|
Skowhegan, Maine
Skowhegan () is the county seat of Somerset County, Maine, United States. As of the 2020 census, the town population was 8,620. Every August, Skowhegan hosts the annual Skowhegan State Fair, the oldest continuously held state fair in the United States. Skowhegan was originally inhabited by the indigenous Abenaki people who named the area Skowhegan, meaning "watching place or fish" and were mostly dispersed by the end of the 4th Anglo-Abenaki War. History Original inhabitants For thousands of years prior to European settlement, this region of Maine was the territory of the Kinipekw (later known as Kennebec) Norridgewock tribe of Abenaki. The Norridgewock village was located on the land now known as Madison. The Abenaki relied on agriculture (corn, beans, and squash) for a large part of their diet, supplemented by hunting, fishing, and the gathering of wild foods. The Skowhegan Falls (which have since been replaced by the Weston Dam) descended 28 feet over a half-mile on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New England Town
The town is the basic unit of Local government in the United States, local government and local division of state authority in the six New England states. Most other U.S. states lack a direct counterpart to the New England town. New England towns overlie the entire area of a state, similar to civil townships in other states where they exist, but they are fully functioning Incorporation (municipal government), municipal corporations, possessing powers similar to city, cities and county, counties in other states. Local government in New Jersey, New Jersey's system of equally powerful townships, boroughs, towns, and cities is the system which is most similar to that of New England. New England towns are often governed by a town meeting, an assembly of eligible town residents. The great majority of municipal corporations in New England are based on the town model; there, statutory forms based on the concept of a Place (United States Census Bureau), compact populated place are uncommon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
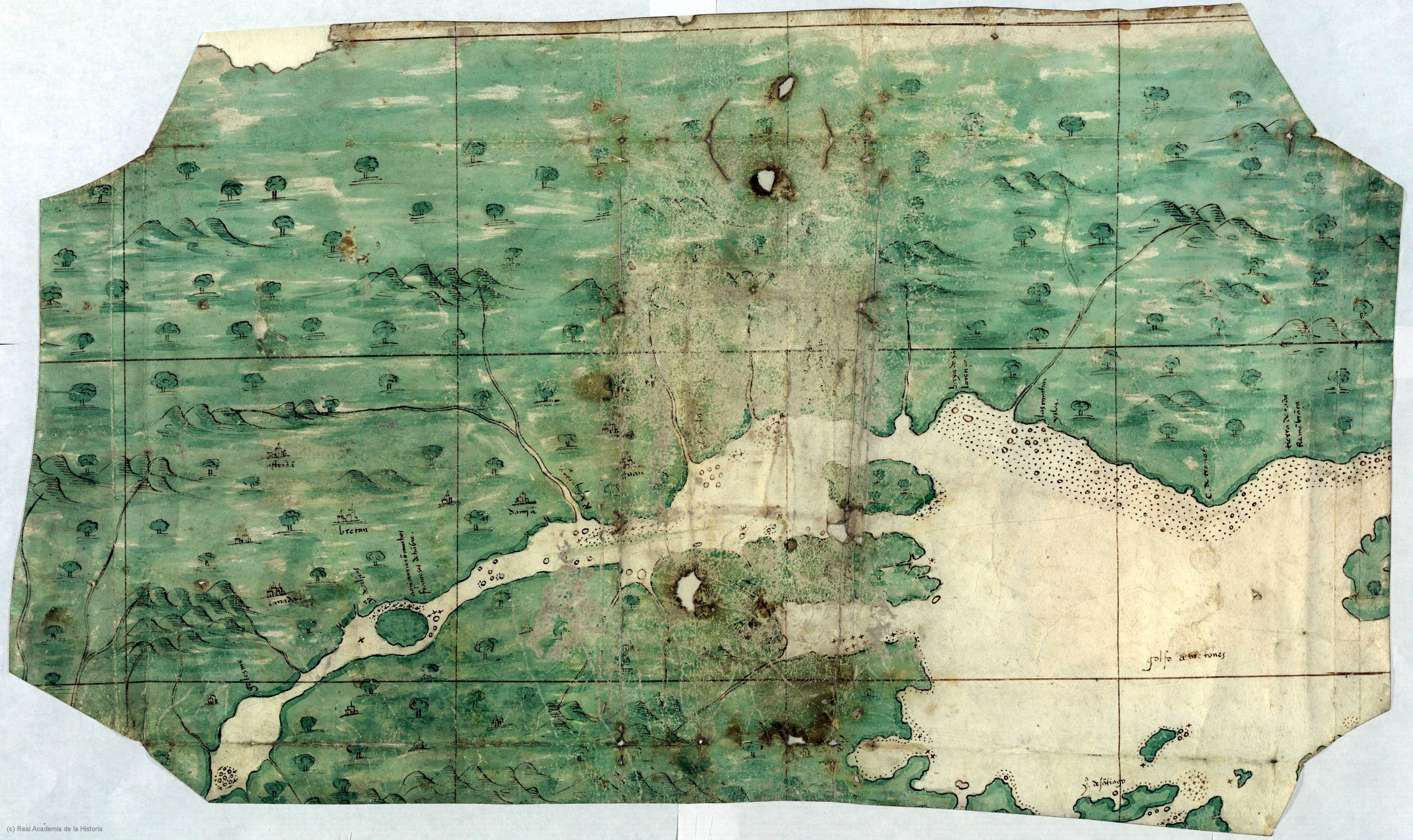
Norridgewock
Norridgewock (Abenaki language, Abenaki: ''Nanrantsouak'') was the name of both an Indigenous village and a Band society, band of the Abenaki ("People of the Dawn") Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans/First Nations in Canada, First Nations, an Eastern Algonquian peoples, Algonquian tribe of the United States and Canada. The French of New France called the village Kennebec. The tribe occupied an area in the interior of Maine. During colonial times, this area was territory disputed between British and French colonists, and was set along the claimed western border of Acadia, the western bank of the Kennebec River. Archaeological evidence has identified several different sites associated with the settlement known as Norridgewock. The last one, where the French Jesuit priest Sebastian Rale had a mission, is today called Old Point, and is located in Madison, Maine, Madison. Other sites are located nearby in Starks, Maine, Starks and the present-day town of Norrid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick to the northeast and Quebec to the north. The Gulf of Maine and Atlantic Ocean are to the east and southeast, and Long Island Sound is to the southwest. Boston is New England's largest city and the capital of Massachusetts. Greater Boston, comprising the Boston–Worcester–Providence Combined Statistical Area, houses more than half of New England's population; this area includes Worcester, Massachusetts, the second-largest city in New England; Manchester, New Hampshire, the largest city in New Hampshire; and Providence, Rhode Island, the capital of and largest city in Rhode Island. In 1620, the Pilgrims (Plymouth Colony), Pilgrims established Plymouth Colony, the second successful settlement in Briti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wabanaki Confederacy
The Wabanaki Confederacy (''Wabenaki, Wobanaki'', translated to "People of the Dawn" or "Easterner"; also: Wabanakia, "Dawnland") is a North American First Nations and Native American confederation of five principal Eastern Algonquian nations: the Abenaki, Mi'kmaq, Wolastoqiyik, Passamaquoddy (''Peskotomahkati'') and Penobscot. There were more tribes, along with many bands, that were once part of the Confederation. Native tribes such as the Nanrantsouak, Alemousiski, Pennacook, Sokoki, and Canibas, through massacres, tribal consolidation, and ethnic label shifting were absorbed into the five larger national identities. Members of the Wabanaki Confederacy, the Wabanakiyak, are located in and named for the area which they call Wabanaki ("Dawnland"), roughly the area that became the French colony of Acadia. The territory boundaries encompass present-day Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont, in the United States, and New Brunswick, mainland Nova Scotia, Cape Breton Island, Pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Norridgewock
The Battle of Norridgewock was a raid on the Abenaki settlement of Norridgewock by a group of colonial militiamen from the New England Colonies. Occurring in contested lands on the edge of the American frontier, the raid resulted in the massacre of the Abenaki inhabitants of Norridgewock by the militiamen. The raid was undertaken to check Abenaki power in the region, limit Catholic proselytizing among the Abenaki (and thereby perceived French influence), and to allow the expansion of New England settlements into Abenaki territory and Acadia. New France defined this area as starting at the Kennebec River in southern Maine. Other motivations for the raid included the special £100 scalp bounty placed on Râle's head by the Massachusetts provincial assembly and the bounty on Abenaki scalps offered by the colony during the conflict. Captains Johnson Harmon, Jeremiah Moulton, and Richard Bourne (Brown) led a force of two hundred colonial New Englanders, which attacked the Abenaki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sébastien Rale
Sébastien Rale (; also Racle, Râle, Rasle, Rasles, and Sebastian Rale; January 20, 1657 – August 23, 1724) was a French Society of Jesus, Jesuit missionary and lexicographer who preached amongst the Abenaki and encouraged their resistance to British colonization of the Americas, British colonization during the early 18th century. This encouragement culminated in Dummer's War (1722–1725), where Rale was killed by a group of New England Colonies, New England militiamen. Rale also worked on an Abenaki-French dictionary during his time in North America. Early years Rale was born in Pontarlier, France and studied in Dijon. In 1675, he joined the Society of Jesus at Dole (Jura), Dole and taught Greek and rhetoric at Nîmes. He volunteered for the American missions in 1689 and came to the Americas in a party led by Louis de Buade de Frontenac, the Governor General of New France. His first missionary work was at an Abenaki village in Saint-François-du-Lac, Quebec, Saint Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Army Rangers
The United States Army Rangers are U.S. Army personnel who have served in any unit which has held the official designation of "Ranger". The term is commonly used to include graduates of the Ranger School, even if they have never served in a "Ranger" unit, because Army regulations and special qualification identifier (SQI) codes provide that the only requirement to earn the "Title: Ranger" is that a soldier "must successfully complete the appropriate training at the Infantry School." In a broader and less formal sense, the term "ranger" has been used, officially and unofficially, in North America since the 17th century, to describe specialized light infantry in small, independent units—usually companies. The first units to be officially designated Rangers were companies recruited in the New England Colonies to fight against Native Americans in King Philip's War. Following that time, the term became more common in official usage, during the French and Indian Wars of the 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeremiah Moulton
Jeremiah Moulton (1688 - 20 July 1765) was a New England militia officer and member of the Massachusetts Council. As a boy during King William's War, Moulton's parents were killed and he was taken captive in the Raid on York (1692) The Raid on York (also known as the Candlemas Massacre) took place on 24 January 1692 during King William's War, when Chief Madockawando and Father Louis-Pierre Thury led 200-300 natives into the town of York (then in the District of Maine and .... References * Moulton Biographical Sketch.1842. {{DEFAULTSORT:Moulton, Jeremiah People of Dummer's War People from colonial Massachusetts Military history of Acadia Military history of Nova Scotia Military history of New England Military history of Canada History of Maine Acadian history 1688 births 1765 deaths People from York, Maine Maine sheriffs American militia officers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johnson Harmon
Colonel Johnson Harmon (or Harman; c. 1675 – 1751) was an army officer in colonial America. He led the expedition during Father Rale's War that killed Father Sébastien Rale in the Battle of Norridgewock. Harmon was heralded as a hero upon his return to Boston. New England Officer and historian Samuel Penahallow proclaimed the attack was "the greatest victory we have obtained in the three or four last wars." Career Harmon was from York and was a teenager during the Raid on York (1692) during King William's War. During Queen Anne's War, in 1707 he was present, with his younger brother John, at Winter Harbour (Biddeford, Maine) he helped repulse the attack of natives in 50 canoes. In this battle Benjamin Donnell was killed by Indians. On 10 October 1710 Bomazeen with 60–70 Indians attacked the village of Winter Harbour, killing 3-4 and taking many more prisoner, including Harmon. (Harmon was part of the expedition that killed Bomazeen, upon their return from the Battle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Shute
Samuel Shute (January 12, 1662 – April 15, 1742) was an English military officer and royal governor of the provinces of Massachusetts and New Hampshire. After serving in the Nine Years' War and the War of the Spanish Succession, he was appointed by King George I as governor of Massachusetts and New Hampshire in 1716. His tenure was marked by virulent disagreements with the Massachusetts assembly on a variety of issues, and by poorly conducted diplomacy with respect to the Native American Wabanaki Confederacy of northern New England that led to Dummer's War (1722–1725). Although Shute was partly responsible for the breakdown in negotiations with the Wabanakis, he returned to England in early 1723 to procure resolutions to his ongoing disagreements with the Massachusetts assembly, leaving conduct of the war to Lieutenant Governor William Dummer. His protests resulted in the issuance in 1725 of the Explanatory Charter, essentially confirming his position in the disputes w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebastian Rale
Sebastian may refer to: People and fictional characters * Sebastian (name), including a list of persons and fictional characters with the name * Saint Sebastian, a Christian saint martyred in the 3rd century * Sebastian of Portugal (1554–1578), the sixteenth king of Portugal and the Algarve * Infante Sebastian of Portugal and Spain (1811–1875), Infante of Portugal (1811) and Infante of Spain (1824) * Sebastián (sculptor) (born 1947), artist based in Mexico * Sebastian (French musician), stage name of French musician, composer, producer, mixer, engineer, vocalist and DJ Sébastien Akchoté-Bozović (born 1981) * Sebastian (singer), stage name of Danish musician Knud Torben Christensen (born 1949) * Sebastian (rapper), stage name of American rapper Garland Mosley Jr., brother of Timbaland * Sin With Sebastian (also known as Sebastian), German musician Sebastian Roth (born 1971) * Mr. Sebastian, professional name of body pierce artist Alan Oversby (1933–1996) * Sebastian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesuit
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rome. It was founded in 1540 by Ignatius of Loyola and six companions, with the approval of Pope Paul III. The Society of Jesus is the largest religious order in the Catholic Church and has played significant role in education, charity, humanitarian acts and global policies. The Society of Jesus is engaged in evangelization and apostolic ministry in 112 countries. Jesuits work in education, research, and cultural pursuits. They also conduct retreats, minister in hospitals and parishes, sponsor direct social and humanitarian works, and promote Ecumenism, ecumenical dialogue. The Society of Jesus is consecrated under the patron saint, patronage of Madonna della Strada, a title of the Blessed Virgin Mary, and it is led by a Superior General of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |