|
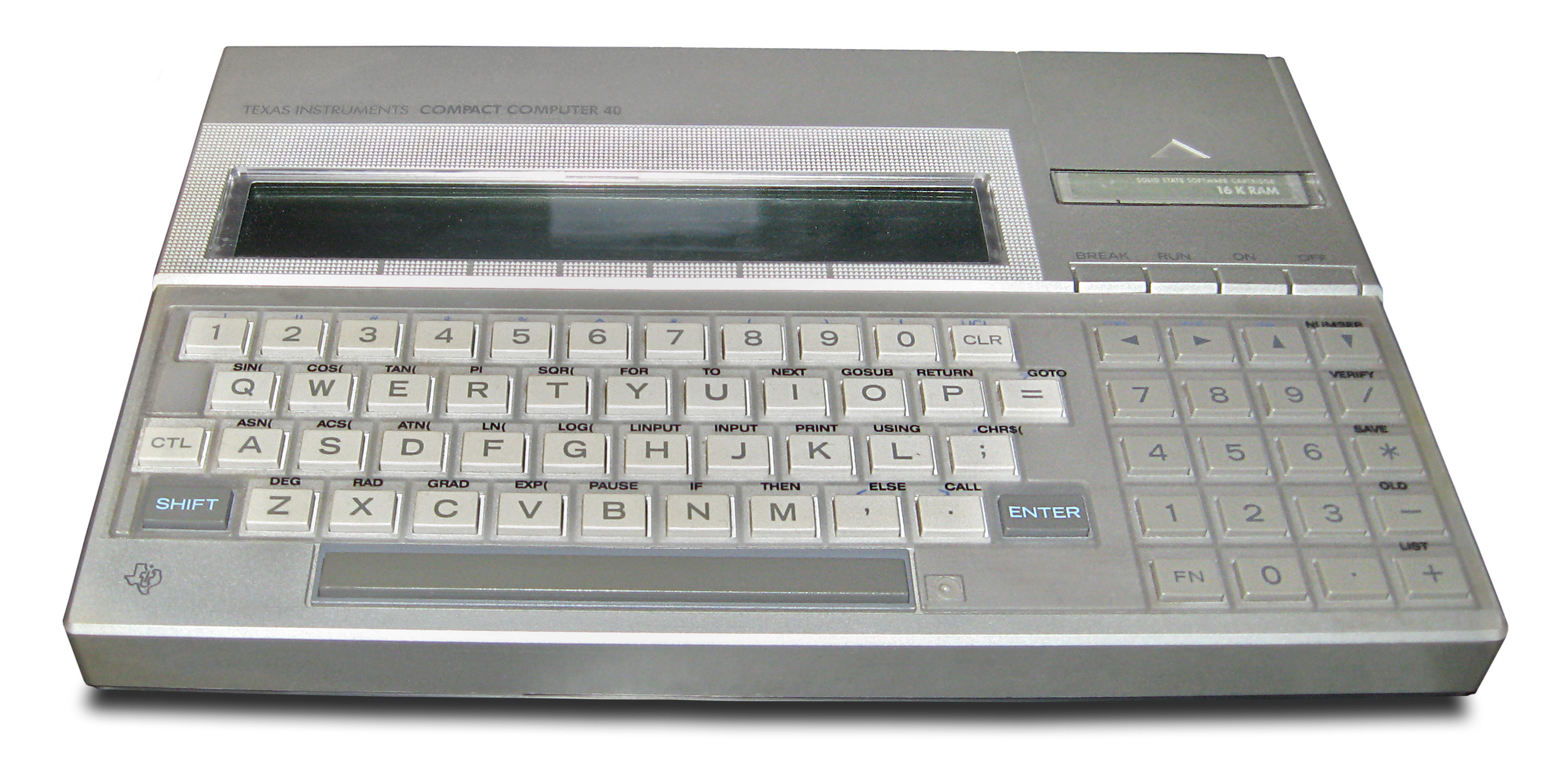
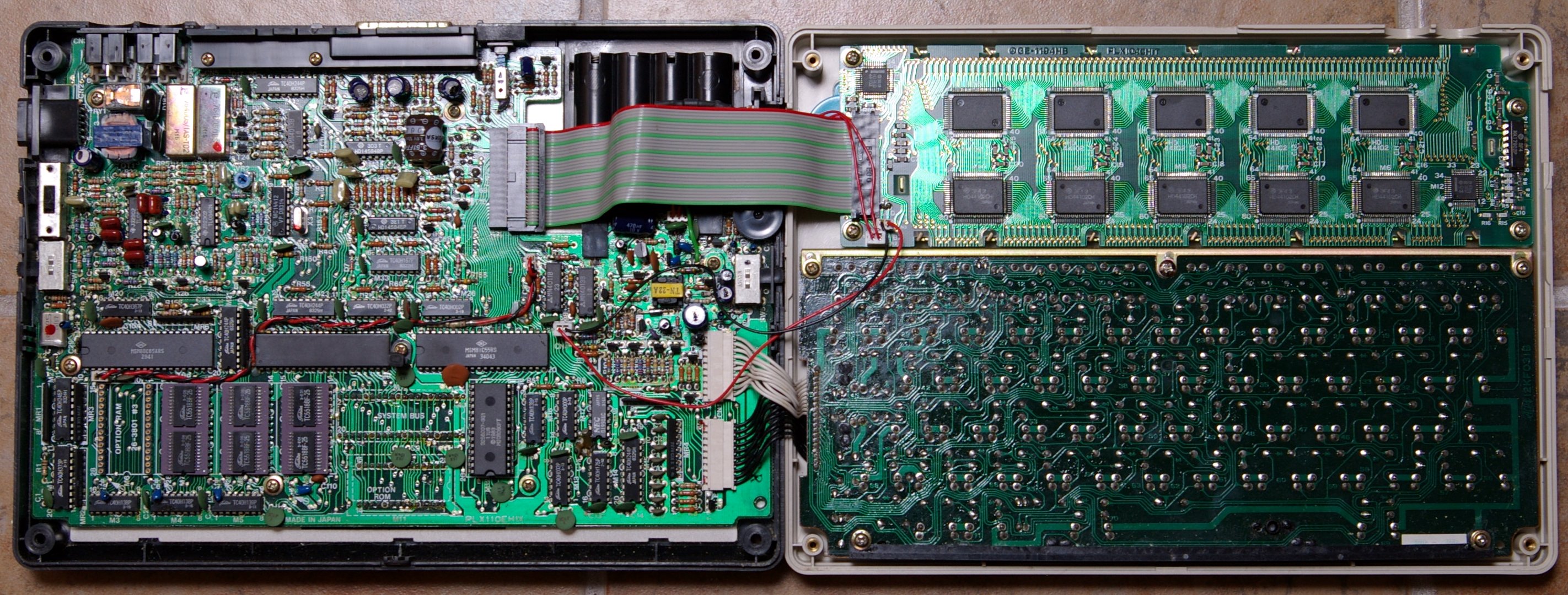
Small, Cheap Computer
Subnotebook, also called ultraportable, superportable, handtop, mini notebook or mini laptop, is a type of laptop computer that is smaller and lighter than a typical notebook-sized laptop. Types and sizes As typical laptop sizes have decreased over the course of the 2010s, and other distinguishing features have become mainstream, the distinction between regular-size and 'subnotebook' laptops has largely disappeared. To the extent that it still exists, 'subnotebook' could be defined as machines with screen smaller than 13" but with a permanently-attached keyboard intended for two-handed typing. Prior to this convergence, subnotebooks were also distinguished from netbooks and ultra-mobile PCs, based on both size and market position. Subnotebooks run full desktop class operating systems, and their CPUs are usually the same as those in desktops although perhaps modified for lower power consumption. Classic subnotebooks were smaller than full-sized laptops but larger than handhel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compaq Contura
The Contura is a line of notebook-sized laptops produced by Compaq from 1992 to 1996. The Contura was Compaq's first attempt at making an affordable, entry-level laptop. Models The main Contura series included models 3/20, 3/25, 3/25c, 4/25, 4/25c, 4/25cx, 400, 400C, 400CX, 410, 410C, 410CX, 420C, 420CX, 430C, and 430CX. These were standard-size notebooks, not ultra-portable subnotebook computers. The "X" designation denoted an active matrix screen. The Compaq Contura Aero 4/25 and 4/33c were among the earliest subnotebook computers that acted as a precursor to netbooks. They were released in 1994 and originally ran MS-DOS and Windows 3.1. They were also able to run Windows 95 after its release in 1995. They were similar to the Armada line of laptop computers, but smaller. Although the 4/25's GPU can produce color, the datasheet for the device states it is incapable of producing color graphics. This does not apply to the 4/33c. This line of notebook PCs from Compaq was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Docking Station
In computing, a docking station, port replicator (hub), or dock provides a simplified way to ''plug-in'' a mobile device, such as connect common peripherals to a laptop, or charge a smartphone. Because a wide range of dockable devices—from mobile phones to wireless mouse—have different connectors, power signaling, and uses, docks are unstandardized and are therefore often designed for a specific type of device. A dock can allow some laptop computers to become a substitute for a desktop computer, without sacrificing the mobile computing functionality of the machine. Portable computers can dock and undock hot, cold or standby, depending on the abilities of the system. In a cold dock or undock, one completely shuts the computer down before docking/undocking. In a hot dock or undock, the computer remains running when docked/undocked. Standby docking or undocking, an intermediate style used in some designs, allows the computer to be docked/undocked while powered on, but requir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Influence Of The IBM PC On The Personal Computer Market
Following the introduction of the IBM Personal Computer (IBM PC) in 1981, many other personal computer architectures became extinct within just a few years. It led to a wave of IBM PC compatible systems being released. Before the IBM PC's introduction Before the IBM PC was introduced, the personal computer market was dominated by systems using the 6502 and Z80 8-bit microprocessors, such as the TRS 80, PET, and Apple II, which used proprietary operating systems, and by computers running CP/M. After IBM introduced the IBM PC, it was not until 1984 that IBM PC and clones became the dominant computers. In 1983, ''Byte (magazine), Byte'' forecast that by 1990, IBM would command only 11% of business computer sales. Commodore was predicted to hold a slim lead in a highly competitive market, at 11.9%. Around 1978, several 16-bit CPUs became available. Examples included the Data General mN601, the Fairchild 9440, the Ferranti F100-L, the General Instrument CP1600 and CP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM Personal Computer
The IBM Personal Computer (model 5150, commonly known as the IBM PC) is the first microcomputer released in the IBM PC model line and the basis for the IBM PC compatible ''de facto'' standard. Released on August 12, 1981, it was created by a team of engineers and designers at International Business Machines (IBM), directed by William C. Lowe and Philip Don Estridge in Boca Raton, Florida. Powered by an x86-architecture Intel 8088 processor, the machine was based on open architecture and third-party peripherals. Over time, expansion cards and software technology increased to support it. The PC had a substantial influence on the personal computer market; the specifications of the IBM PC became one of the most popular computer design standards in the world. The only significant competition it faced from a non-compatible platform throughout the 1980s was from Apple's Macintosh product line, as well as consumer-grade platforms created by companies like Commodore and Atari. Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM PC Compatible
An IBM PC compatible is any personal computer that is hardware- and software-compatible with the IBM Personal Computer (IBM PC) and its subsequent models. Like the original IBM PC, an IBM PC–compatible computer uses an x86-based central processing unit, sourced either from Intel or a second source like AMD, Cyrix or other vendors such as Texas Instruments, Fujitsu, OKI, Mitsubishi or NEC and is capable of using interchangeable commodity hardware such as expansion cards. Initially such computers were referred to as PC clones, IBM clones or IBM PC clones, but the term "IBM PC compatible" is now a historical description only, as the vast majority of microcomputers produced since the 1990s are IBM compatible. IBM itself no longer sells personal computers, having sold its division to Lenovo in 2005. " Wintel" is a similar description that is more commonly used for modern computers. The designation "PC", as used in much of personal computer history, has not meant "pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NEC UltraLite
The UltraLite is a line of Notebook (laptop), notebook-sized laptops first released by NEC in 1988. The original model was released in October 1988, alongside the heavier and more-capable NEC ProSpeed, ProSpeed. The UltraLite was the first notebook computer on the market IBM PC compatible, compatible with the IBM Personal Computer, IBM PC. Quoted in The original model was based on the NEC V30 microprocessor; the computer includes MS-DOS 3.3 built into Read-only memory, ROM. ''PC Magazine'' featured the UltraLite on its cover in November 1988Front Cover:NEC's Incredible 4-Pound DOS Laptop 1988-11-15, Volume 7 Number 19, PC Magazine and shortly thereafter journalists began referring to any A4 paper, A4-sized computer as "notebooks", to distinguish them from the larger and heavier laptops ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tandy 200
The TRS-80 Model 100 is a notebook-sized portable computer introduced in April 1983. It was the first commercially successful notebook computer, as well as one of the first notebook computers ever released. It features a keyboard and liquid-crystal display, in a battery-powered package roughly the size and shape of a notepad or large book. The 224-page, spiral-bound User Manual is nearly the same size as the computer itself. It was made by Kyocera, and originally sold in Japan as the Kyotronic 85. Although a slow seller for Kyocera, the rights to the machine were purchased by Tandy Corporation. The computer was sold through Radio Shack stores in the United States and Canada and affiliated dealers in other countries. It became one of the company's most popular models, with over 6 million units sold worldwide. The Olivetti M-10 and the NEC PC-8201 and PC-8300 were also built on the same Kyocera platform, with some design and hardware differences. It was originally marketed as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TRS-80 Model 100
The TRS-80 Model 100 is a Notebook form factor, notebook-sized portable computer introduced in April 1983. It was the first commercially successful notebook computer, as well as one of the first notebook computers ever released. It features a keyboard and liquid-crystal display, in a battery-powered package roughly the size and shape of a notepad or large book. The 224-page, spiral-bound User Manual is nearly the same size as the computer itself. It was made by Kyocera, and originally sold in Japan as the Kyotronic 85. Although a slow seller for Kyocera, the rights to the machine were purchased by Tandy Corporation. The computer was sold through Radio Shack stores in the United States and Canada and affiliated dealers in other countries. It became one of the company's most popular models, with over 6 million units sold worldwide. The Olivetti M-10 and the NEC PC-8201 and PC-8300 were also built on the same Kyocera platform, with some design and hardware differences. It was orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
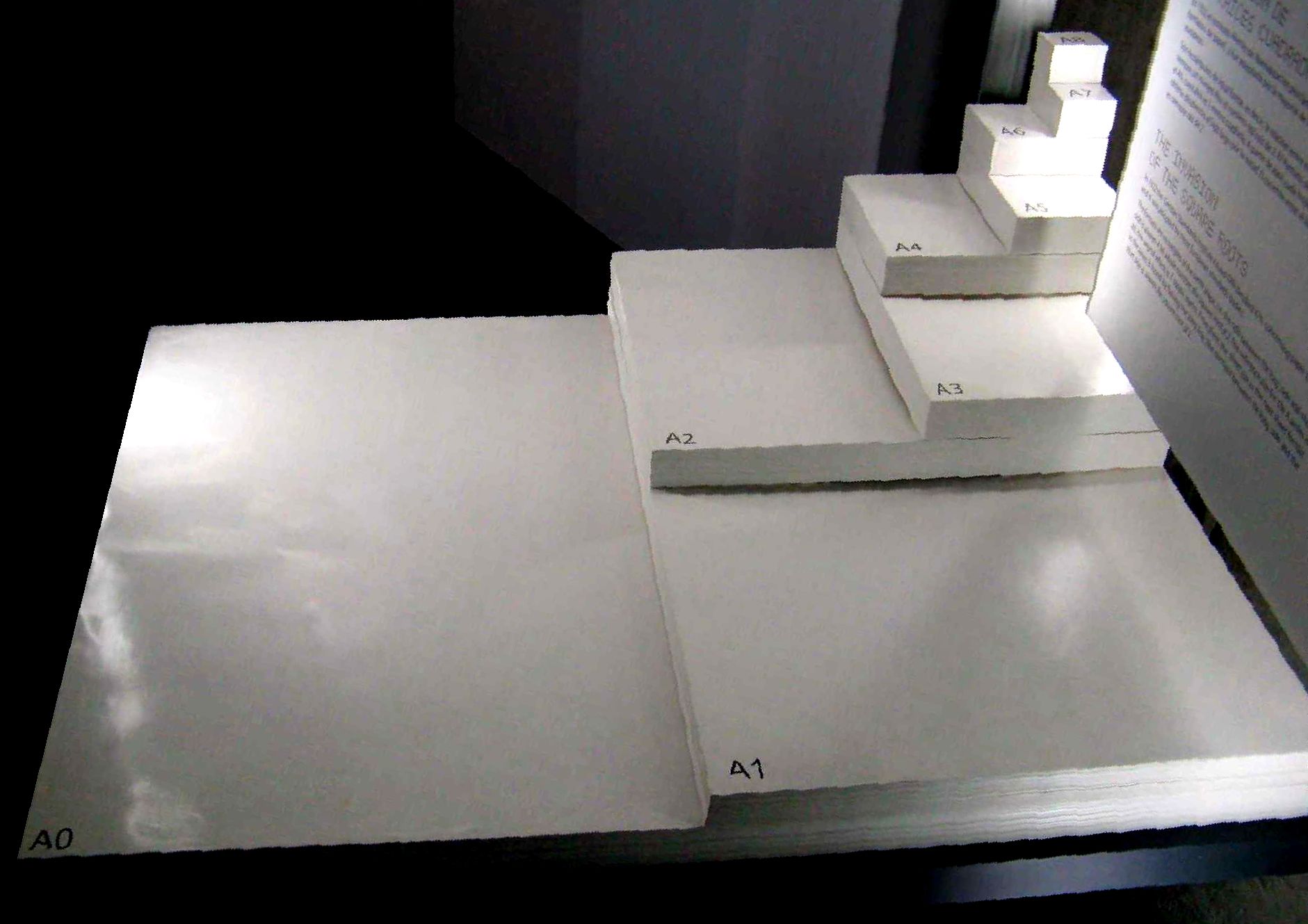
A4 Paper
ISO 216 is an International Organization for Standardization, international standard for paper sizes, used around the world except in North America and parts of Latin America. The standard defines the "A", "B" and "C" series of paper sizes, which includes the A4, the most commonly available paper size worldwide. Two supplementary standards, ISO 217 and ISO 269, define related paper sizes; the ISO 269 "C" series is commonly listed alongside the A and B sizes. All ISO 216, ISO 217 and ISO 269 paper sizes (except some envelopes) have the same aspect ratio, square root of 2, , within rounding to millimetres. This ratio has the unique property that when cut or folded in half widthways, the halves also have the same aspect ratio. Each ISO paper size is one half of the area of the next larger size in the same series. Dimensions of A, B and C series History The oldest known mention of the advantages of basing a paper size on an aspect ratio of \sqrt is found in a letter writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epson HX-20
The HX-20 (also known as the HC-20) was an early laptop computer released by Epson, Seiko Epson in July 1982. It was the first Notebook (laptop), notebook-sized portable computer, occupying roughly the footprint of an A4 paper, A4 notebook while being lightweight enough to hold comfortably with one hand at and small enough to fit inside an average briefcase. Despite praise from journalists for its technical innovations, the computer was not a commercial success outside of Japan. Radio Shack's TRS-80 Model 100 (the American version of a Kyocera notebook), released in 1983, is thus credited as the first commercially successful notebook computer. History The concept behind the HX-20 was first devised in July 1980 by Yukio Yokozawa, who worked for Suwa Seikosha, now the Seiko Epson subsidiary of the Japanese Seiko Group, receiving a patent for the invention. It was announced in 1981 as the HC-20 in Japan, and was introduced by Epson in North America as the HX-20 at the 1981 COMDE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrabook
Ultrabook is a class of premium consumer-grade notebook computers. The term was originated by and is trademarked by Intel, replacing the earlier Centrino mobile platform. Introduced in 2011, they were originally marketed as featuring ultra thin form factor and light weight design without compromising battery life or performance, running on Intel Core processors. When newly introduced, Ultrabooks were generally small enough compared to average laptop models to qualify as subnotebooks. As ultrabook features became more mainstream in the mid-late 2010s, explicitly branding laptop models as "ultrabooks" became much less frequent. As of 2021, while Intel maintains the Ultrabook trademark, it is rarely used for new models and has been superseded in Intel's own marketing by the Intel Evo branding. History In 2011, Intel Capital press officer Jordan Balk Schaer announced a new fund to support startups working on technologies in line with the company's concept for next generation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ChromeOS
ChromeOS, sometimes styled as chromeOS and formerly styled as Chrome OS, is an operating system designed and developed by Google. It is derived from the open-source operating system and uses the Google Chrome web browser as its principal user interface. Google announced the project in July 2009, initially describing it as an operating system where applications and user data would reside in the cloud. ChromeOS was used primarily to run web applications. ChromeOS supports progressive web applications, Android apps from Google Play and Linux applications. History In 2006, Jeff Nelson, a Google employee, created the concept of what would become ChromeOS, initially codenamed "Google OS" as a Linux distribution focused on speed. Early Google OS versions used Firefox as Chrome had not been released, though it switched to Chrome sometime in 2007 due to internal betas being passed around Google. To ascertain marketing requirements, developers relied on informal metrics, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |