbulent Hagen–Poiseuille equation In fluid dynamics, the Hagen–Poiseuille equation is a physical law that gives the pressure drop in a fluid flowing through a long cylindrical pipe. The assumptions of the equation are that the flow is la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Model
A mathematical model is an abstract and concrete, abstract description of a concrete system using mathematics, mathematical concepts and language of mathematics, language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed ''mathematical modeling''. Mathematical models are used in applied mathematics and in the natural sciences (such as physics, biology, earth science, chemistry) and engineering disciplines (such as computer science, electrical engineering), as well as in non-physical systems such as the social sciences (such as economics, psychology, sociology, political science). It can also be taught as a subject in its own right. The use of mathematical models to solve problems in business or military operations is a large part of the field of operations research. Mathematical models are also used in music, linguistics, and philosophy (for example, intensively in analytic philosophy). A model may help to explain a system and to study the effects of different components, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blausen 0872 UpperRespiratorySystem
Blausen Medical Communications, Inc. (BMC) is the creator and owner of a library of two- and three-dimensional medical and scientific images and animations, a developer of information technology allowing access to that content, and a business focused on licensing and distributing the content. It was founded by Bruce Blausen in Houston, Texas, in 1991, and is privately held. Background Blausen Medical Communications is a privately held company founded by Bruce Blausen in Houston, Texas in 1991. BMC created and owns a library of medical and scientific images and animations, and has developed information technology tools allowing access to the library; as well, it licenses and otherwise works to distribute the content. As of this date, BMC's animation library comprised approximately 1,500 animations and over 27,000 two- and three-dimensional images designed for point-of-care patient education, which could be accessed by consumers or professional caregivers (primarily via hospital o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decibel
The decibel (symbol: dB) is a relative unit of measurement equal to one tenth of a bel (B). It expresses the ratio of two values of a Power, root-power, and field quantities, power or root-power quantity on a logarithmic scale. Two signals whose level (logarithmic quantity), levels differ by one decibel have a power ratio of 101/10 (approximately ) or root-power ratio of 101/20 (approximately ). The strict original usage above only expresses a relative change. However, the word decibel has since also been used for expressing an Absolute scale, absolute value that is relative to some fixed reference value, in which case the dB symbol is often suffixed with letter codes that indicate the reference value. For example, for the reference value of 1 volt, a common suffix is "#Voltage, V" (e.g., "20 dBV"). As it originated from a need to express power ratios, two principal types of scaling of the decibel are used to provide consistency depending on whether the scaling refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Mass Index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (Mass versus weight, weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the human body weight, body mass divided by the square (algebra), square of the human height, body height, and is expressed in Units of measurement, units of kg/m2, resulting from mass in kilograms (kg) and height in metres (m). The BMI may be determined first by measuring its components by means of a weighing scale and a stadiometer. The multiplication and division may be carried out directly, by hand or using a calculator, or indirectly using a lookup table (or chart). The table displays BMI as a function of mass and height and may show other units of measurement (converted to Metric system, metric units for the calculation). The table may also show contour lines or colours for different BMI categories. The BMI is a convenient rule of thumb used to broadly categorize a person as based on tissue mass (muscle, fat, and bone) and height. Major adult B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroencephalogram
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The bio signals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex and allocortex. It is typically non-invasive, with the EEG electrodes placed along the scalp (commonly called "scalp EEG") using the International 10–20 system, or variations of it. Electrocorticography, involving surgical placement of electrodes, is sometimes called "intracranial EEG". Clinical interpretation of EEG recordings is most often performed by visual inspection of the tracing or quantitative EEG analysis. Voltage fluctuations measured by the EEG bio amplifier and electrodes allow the evaluation of normal brain activity. As the electrical activity monitored by EEG originates in neurons in the underlying brain tissue, the recordings made by the electrodes on the surface of the scalp vary in accordance with their orie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen Saturation
Oxygen saturation (symbol SO2) is a relative measure of the concentration of oxygen that is Dissolution (chemistry), dissolved or carried in a given medium as a proportion of the maximal concentration that can be dissolved in that medium at the given temperature. It can be measured with a dissolved oxygen probe such as an oxygen sensor or an optode in liquid media, usually water. The standard unit of oxygen saturation is percent (%). Oxygen saturation can be measured regionally and noninvasively. Artery, Arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) is commonly measured using pulse oximetry. Tissue saturation at peripheral scale can be measured using near-infrared spectroscopy, NIRS. This technique can be applied on both muscle and brain. In medicine In medicine, oxygen saturation refers to ''oxygenation'', or when oxygen molecules () enter the Tissue (biology), tissues of the body. In this case blood is oxygenated in the lungs, where oxygen molecules travel from the air into the blood. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insomnia
Insomnia, also known as sleeplessness, is a sleep disorder where people have difficulty sleeping. They may have difficulty falling asleep, or staying asleep for as long as desired. Insomnia is typically followed by daytime sleepiness, low energy, irritability, and a depression (mood), depressed mood. It may result in an increased risk of accidents of all kinds as well as problems focusing and learning. Insomnia can be short term, lasting for days or weeks, or long term, lasting more than a month. The concept of the word ''insomnia'' has two distinct possibilities: insomnia disorder (ID) or insomnia symptoms, and many abstracts of randomized controlled trials and systematic reviews often underreport on which of these two possibilities the word refers to. Insomnia can occur independently or as a result of another problem. Conditions that can result in insomnia include psychological stress, chronic pain, heart failure, hyperthyroidism, heartburn, restless leg syndrome, menopause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |