|
Sling Psychrometer
image:Haar-Hygrometer.jpg, A hair tension dial hygrometer with a nonlinear scale. A hygrometer is an instrument that measures humidity: that is, how much water vapor is present. Humidity measurement instruments usually rely on measurements of some other quantities, such as temperature, pressure, mass, and mechanical or electrical changes in a substance as moisture is absorbed. By calibration and calculation, these measured quantities can be used to indicate the humidity. Modern electronic devices use the temperature of condensation (called the dew point), or they sense changes in electrical capacitance or Electrical resistance, resistance. The maximum amount of water vapor that can be present in a given volume (at Relative humidity, saturation) varies greatly with temperature; at low temperatures a lower mass of water per unit volume can remain as vapor than at high temperatures. Thus a change in the temperature changes the relative humidity. A prototype hygrometer was invented b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather House
A weather house is a folk art device in the shape of a small German or Alpine chalet that indicates the weather. A typical weather house has two doors side by side. The left side has a girl or woman, the right side a boy or man. The female figure comes out of the house when the weather is sunny and dry, while the male (often carrying an umbrella) comes out to indicate rain. Description In fact, a weather house functions as a hygrometer embellished by folk art. The male and female figures ride on a balance bar, which is suspended by a piece of catgut or hair. The gut relaxes or shrinks based on the humidity in the surrounding air, relaxing when the air is wet and tensing when the air is dry. This action swings one figure or the other out of the house depending on the humidity. Some variants function as a barometer: low pressure indicates bad (rainy) weather, high pressure good (sunny) weather. History The first written mention is in 1726, ''Theatrum Aerostaticum'' by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dielectric Constant
The relative permittivity (in older texts, dielectric constant) is the permittivity of a material expressed as a ratio with the electric permittivity of a vacuum. A dielectric is an insulating material, and the dielectric constant of an insulator measures the ability of the insulator to store electric energy in an electrical field. Permittivity is a material's property that affects the Coulomb force between two point charges in the material. Relative permittivity is the factor by which the electric field between the charges is decreased relative to vacuum. Likewise, relative permittivity is the ratio of the capacitance of a capacitor using that material as a dielectric, compared with a similar capacitor that has vacuum as its dielectric. Relative permittivity is also commonly known as the dielectric constant, a term still used but deprecated by standards organizations in engineering as well as in chemistry. Definition Relative permittivity is typically denoted as (som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International System Of Quantities
The International System of Quantities (ISQ) is a standard system of Quantity, quantities used in physics and in modern science in general. It includes basic quantities such as length and mass and the relationships between those quantities. This system underlies the International System of Units (SI) but does not itself determine the units of measurement used for the quantities. The system is formally described in a multi-part ISO standard ISO/IEC 80000 (which also defines many other quantities used in science and technology), first completed in 2009 and subsequently revised and expanded. Base quantities The base quantities of a given system of physical quantity, physical quantities is a subset of those quantities, where no base quantity can be expressed in terms of the others, but where every quantity in the system can be expressed in terms of the base quantities. Within this constraint, the set of base quantities is chosen by convention. There are seven ISQ base quant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket Wrench
A socket wrench (or socket spanner) is a type of spanner (or wrench in North American English) that uses a closed ''socket'' format, rather than a typical open wrench/spanner to turn a fastener, typically in the form of a nut or bolt. The most prevalent form is the ratcheting socket wrench, often informally called a ratchet. A ratchet incorporates a reversible ratcheting mechanism which allows the user to pivot the tool back and forth to turn its socket instead of removing and repositioning a wrench to do so. Other common methods of driving sockets include pneumatic impact wrenches, hydraulic torque wrenches, torque multipliers and breaker bars. Some lesser known hybrid drivers include striking wrench tools with square drive, and hydraulic impact wrenches (typically powered by on site hydraulic power such as present with military tanks, and many rail car applications). Interchangeable sockets The basic contemporary form of socket is hexagonal, referred to as "6-point" for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sling Psychrometer
image:Haar-Hygrometer.jpg, A hair tension dial hygrometer with a nonlinear scale. A hygrometer is an instrument that measures humidity: that is, how much water vapor is present. Humidity measurement instruments usually rely on measurements of some other quantities, such as temperature, pressure, mass, and mechanical or electrical changes in a substance as moisture is absorbed. By calibration and calculation, these measured quantities can be used to indicate the humidity. Modern electronic devices use the temperature of condensation (called the dew point), or they sense changes in electrical capacitance or Electrical resistance, resistance. The maximum amount of water vapor that can be present in a given volume (at Relative humidity, saturation) varies greatly with temperature; at low temperatures a lower mass of water per unit volume can remain as vapor than at high temperatures. Thus a change in the temperature changes the relative humidity. A prototype hygrometer was invented b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refrigerant
A refrigerant is a working fluid used in the cooling, heating, or reverse cooling/heating cycles of air conditioning systems and heat pumps, where they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Refrigerants are heavily regulated because of their toxicity and flammability, as well as the contribution of CFC and HCFC refrigerants to ozone depletion and the contribution of HFC refrigerants to climate change. Refrigerants are used in a direct expansion (DX) circulating system to transfer energy from one environment to another, typically from inside a building to outside or vice versa. These can be air conditioner cooling only systems, cooling & heating reverse DX systems, or heat pump and heating only DX cycles. Refrigerants are controlled substances that are classified by several international safety regulations and, depending on their classification, may only be handled by qualified engineers due to extreme pressure, temperature, flammability, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
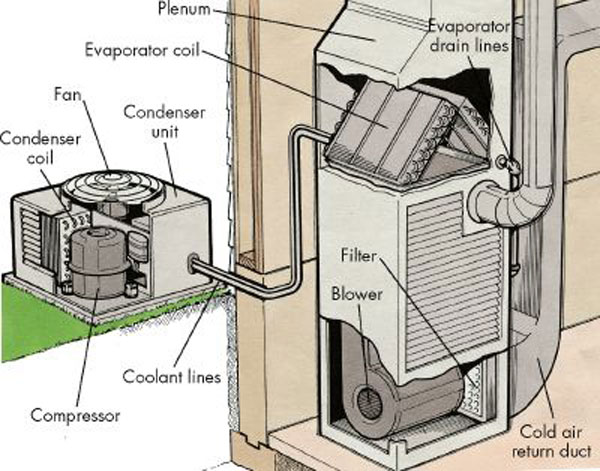
Heating, Ventilation, And Air Conditioning
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC ) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer. "Refrigeration" is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation as HVAC&R or HVACR, or "ventilation" is dropped, as in HACR (as in the designation of HACR-rated circuit breakers). HVAC is an important part of residential structures such as single family homes, apartment buildings, hotels, and senior living facilities; medium to large industrial and office buildings such as skyscrapers and hospitals; vehicles such as cars, trains, airplanes, ships and submarines; and in marine environments, where safe and Sick building syndrome, healthy building conditions are regulated with respect to temperature and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteorology
Meteorology is the scientific study of the Earth's atmosphere and short-term atmospheric phenomena (i.e. weather), with a focus on weather forecasting. It has applications in the military, aviation, energy production, transport, agriculture, construction, weather warnings and disaster management. Along with climatology, atmospheric physics and atmospheric chemistry, meteorology forms the broader field of the atmospheric sciences. The interactions between Earth's atmosphere and its oceans (notably El Niño and La Niña) are studied in the interdisciplinary field of hydrometeorology. Other interdisciplinary areas include biometeorology, space weather and planetary meteorology. Marine weather forecasting relates meteorology to maritime and coastal safety, based on atmospheric interactions with large bodies of water. Meteorologists study meteorological phenomena driven by solar radiation, Earth's rotation, ocean currents and other factors. These include everyday ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychrometrics
Psychrometrics (or psychrometry, ; also called hygrometry) is the field of engineering concerned with the physical and thermodynamic properties of gas-vapor mixtures. History With the inventions of the hygrometer and thermometer, the theories of combining the two began to emerge during the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. In 1818, a German inventor, Ernst Ferdinand August (1795-1870), patented the term “psychrometer”, from the Greek language meaning “cold measure”. The psychrometer is a hygrometer, hygrometric instrument based on the principle that dry air enhances evaporation, unlike wet air, which slows it. Common applications Although the principles of psychrometry apply to any physical system consisting of gas-vapor mixtures, the most common system of interest is the mixture of water vapor and air, because of its application in HVAC, heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning and meteorology. In human terms, our thermal comfort is in large part a consequence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniell Hygrometer-MHS 2191-P4070317-gradient
Daniell is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Alexander Daniell (1599–1668), Cornish landowner * Alfred Daniell (1853–1937) * Ave Daniell (1914–1999), American (gridiron) footballer * Charles Daniell (1827–1889), Major-General, British Army * David Daniell (author) (1929–2016), biographer of William Tyndale * David Daniell (cyclist) (born 1989), English competitive cyclist * David Daniell (musician) (born 1972), American guitarist and composer * David Scott Daniell (1906–1965) * De'Anyers family * Edward Daniell (cricketer) (1815–1875), English cricketer * Edward Thomas Daniell (1804–1842), English landscape painter and etcher * Francis Henry Blackburne Daniell (1845–1921) was an Anglo-Irish barrister and historian * Geoffrey Daniell (1516–1586) * George Daniell (medical doctor) (1864–1937), medical practitioner and anaesthesiologist * George Daniell (photographer) (1911–2002), American photographer * George Daniell (priest) ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making up a substance. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), with the third being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |