|
Slaný Speedway
Slaný (; ) is a town in Kladno District in the Central Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 17,000 inhabitants. The historic town centre is well preserved and is protected as an Cultural monument (Czech Republic)#Monument zones, urban monument zone. Administrative division Slaný consists of ten municipal parts (in brackets population according to the 2021 census): *Slaný (13,728) *Blahotice (27) *Dolín (412) *Kvíc (467) *Kvíček (790) *Lotouš (61) *Netovice (77) *Otruby (110) *Trpoměchy (154) *Želevčice (119) Etymology The word ''slaný'' literally means 'salty' in Czech. According to the Wenceslaus Hajek's chronicle records, Slaný was founded at the site of a salt spring below the hill of Slánská hora. Geography Slaný is located about north of Kladno and northwest of Prague. It lies in the Prague Plateau. The highest point and a dominant feature of the town's panorama is the hill Slánská hora at above sea level. The stream of Červený potok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obec
(, ; plural ) is the Czech and Slovak word for a municipality (in the Czech Republic, in Slovakia and abroad). The literal meaning of the word is " commune" or " community". It is the smallest administrative unit that is governed by elected representatives. Cities and towns are also municipalities. Definition The legal definition (according to the Czech code of law with similar definition in the Slovak code of law) is: ''"The municipality is a basic territorial self-governing community of citizens; it forms a territorial unit, which is defined by the boundary of the municipality."'' Every municipality is composed of one or more cadastral areas. Every municipality is also composed of one or more municipal parts (), which are usually town quarters or villages. A municipality can have its own flag and coat of arms. Czech Republic Almost the entire area of the Czech Republic is divided into municipalities, with the only exception being military training areas. The smaller mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gotthard Of Hildesheim
Gotthard (or Godehard) (960 – 5 May 1038 AD; ), also known as ''Gothard'' or ''Godehard the Bishop'', was a German bishop venerated as a saint. Life Gotthard was born in 960 near Niederalteich, Niederaltaich in the diocese of Passau. Gotthard studied the humanities and theology at Niederaltaich Abbey, where his father Ratmund was a vassal of the canons. While at the abbey, Gotthard became a canon under Abbot Erkanbert. Gotthard then continued his studies at the archiepiscopal court of Salzburg, where he served as an ecclesiastical administrator. After traveling through various countries, including Italy, Gotthard completed his advanced studies under the guidance of Liutfrid in the cathedral school at Passau. He then joined the canons at Niederaltaich and was appointed Provost (religion), provost. When Henry II of Bavaria decided to transform the Chapter (religion), chapter house of Niederaltaich into a Benedictine monastery Gotthard remained there as a novice, subsequently b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque Architecture
Baroque architecture is a highly decorative and theatrical style which appeared in Italy in the late 16th century and gradually spread across Europe. It was originally introduced by the Catholic Church, particularly by the Jesuits, as a means to combat the Reformation and the Protestantism, Protestant church with a new architecture that inspired surprise and awe. It reached its peak in the High Baroque (1625–1675), when it was used in churches and palaces in Italy, Spain, Portugal, France, Bavaria and Austria. In the Late Baroque period (1675–1750), it reached as far as Russia, the Ottoman Baroque architecture, Ottoman Empire and the Spanish colonization of the Americas, Spanish and Portuguese colonization of the Americas, Portuguese colonies in Latin America. In about 1730, an even more elaborately decorative variant called Rococo appeared and flourished in Central Europe. Baroque architects took the basic elements of Renaissance architecture, including domes and colonnades, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martinic Family
The Martinic family or House of Martinice ( or ''z Martinic'', ) was a Bohemia Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...n noble family, claimed to be descended from the old Vršovci clan. The family have been part of the Bohemian ancient nobility. As of 1322, the family possessed the castle Martinice near Votice in the southern part of Central Bohemia. Members include Jaroslav Bořita of Martinice, who was victim of the 1618 Defenestration of Prague. The family became extinct in the male line (1788), but the name survived in the Clam-Martinic family, when in 1791 Carl Josef, Count of Clam, a member of the old Austrian noble family Clam, married Maria Anna, Imperial Countess of Martinic. Their descendants include Austrian statesman Heinrich Clam-Martinic. Literature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
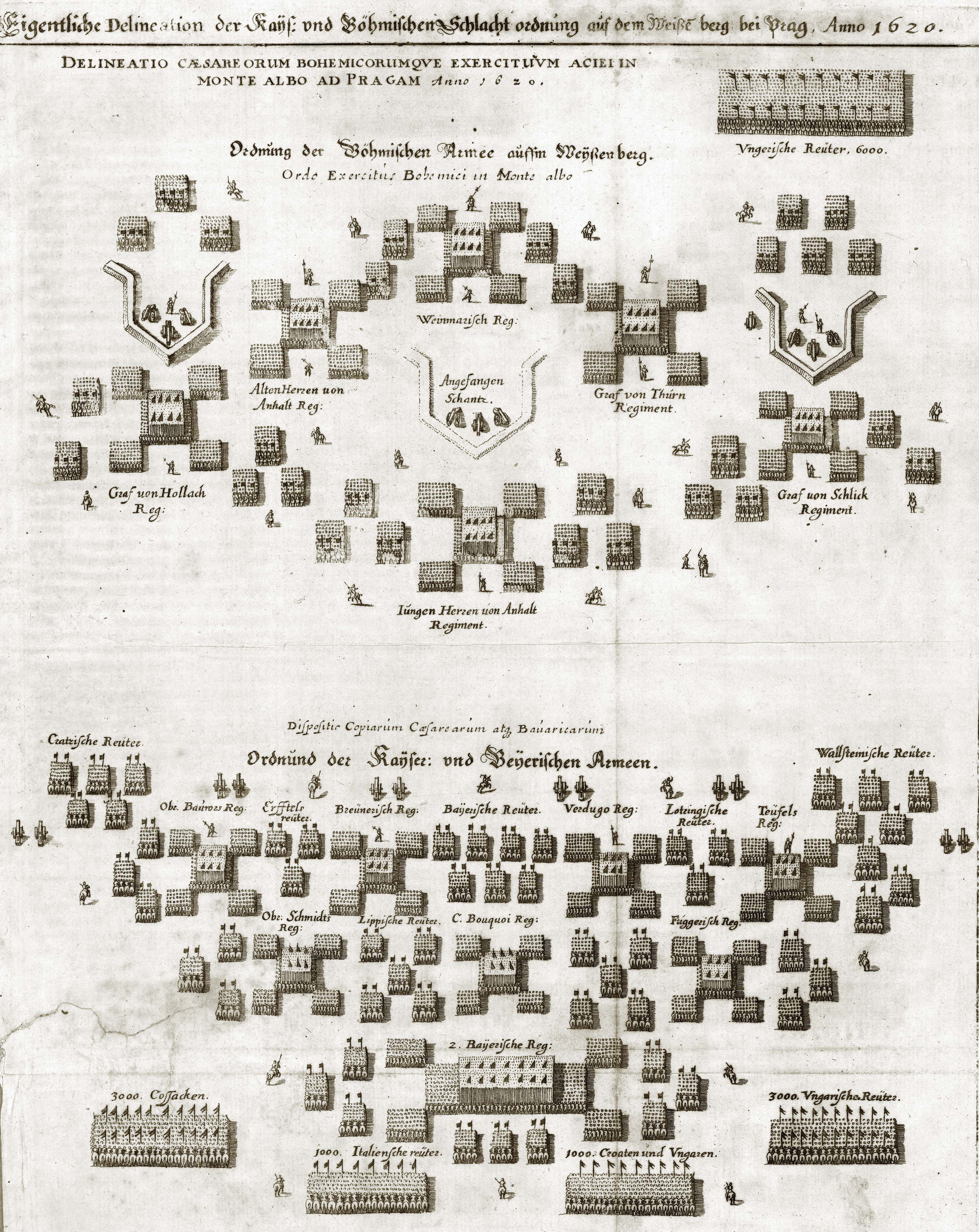
Battle Of White Mountain
The Battle of White Mountain (; ) was an important battle in the early stages of the Thirty Years' War. It led to the defeat of the Bohemian Revolt and ensured Habsburg control for the next three hundred years. It was fought on 8 November 1620. An army of 21,000 Bohemians and mercenaries under Christian of Anhalt was defeated by 23,000 men of the combined armies of Ferdinand II, Holy Roman Emperor, led by Charles Bonaventure de Longueval, Count of Bucquoy, and the German Catholic League led by Johann Tserclaes, later Count of Tilly, at Bílá Hora ("White Mountain") near Prague. Bohemian casualties were not severe but their morale collapsed and Imperial forces occupied Prague the next day. Prelude In the early 17th century most of the Bohemian estates, although under the dominion of the predominantly Catholic Holy Roman Empire, had large Protestant populations, and had been granted rights and protections allowing them varying degrees of religious and political freedom. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick V Of The Palatinate
Frederick may refer to: People * Frederick (given name), the name Given name Nobility = Anhalt-Harzgerode = * Frederick, Prince of Anhalt-Harzgerode (1613–1670) = Austria = * Frederick I, Duke of Austria (Babenberg), Duke of Austria from 1195 to 1198 * Frederick II, Duke of Austria (1219–1246), last Duke of Austria from the Babenberg dynasty * Frederick the Fair (Frederick I of Austria (Habsburg), 1286–1330), Duke of Austria and King of the Romans = Baden = * Frederick I, Grand Duke of Baden (1826–1907), Grand Duke of Baden * Frederick II, Grand Duke of Baden (1857–1928), Grand Duke of Baden = Bohemia = * Frederick, Duke of Bohemia (died 1189), Duke of Olomouc and Bohemia = Britain = * Frederick, Prince of Wales (1707–1751), eldest son of King George II of Great Britain = Brandenburg/Prussia = * Frederick I, Elector of Brandenburg (1371–1440), also known as Frederick VI, Burgrave of Nuremberg * Frederick II, Elector of Brandenburg (1413–1470), M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine, or disease, while parts of Germany reported population declines of over 50%. Related conflicts include the Eighty Years' War, the War of the Mantuan Succession, the Franco-Spanish War (1635–1659), Franco-Spanish War, the Torstenson War, the Dutch-Portuguese War, and the Portuguese Restoration War. The war had its origins in the 16th-century Reformation, which led to religious conflict within the Holy Roman Empire. The 1555 Peace of Augsburg attempted to resolve this by dividing the Empire into Catholic and Lutheran states, but the settlement was destabilised by the subsequent expansion of Protestantism beyond these boundaries. Combined with differences over the limits of imperial authority, religion was thus an important factor in star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bohemian Revolt
The Bohemian Revolt (; ; 1618–1620) was an uprising of the Kingdom of Bohemia, Bohemian Estates of the realm, estates against the rule of the Habsburg dynasty that began the Thirty Years' War. It was caused by both religious and power disputes. The estates were almost entirely Protestant, mostly Utraquism, Utraquist Hussite but there was also German Bohemians, a substantial German population that endorsed Lutheranism. The dispute culminated after several battles in the final Battle of White Mountain, where the estates suffered a decisive defeat. This started Counter-Reformation, re-Catholisation of the Czech lands, but also expanded the scope of the Thirty Years' War by drawing Denmark-Norway, Denmark and History of Sweden (1611–1648), Sweden into it. The conflict spread to the rest of Europe and devastated vast areas of Central Europe, including the Czech lands, which were particularly stricken by its violent atrocities. Rebellion Without heirs, Emperor Matthias, Holy R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Of Poděbrady
George of Kunštát and Poděbrady (23 April 1420 – 22 March 1471), also known as Poděbrad or Podiebrad (; ), was the sixteenth King of Bohemia, who ruled in 1458–1471. He was a leader of the Hussites, but moderate and tolerant toward the Catholic faith. His rule was marked by great efforts to preserve peace and tolerance between the Hussites and Catholics in the religiously divided Crown of Bohemia – hence his contemporary nicknames: "King of two peoples" () and "Friend of peace" (''přítel míru''). During the 19th century, in period of the so-called Czech National Revival, he began to be praised (even somewhat idealized) as the last Czech national monarch (in terms of ethnic awareness), a great diplomat and a courageous fighter against the domination of the Catholic Church. In modern times he is remembered mainly for his idea and attempt to establish common European Christian institutions, which is now seen as an early historical vision of European unity. Early li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Eschatology
Christian eschatology is a minor branch of study within Christian theology which deals with the doctrine of the "last things", especially the Second Coming of Christ, or Parousia. The word eschatology derives from two Greek roots meaning "last" () and "study" (-) – involves the study of "end things", whether of the end of an individual life, of the end of the age, of the end of the Worldly, world, or of the nature of the Kingdom of God (Christianity), Kingdom of God. Broadly speaking, Christian eschatology focuses on the ultimate destiny of individual souls and of the entire Genesis creation narrative, created order, based primarily upon Bible, biblical texts within the Old Testament, Old and New Testaments. Christian eschatology looks to study and discuss matters such as death and the afterlife, Heaven in Christianity, Heaven and Hell in Christianity, Hell, the Second Coming of Jesus, the resurrection of the dead, the rapture, the tribulation, millennialism, the Eschatology, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hussite
file:Hussitenkriege.tif, upright=1.2, Battle between Hussites (left) and Crusades#Campaigns against heretics and schismatics, Catholic crusaders in the 15th century file:The Bohemian Realm during the Hussite Wars.png, upright=1.2, The Lands of the Bohemian Crown during the Hussite Wars. The movement began during the Renaissance in Prague and quickly spread south and then through the rest of the Kingdom of Bohemia. Eventually, it expanded into the remaining domains of the Bohemian Crown as well. The Hussites (Czech language, Czech: ''Husité'' or ''Kališníci'', "Chalice People"; Latin: ''Hussitae'') were a Czech Proto-Protestantism, proto-Protestant Christian movement influenced by both the Byzantine Rite and John Wycliffe that followed the teachings of reformer Jan Hus (floruit, fl. 1401–1415), a part of the Bohemian Reformation. The Czech lands had originally been Christianized by Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Greek missionaries Saints Cyril and Methodius, who introduced the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
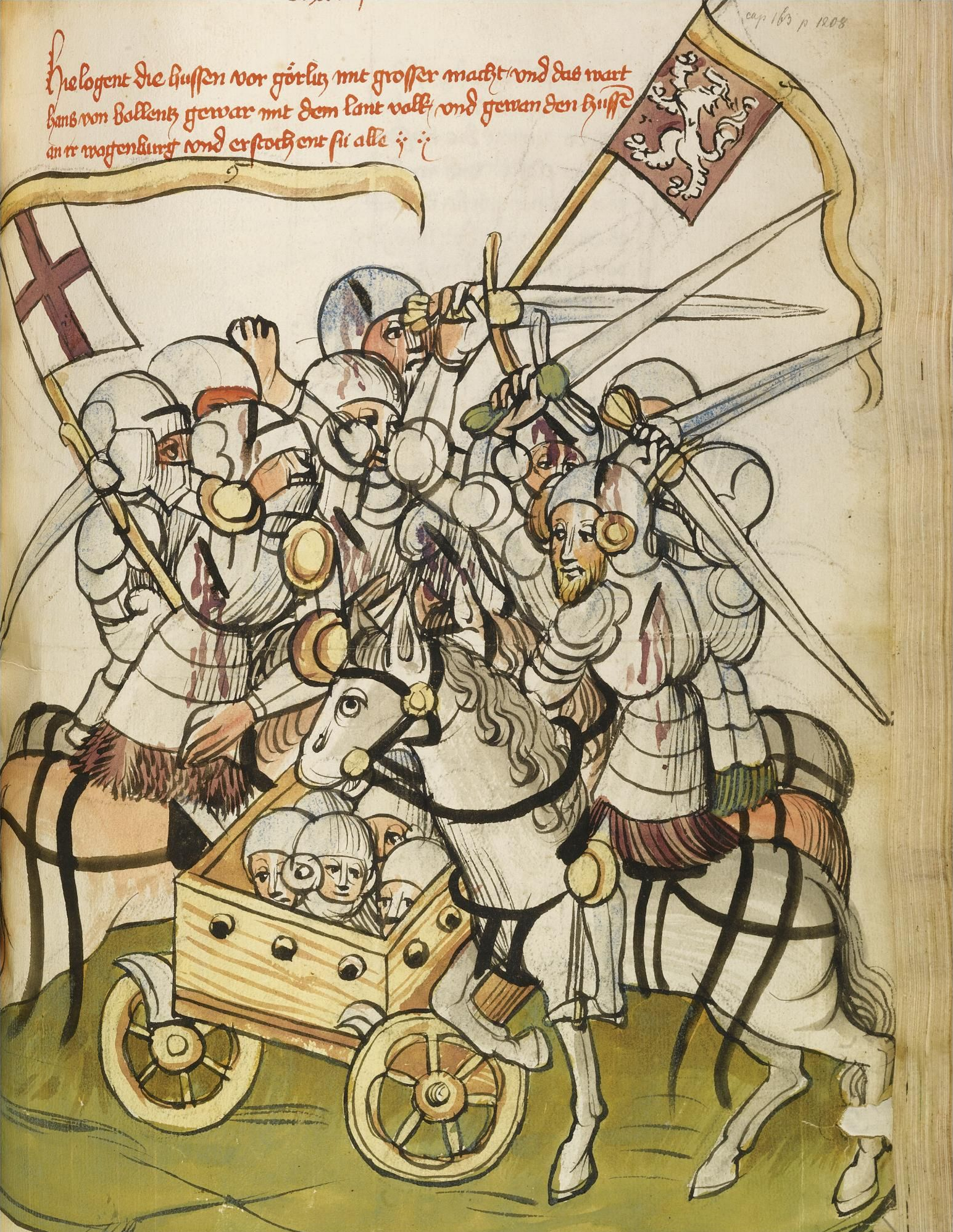
Hussite Wars
The Hussite Wars, also called the Bohemian Wars or the Hussite Revolution, were a series of civil wars fought between the Hussites and the combined Catholic forces of Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, Holy Roman Emperor Sigismund, the Papacy, and European monarchs loyal to the Catholic Church, as well as various Hussite factions. At a late stage of the conflict, the Utraquists changed sides in 1432 to fight alongside Roman Catholics and opposed the Taborites and other Hussite factions. These wars lasted from 1419 to approximately 1434. The unrest began after pre-Protestant Christian reformer Jan Hus was executed by the Catholic Church in 1415 for heresy. Because Sigismund had plans to be crowned the Holy Roman Emperor (requiring papal coronation), he suppressed the religion of the Hussites, yet it continued to spread. When King Wenceslaus IV of Bohemia, brother of Sigismund, died of natural causes a few years later, the tension stemming from the Hussites grew stronger. In Prague ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |