|
Skelton Névé
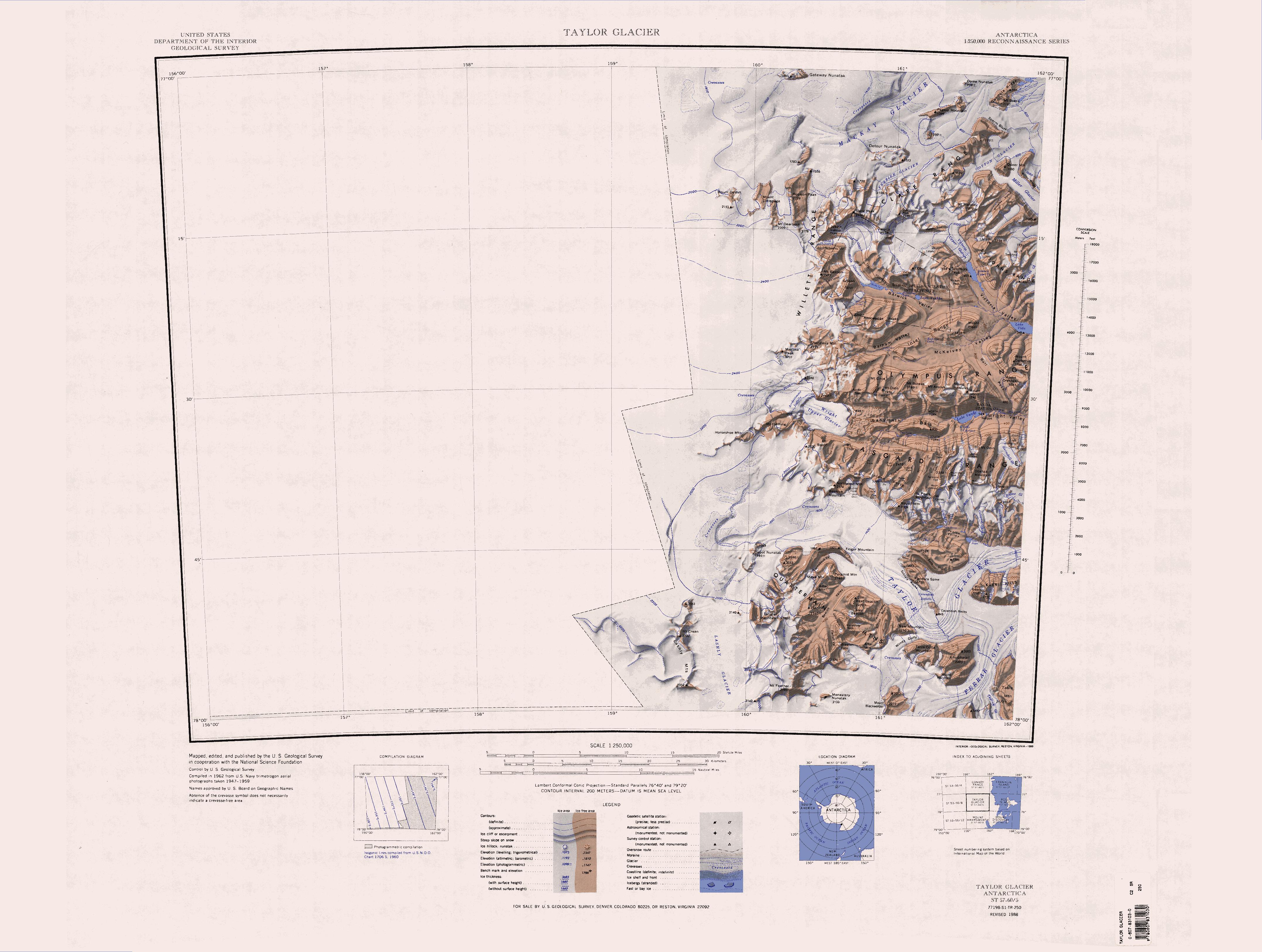
Skelton Glacier () is a large glacier flowing from the polar plateau into the Ross Ice Shelf at Skelton Inlet on the Hillary Coast, south of Victoria Land, Antarctica. Naming and exploration Skelton Glacier was named after the Skelton Inlet by the New Zealand party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (CTAE), 1956–58. The glacier was chosen in 1957 as the New Zealand party's route from the Ross Ice Shelf to the Antarctic Plateau. The Arctic Institute of North America organized two ground traverses in the antarctic summer of 1959–60 sponsored by the United States Antarctic Research Program. The first left New Zealand's Scott Base on 16 October 1959, crossed part of the Ross Ice Shelf, and on 27 October 1959 reached the foot of the Skelton Glacier. They traversed up the heavily crevassed glacier to a fuel cache deposited on the edge of the Victoria Land plateau by planes of the United States Navy and Air Force. From there they travelled more than to the end station ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ross Dependency
The Ross Dependency is a region of Antarctica defined by a circular sector, sector originating at the South Pole, passing along longitudes 160th meridian east, 160° east to 150th meridian west, 150° west, and terminating at latitude 60th parallel south, 60° south. It is claimed by New Zealand, a claim mutually accepted only by Australia, the United Kingdom, UK, France and Norway, which are countries that also have territorial claims in Antarctica. Under the 1961 Antarctic Treaty System, Antarctic Treaty, of which all territorial claimants are signatories, including New Zealand, all claims are held in abeyance. Article IV states: "No acts or activities taking place while the present Treaty is in force shall constitute a basis for asserting, supporting or denying a claim to territorial sovereignty in Antarctica or create any rights of sovereignty in Antarctica". The Dependency takes its name from James Clark Ross, Sir James Clark Ross, who discovered the Ross Sea and includes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Bluff
The Worcester Range () is a high coastal range, about long, in Antarctica. It stands between Skelton Glacier and Mulock Glacier on the western side of the Ross Ice Shelf. It is southwest of the Royal Society Range and north of the Conway Range of the Cook Mountains. Exploration and naming The Worcester Range was probably named after the training ship in the Thames, in which many officers of early British Antarctic expeditions trained. It was discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedition (BrNAE), 1901–04. The name seems to have been first applied on the charts of the Nimrod Expedition, British Antarctic Expedition, 1907–09. Location The range is part of the Prince Albert-McMurdo Range, which also includes the Prince Albert Mountains, in the Victoria Land region of New Zealand's Ross Dependency claim. These ranges are part of the larger Transantarctic Mountains, which span the continent. The Worcester Range is bounded to the east by the Skelton Glacier, which f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
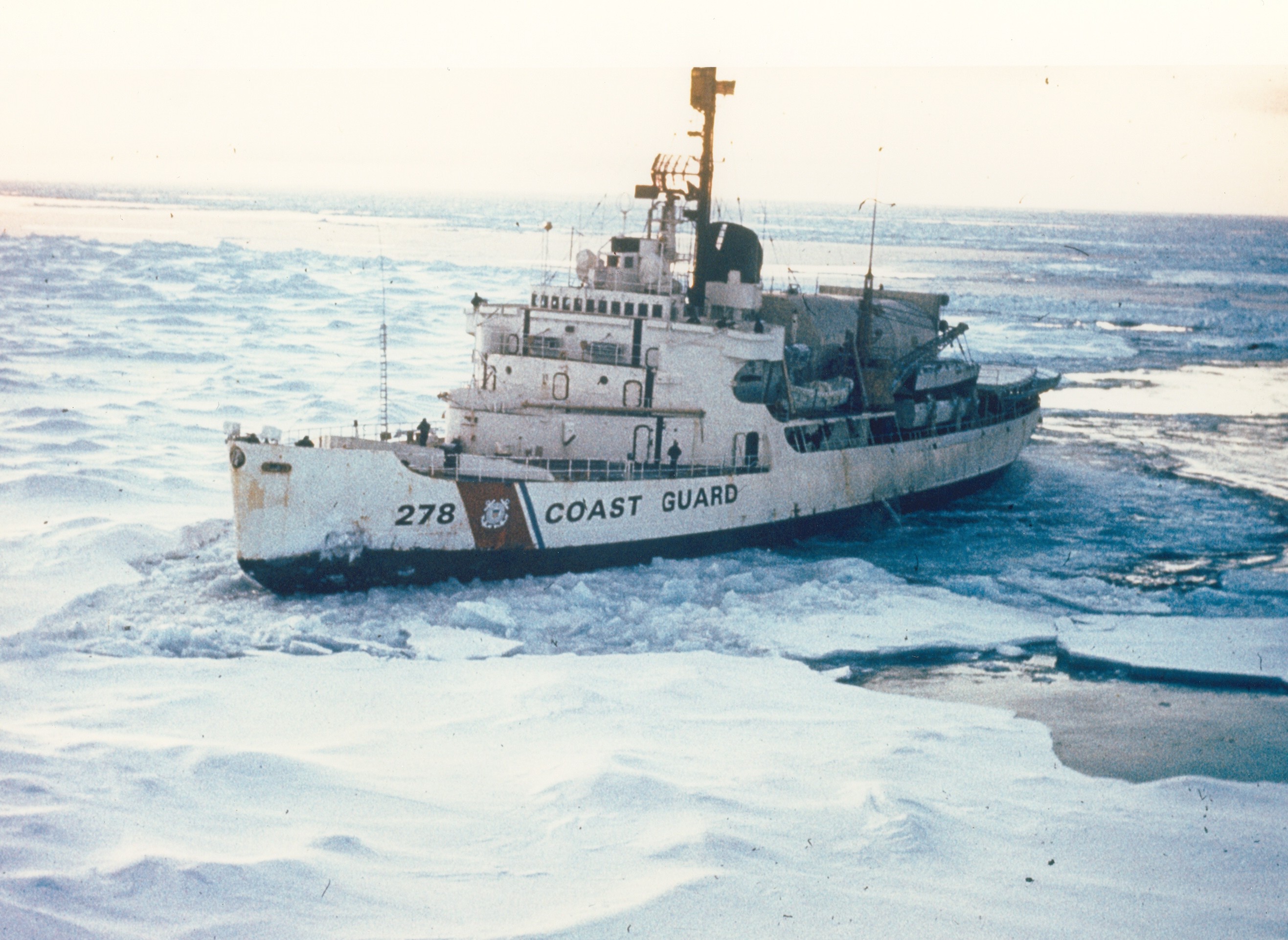
USCGC Staten Island
USCGC ''Staten Island'' (WAGB-278) was a United States Coast Guard . Laid down on 9 June 1942 and launched on 28 December 1942, the ship was commissioned on 26 February 1944, and almost immediately afterward transferred to the Soviet Union, under the Lend Lease program, under the name ''Severny Veter'', which loosely translates as ''Northwind'', until 19 December 1951. When returned to the United States Navy, she was designated USS ''Northwind'' until 15 April 1952, when she was renamed USS ''Staten Island'' to distinguish her from her successor which had been laid down shortly after she was lent to the Soviet Union. The ship was transferred to the U.S. Coast Guard as USCGC ''Staten Island'' in February 1965, and served until November 1974, before being scrapped. Construction ''Staten Island'' was one of the icebreakers designed by Lieutenant commander Edward Thiele and Gibbs & Cox of New York, who modeled them after plans for European icebreakers he obtained before the start o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angino Buttress
Angino Buttress is a prominent buttress-type mountain near the center of the Skelton Icefalls in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1964 for Ernest E. Angino, geologist at McMurdo Station McMurdo Station is an American Antarctic research station on the southern tip of Ross Island. It is operated by the United States through the United States Antarctic Program (USAP), a branch of the National Science Foundation. The station is ..., 1959–60. See also * Mount Metschel References * Mountains of Oates Land {{OatesLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warren Range
Warren Range () is an Antarctic mountain range about 15 nautical miles (28 km) long just west of Boomerang Range, with which it lies parallel, in Oates Land. Discovered by the Northern Survey Party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–58), which called the highest summit " Mount Warren" after Guyon Warren, a member of the party in 1957–58. To avoid confusion with another mountain of the same name, the name Warren has instead been applied to the whole rang Features Geographical features include: * Deception Glacier * Mount Guyon * Mount Ritchie * Skelton Icefalls Skelton Glacier () is a large glacier flowing from the polar plateau into the Ross Ice Shelf at Skelton Inlet on the Hillary Coast, south of Victoria Land, Antarctica. Naming and exploration Skelton Glacier was named after the Skelton Inlet by ... * Wise Peak Nearby features are: * Hamner Nunatak * Mount Darbyshire Mountain ranges of Oates Land {{OatesLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lashly Mountains
The Lashly Mountains () are a small group of mountains, the most prominent at being Mount Crean, standing south of the head of Taylor Glacier and west of Lashly Glacier, in Victoria Land, Antarctica. Exploration and naming The Lashly Mountains were discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedition (1901–04) and named for William Lashly, a member of the party which explored this area. Location The Lashley Mountains are on the edge of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet. They are west of the Quartermain Mountains and Mount Feather, from which they are separated by the Lashly Glacier, which flows south into The Portal. Mount Crean is the highest peak of the range. Portal Mountain lies to the south of the range, above the Skelton Névé. Geology The Lashly Mountains lie between the intrusive rocks of the McMurdo Dry Valleys and the extrusive rocks of the Transantarctic Mountains. Samples from an unnamed nunatak north of Mount Crean indicated an extrusive origin. The Lashly Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evteev Glacier
} The Mulock Glacier () is a large, heavily crevassed glacier which flows into the Ross Ice Shelf south of the Skelton Glacier in the Ross Dependency, Antarctica. Name The Mulock Glacier was named by the New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee (e NZAPC) in association with Mulock Inlet for Lieutenant George Mulock, Royal Navy, surveyor with the expedition. Glaciology The main trunk of the Mulock Glacier is about long and drops about from the edge of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet to its grounding line at its mouth. It has the largest catchment area between David Glacier and Byrd Glacier, and drains about 5.23±0.59 gigatonnes of ice per year into the Ross Ice Shelf. Its discharge rate is roughly in balance with the accumulation rate in its catchment area. Velocities vary along its course, probably due to changes in the ground slope below the glacier. In 1960–61 ice velocities along the grounded center line were about per year. In 2001–02 these had risen to about per y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nunatak
A nunatak (from Inuit language, Inuit ) is the summit or ridge of a mountain that protrudes from an ice field or glacier that otherwise covers most of the mountain or ridge. They often form natural pyramidal peaks. Isolated nunataks are also called glacial islands, and smaller nunataks rounded by glacial action may be referred to as rognons. The word is of Greenlandic language, Greenlandic origin and has been used in English since the 1870s. Description The term ''nunatak'' is typically used in areas where a permanent ice sheet is present and the ridge protrudes above the sheet.J. J. Zeeberg, ''Climate and Glacial History of the Novaya Zemlya Archipelago, Russian Arctic''. pp. 82–84 Nunataks present readily identifiable landmark reference points in glaciers or ice caps and are often named. While some are isolated, they can also form dense clusters, such as Queen Louise Land in Greenland. Nunataks are generally angular and jagged, hampering the formation of glacial ice on thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portal Mountain
The Lashly Mountains () are a small group of mountains, the most prominent at being Mount Crean, standing south of the head of Taylor Glacier and west of Lashly Glacier, in Victoria Land, Antarctica. Exploration and naming The Lashly Mountains were discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedition (1901–04) and named for William Lashly, a member of the party which explored this area. Location The Lashley Mountains are on the edge of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet. They are west of the Quartermain Mountains and Mount Feather, from which they are separated by the Lashly Glacier, which flows south into The Portal. Mount Crean is the highest peak of the range. Portal Mountain lies to the south of the range, above the Skelton Névé. Geology The Lashly Mountains lie between the intrusive rocks of the McMurdo Dry Valleys and the extrusive rocks of the Transantarctic Mountains. Samples from an unnamed nunatak north of Mount Crean indicated an extrusive origin. The Lashl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |