|
Sludge
Sludge (possibly , or some dialect related to slush) is a semi-solid slurry that can be produced from a range of industrial processes, from water treatment, wastewater treatment or on-site sanitation systems. It can be produced as a settled suspension obtained from conventional drinking water treatment, as sewage sludge from wastewater treatment processes or as fecal sludge from pit latrines and septic tanks. The term is also sometimes used as a generic term for solids separated from suspension in a liquid; this soupy material usually contains significant quantities of interstitial water (between the solid particles). Sludge can consist of a variety of particles, such as animal manure. Industrial wastewater treatment plants produce solids that are also referred to as sludge. This can be generated from biological or physical-chemical processes. In the activated sludge process for wastewater treatment, the terms "waste activated sludge" and "return activated sludge" are used. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sewage Sludge
Sewage sludge is the residual, semi-solid material that is produced as a by-product during sewage treatment of industrial or municipal wastewater. The term "septage" also refers to sludge from simple wastewater treatment but is connected to simple on-site sanitation systems, such as septic tanks. After treatment, and dependent upon the quality of sludge produced (for example with regards to heavy metal content), sewage sludge is most commonly either disposed of in landfills, dumped in the ocean or applied to land for its fertilizing properties, as pioneered by the product Milorganite. The term " Biosolids" is often used as an alternative to the term sewage sludge in the United States, particularly in conjunction with reuse of sewage sludge as fertilizer after sewage sludge treatment. Biosolids can be defined as organic wastewater solids that can be reused after stabilization processes such as anaerobic digestion and composting. Opponents of sewage sludge reuse reject this t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
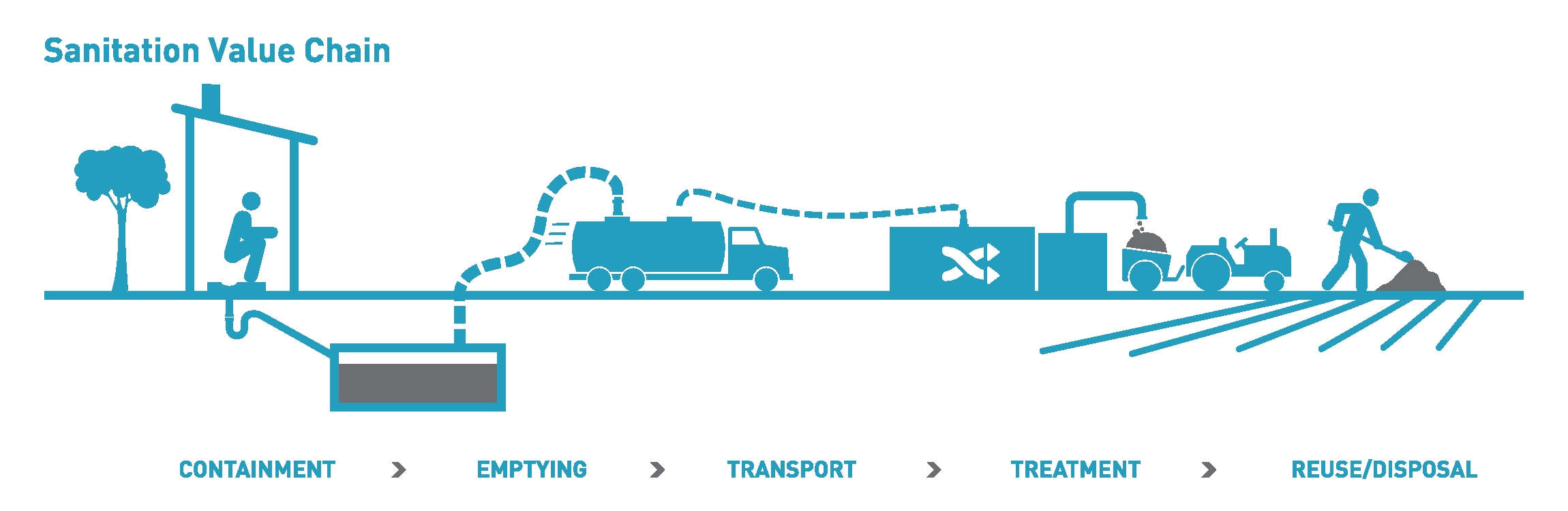
Fecal Sludge Management
Fecal sludge management (FSM) (or faecal sludge management in British English) is the storage, collection, transport, treatment and safe end use or disposal of fecal sludge. Together, the collection, transport, treatment and end use of fecal sludge constitute the "value chain" or "service chain" of fecal sludge management. Fecal sludge is defined very broadly as what accumulates in onsite sanitation systems (e.g. pit latrines, septic tanks and container-based solutions) and specifically is not transported through a sewer. It is composed of human excreta, but also anything else that may go into an onsite containment technology, such as flushwater, cleansing materials (e.g. toilet paper and anal cleansing materials), menstrual hygiene products, grey water (i.e. bathing or kitchen water, including fats, oils and grease), and solid waste. Fecal sludge that is removed from septic tanks is called septage. It is estimated that one-third of the world's population is served by onsite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Activated Sludge
The activated sludge process is a type of biological wastewater treatment process for treating sewage or Industrial wastewater treatment, industrial wastewaters using aeration and a biological floc (biofilm), floc composed of bacteria and protozoa. It is one of several biological wastewater treatment alternatives in secondary treatment, which deals with the removal of biodegradable organic matter and suspended solids. It uses air (or oxygen) and microorganisms to Biological oxidizer, biologically oxidize organic pollutants, producing a waste sludge (or Flocculation, floc) containing the oxidized material. The activated sludge process for removing carbonaceous pollution begins with an aeration tank where air (or oxygen) is injected into the waste water. This is followed by a settling tank to allow the biological flocs (the sludge blanket) to settle, thus separating the biological sludge from the clear treated water. Part of the waste sludge is recycled to the aeration tank and the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pit Latrine
A pit latrine, also known as pit toilet, is a type of toilet that collects human waste in a hole in the ground. Urine and feces enter the pit through a drop hole in the floor, which might be connected to a toilet seat or squatting pan for user comfort. Pit latrines can be built to function without water ( dry toilet) or they can have a water seal (pour-flush pit latrine). When properly built and maintained, pit latrines can decrease the spread of disease by reducing the amount of human feces in the environment from open defecation. This decreases the transfer of pathogens between feces and food by flies. These pathogens are major causes of infectious diarrhea and intestinal worm infections. Infectious diarrhea resulted in about 700,000 deaths in children under five years old in 2011 and 250 million lost school days. Pit latrines are a low-cost method of separating feces from people. A pit latrine generally consists of three major parts: a hole in the ground, a concrete slab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Septic Tank
A septic tank is an underground chamber made of concrete, fiberglass, or plastic through which domestic wastewater (sewage) flows for basic sewage treatment. Settling and anaerobic digestion processes reduce solids and organics, but the treatment efficiency is only moderate (referred to as "primary treatment"). Septic tank systems are a type of simple onsite sewage facility. They can be used in areas that are not connected to a sewerage system, such as rural areas. The treated liquid effluent is commonly disposed in a septic drain field, which provides further treatment. Nonetheless, groundwater pollution may occur and is a problem. The term "septic" refers to the Anaerobic digestion, anaerobic bacterial environment that develops in the tank that decomposes or mineralizes the waste discharged into the tank. Septic tanks can be coupled with other Onsite sewage facility, onsite wastewater treatment units such as biofilters or aerobic systems involving artificially forced aeration. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Industrial Wastewater Treatment
Industrial wastewater treatment describes the processes used for Wastewater treatment, treating wastewater that is produced by industries as an undesirable by-product. After treatment, the treated industrial wastewater (or effluent) may be reused or released to a sanitary sewer or to a surface water in the environment. Some industrial facilities generate wastewater that can be treated in Sewage treatment, sewage treatment plants. Most industrial processes, such as petroleum refineries, chemical and petrochemical plants have their own specialized facilities to treat their wastewaters so that the pollutant concentrations in the treated wastewater comply with the regulations regarding disposal of wastewaters into Sewerage, sewers or into rivers, lakes or oceans. This applies to industries that generate wastewater with high concentrations of organic matter (e.g. oil and grease), toxic pollutants (e.g. heavy metals, volatile organic compounds) or nutrients such as ammonia. Some indust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems aim to protect human health by providing a clean environment that will stop the transmission of disease, especially through the fecal–oral route.SuSanA (2008)Towards more sustainable sanitation solutions . Sustainable Sanitation Alliance (SuSanA) For example, diarrhea, a main cause of malnutrition and stunted growth in children, can be reduced through adequate sanitation. There are many other diseases which are easily transmitted in communities that have low levels of sanitation, such as ascariasis (a type of intestinal worm infection or helminthiasis), cholera, hepatitis, polio, schistosomiasis, and trachoma, to name just a few. A range of sanitation technologies and approaches exists. Some examples are community-led total sanita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Water Purification
Water purification is the process of removing undesirable chemicals, biological contaminants, suspended solids, and gases from water. The goal is to produce water that is fit for specific purposes. Most water is purified and disinfected for human consumption (drinking water), but water purification may also be carried out for a variety of other purposes, including medical, pharmacological, chemical, and industrial applications. The history of water purification includes a wide variety of methods. The methods used include physical processes such as filtration, sedimentation, and distillation; biological processes such as slow sand filters or biologically active carbon; chemical processes such as flocculation and chlorination; and the use of electromagnetic radiation such as ultraviolet light. Water purification can reduce the concentration of particulate matter including suspended particles, parasites, bacteria, algae, viruses, and fungi as well as reduce the concentration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wastewater Treatment
Wastewater treatment is a process which removes and eliminates contaminants from wastewater. It thus converts it into an effluent that can be returned to the water cycle. Once back in the water cycle, the effluent creates an acceptable impact on the environment. It is also possible to reuse it. This process is called Reclaimed water, water reclamation. The treatment process takes place in a wastewater treatment plant. There are several kinds of wastewater which are treated at the appropriate type of wastewater treatment plant. For domestic wastewater the treatment plant is called a Sewage Treatment. Municipal wastewater or sewage are other names for domestic wastewater. For industrial wastewater, treatment takes place in a separate Industrial wastewater treatment, or in a sewage treatment plant. In the latter case it usually follows pre-treatment. Further types of wastewater treatment plants include Agricultural wastewater treatment and leachate treatment plants. One common proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol P and atomic number 15. All elemental forms of phosphorus are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive and are therefore never found in nature. They can nevertheless be prepared artificially, the two most common allotropes being white phosphorus and red phosphorus. With as its only stable isotope, phosphorus has an occurrence in Earth's crust of about 0.1%, generally as phosphate rock. A member of the pnictogen family, phosphorus readily forms a wide variety of organic compound, organic and inorganic compound, inorganic compounds, with as its main oxidation states +5, +3 and −3. The isolation of white phosphorus in 1669 by Hennig Brand marked the scientific community's first discovery since Antiquity of an element. The name phosphorus is a reference to the Phosphorus (morning star), god of the Morning star in Greek mythology, inspired by the faint glow of white phosphorus when exposed to oxygen. This property is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dewatering
Dewatering is the removal of water from a location. This may be done by wet classification, centrifugation, filtration, or similar solid-liquid separation processes, such as removal of residual liquid from a filter cake by a filter press as part of various industrial processes. Construction dewatering, unwatering, or water control are common terms used to describe removal or draining groundwater or surface water from a riverbed, construction site, caisson, or mine shaft, by pumping or evaporation. On a construction site, this dewatering may be implemented before subsurface excavation for foundations, shoring, or cellar space to lower the water table. This frequently involves the use of submersible "dewatering" pumps, centrifugal ("trash") pumps, eductors, or application of vacuum to well points. The international business research company Visiongain valued the global dewatering pump market at $6.4 billion in 2018. Processes Deep wells A deep well typically consists of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
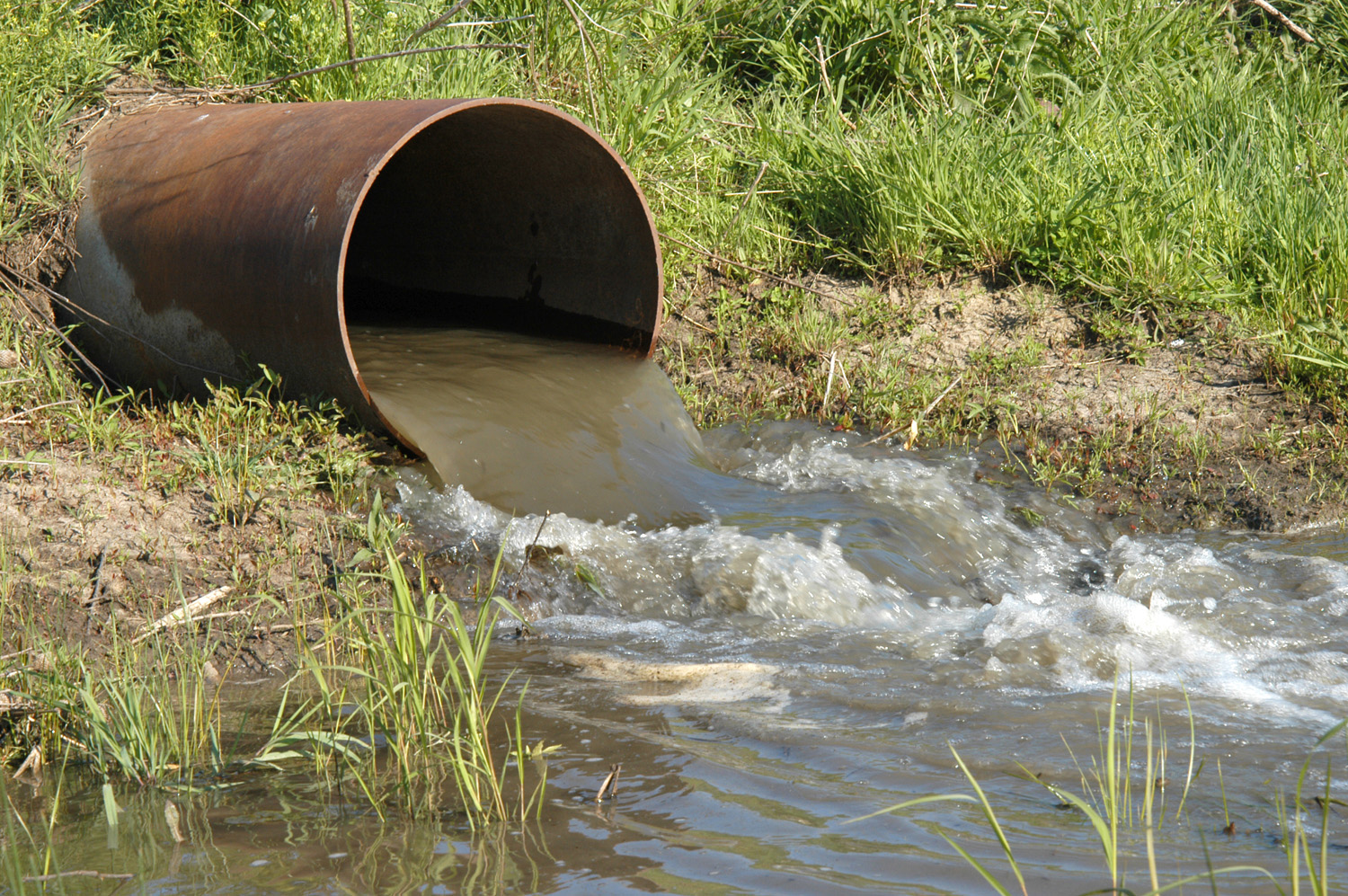
Chemical Sludge
Effluent is wastewater from sewers or industrial outfalls that flows directly into surface waters, either untreated or after being treated at a facility. The term has slightly different meanings in certain contexts, and may contain various pollutants depending on the source. Definition Effluent is defined by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) as "wastewater–treated or untreated–that flows out of a treatment plant, sewer, or industrial outfall. Generally refers to wastes discharged into surface waters". The ''Compact Oxford English Dictionary'' defines effluent as "liquid waste or sewage discharged into a river or the sea". Wastewater is not usually described as effluent while being recycled, re-used, or treated until it is released to surface water. Wastewater percolated or injected into groundwater may not be described as effluent if soil is assumed to perform treatment by filtration or ion exchange; although concealed flow through fractured bedrock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |