|
Sinkholes
A sinkhole is a depression or hole in the ground caused by some form of collapse of the surface layer. The term is sometimes used to refer to doline, enclosed depressions that are also known as shakeholes, and to openings where surface water enters into underground passages known as ''ponor'', swallow hole or swallet. A ''cenote'' is a type of sinkhole that exposes groundwater underneath. ''Sink'', and ''stream sink'' are more general terms for sites that drain surface water, possibly by infiltration into sediment or crumbled rock. Most sinkholes are caused by Karst topography, karst processes – the chemical dissolution of carbonate rocks, collapse or suffosion processes. Sinkholes are usually circular and vary in size from tens to hundreds of Metre, meters both in diameter and depth, and vary in form from soil-lined bowls to bedrock-edged chasms. Sinkholes may form gradually or suddenly, and are found worldwide. Formation Natural processes Sinkholes may capture surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
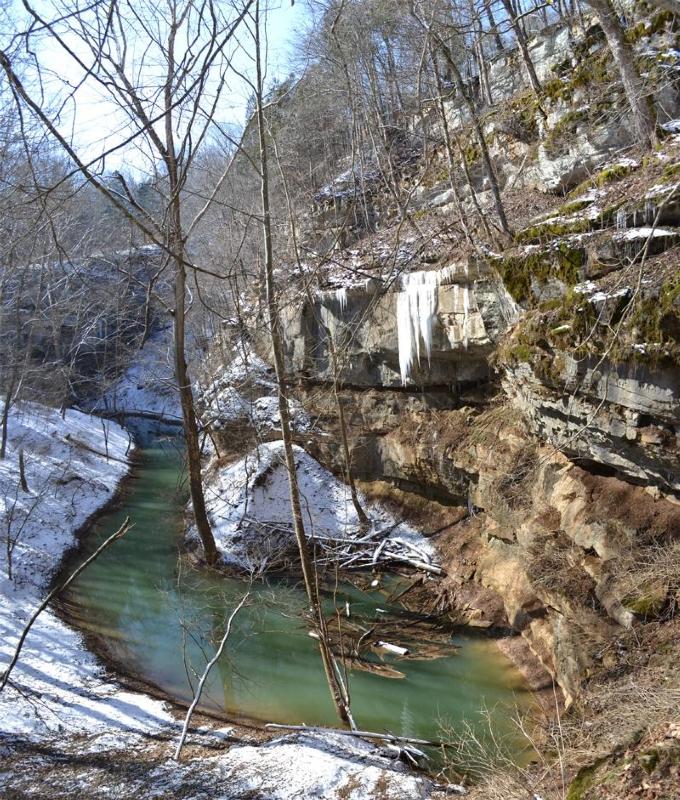
Cedar Sink
Cedar Sink is a vertical-walled large depression or sinkhole in the ground, located in Edmonson County, Kentucky and contained within and managed by Mammoth Cave National Park. The sinkhole measures from the top sandstone plateau to the bottom of the sink and was caused by collapse of the surface soil. The landscape is karst topography, which means the region is influenced by the dissolution of soluble rocks. Sinkholes, caves, and Sinkhole, dolines typically characterize these underground drainage systems. Cedar Sink has a bottom area of about and has more fertile soil compared to the ridgetops. Geomorphology Rock age The rocks of Cedar Sink and the surrounding area are from the Mississippian (geology), Mississippian (also known as Lower Carboniferous or Early Carboniferous) subperiod that occurred 358.9 to 323.2 million years ago. Cedar Sink formation The Big Clifty Sandstone caprock has been breached, exposing the limestone Girkin Formation and resulting in a relief approxima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
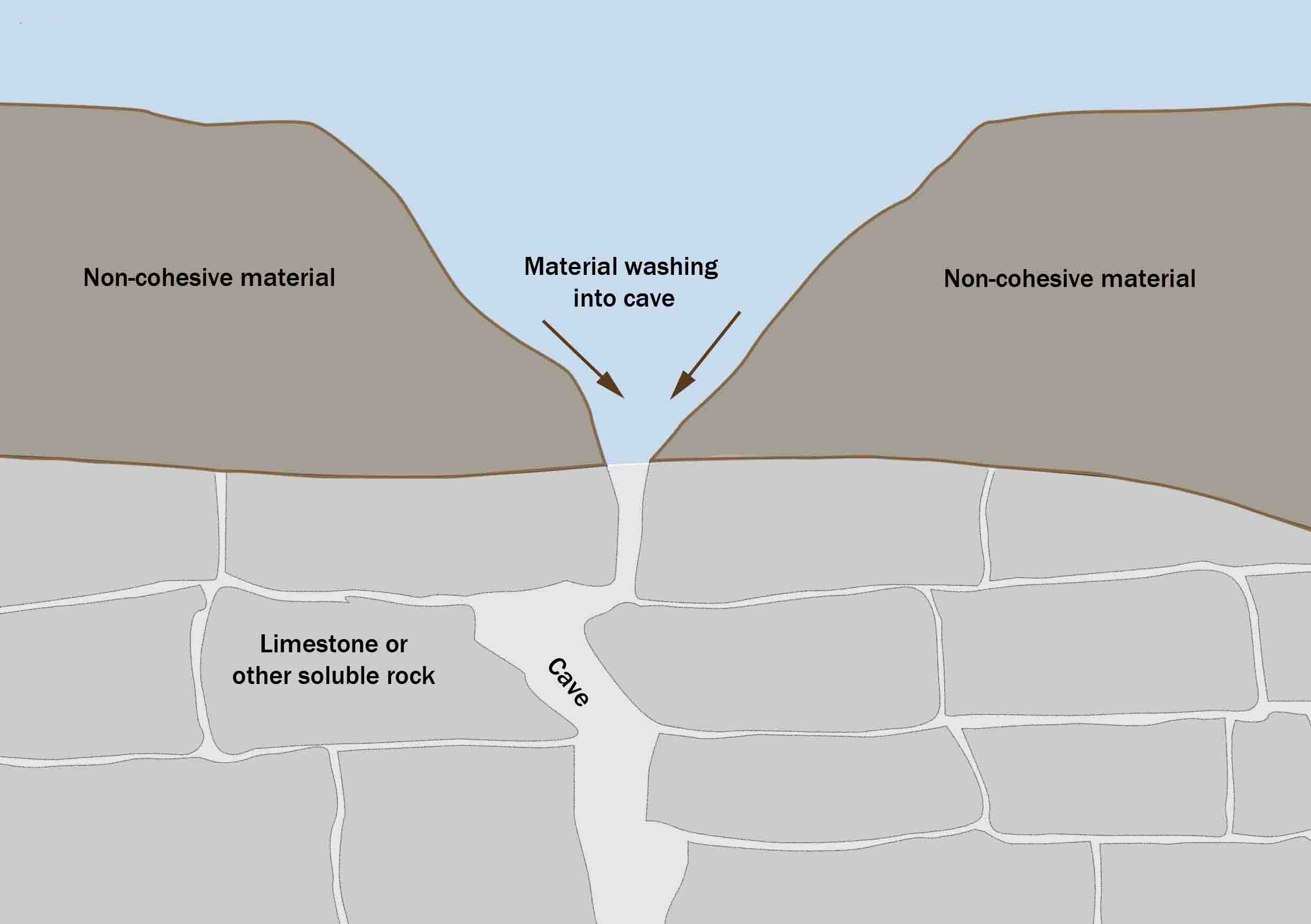
Suffosion
Suffosion is one of the two geological processes by which subsidence sinkholes or dolines are formed, the other being due to collapse of an underlying cave or void, with most sinkholes formed by the suffosion process. Suffosion sinkholes are normally associated with karst topography although they may form in other types of rock including chalk, gypsum and basalt. In the karst of the UK's Yorkshire Dales, numerous surface depressions known locally as "shakeholes" are the result of glacial till washing into fissures in the underlying limestone. Process Suffosion occurs when loose soil, loess A loess (, ; from ) is a clastic rock, clastic, predominantly silt-sized sediment that is formed by the accumulation of wind-blown dust. Ten percent of Earth's land area is covered by loesses or similar deposition (geology), deposits. A loess ..., or other non-cohesive material lies on top of a limestone substratum containing fissures and joints. Rain and surface water gradually wash this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karst Topography
Karst () is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble carbonate rocks such as limestone and Dolomite (rock), dolomite. It is characterized by features like poljes above and drainage systems with sinkholes and caves underground. There is some evidence that karst may occur in more weathering-resistant rocks such as quartzite given the right conditions. Subterranean drainage may limit surface water, with few to no rivers or lakes. In regions where the dissolved bedrock is covered (perhaps by debris) or confined by one or more superimposed non-soluble rock strata, distinctive karst features may occur only at subsurface levels and can be totally missing above ground. The study of ''paleokarst'' (buried karst in the stratigraphic column) is important in petroleum geology because as much as 50% of the world's Oil and gas reserves and resource quantification, hydrocarbon reserves are hosted in carbonate rock, and much of this is found in porous karst systems. Etymology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenote
A cenote ( or ; ) is a natural pit, or sinkhole, resulting when a collapse of limestone bedrock exposes groundwater. The term originated on the Yucatán Peninsula of Mexico, where the ancient Maya commonly used cenotes for water supplies, and occasionally for sacrificial offerings. The name derives from a word used by the lowland Yucatec Maya——to refer to any location with accessible groundwater. In Mexico the Yucatán Peninsula alone has an estimated 10,000 cenotes, water-filled sinkholes naturally formed by the collapse of limestone, and located across the peninsula. Some of these cenotes are at risk from the construction of the new tourist Maya Train. Cenotes are common geological forms in low-altitude regions, particularly on islands (such as Cefalonia, Greece), coastlines, and platforms with young post-Paleozoic limestone with little soil development. The term ''cenote'', originally applying only to the features in Yucatán, has since been applied by researchers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ponor
A ponor is a natural opening where surface water enters into underground passages; they may be found in Karst topography, karst landscapes where the geology and the geomorphology is typically dominated by porous limestone rock. Ponors can drain stream or lake water continuously or can at times work as Spring (hydrology), springs, similar to estavelles. Morphologically, ponors come in forms of large pits and caves, large fissures and caverns, networks of smaller cracks, and sedimentary, Alluvium, alluvial drains. Etymology The name for the karst formation ponor comes from Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene. It derives from the proto-Slavic language, proto-Slavic word ''*nora'', meaning ''pit'', ''hole''. Several places in southeast Europe (Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech Republic, Hungary, Romania, Montenegro, Slovenia) Ponor (other), bear the name ''Ponor'' due to associated karst openings. Description Whereas a sinkhole (doline) is a depression of surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subsidence
Subsidence is a general term for downward vertical movement of the Earth's surface, which can be caused by both natural processes and human activities. Subsidence involves little or no horizontal movement, which distinguishes it from slope movement. Processes that lead to subsidence include dissolution of underlying carbonate rock by groundwater; gradual compaction of sediments; withdrawal of fluid lava from beneath a solidified crust of rock; mining; pumping of subsurface fluids, such as groundwater or petroleum; or warping of the Earth's crust by tectonic forces. Subsidence resulting from tectonic deformation of the crust is known as tectonic subsidence and can create accommodation for sediments to accumulate and eventually lithify into sedimentary rock. Ground subsidence is of global concern to geologists, geotechnical engineers, surveyors, engineers, urban planners, landowners, and the public in general.National Research Council, 1991. ''Mitigating losses from land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
07 Imotski Crveno Jezero (1)
7 (seven) is the natural number following 6 and preceding 8. It is the only prime number preceding a cube. As an early prime number in the series of positive integers, the number seven has symbolic associations in religion, mythology, superstition and philosophy. The seven classical planets resulted in seven being the number of days in a week. 7 is often considered lucky in Western culture and is often seen as highly symbolic. Evolution of the Arabic digit For early Brahmi numerals, 7 was written more or less in one stroke as a curve that looks like an uppercase vertically inverted (ᒉ). The western Arab peoples' main contribution was to make the longer line diagonal rather than straight, though they showed some tendencies to making the digit more rectilinear. The eastern Arab peoples developed the digit from a form that looked something like 6 to one that looked like an uppercase V. Both modern Arab forms influenced the European form, a two-stroke form consisting of a ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonate Rock
Carbonate rocks are a class of sedimentary rocks composed primarily of carbonate minerals. The two major types are limestone, which is composed of calcite or aragonite (different crystal forms of CaCO3), and Dolomite (rock), dolomite rock (also known as dolostone), which is composed of Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2). They are usually Dunham classification, classified on the basis of texture and grain size. Importantly, carbonate rocks can exist as metamorphic and igneous rocks, too. When recrystallized carbonate rocks are Metamorphic rock, metamorphosed, marble is created. Rare igneous rock, igneous carbonate rocks even exist as Intrusive rock, intrusive carbonatites and, even rarer, there exists volcanic carbonate lava. Carbonate rocks are also crucial components to understanding Geological history of Earth, geologic history due to processes such as diagenesis in which carbonates undergo compositional changes based on kinetic effects. The correlation between this compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kentucky
Kentucky (, ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north, West Virginia to the northeast, Virginia to the east, Tennessee to the south, and Missouri to the west. Its northern border is defined by the Ohio River. Its capital is Frankfort, Kentucky, Frankfort and its List of cities in Kentucky, most populous city is Louisville, Kentucky, Louisville. As of 2024, the state's population was approximately 4.6 million. Previously part of Colony of Virginia, colonial Virginia, Kentucky was admitted into the Union as the fifteenth state on June 1, 1792. It is known as the "Bluegrass State" in reference to Kentucky bluegrass, a species of grass introduced by European settlers which has long supported the state's thoroughbred horse industry. The fertile soil in the central and western parts of the state led to the development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underground Stream
A subterranean river (also known as an underground river) is a river or watercourse that runs wholly or partly beneath the ground, one where the riverbed does not represent the surface of the Earth. It is distinct from an aquifer, which may flow like a river but is contained within a permeable layer of rock or other unconsolidated materials. A river flowing below ground level in an open gorge is not classed as subterranean. Some natural rivers may be entirely subterranean, collecting in and flowing through cave systems. In karst topography, rivers that originate above ground can disappear into sinkholes, continuing underground until they reappear on the surface downstream, possibly having merged with other subterranean rivers. The longest subterranean river in the world is the Sistema Sac Actun cave system in Mexico. Subterranean rivers can also be the result of covering over a river or diverting its flow into culverts, usually as part of urban development.Richard J. Heggen: Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground Water
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an ''aquifer'' when it can yield a usable quantity of water. The depth at which soil pore spaces or fractures and voids in rock become completely saturated with water is called the ''water table''. Groundwater is recharged from the surface; it may discharge from the surface naturally at springs and seeps, and can form oases or wetlands. Groundwater is also often withdrawn for agricultural, municipal, and industrial use by constructing and operating extraction wells. The study of the distribution and movement of groundwater is ''hydrogeology'', also called groundwater hydrology. Typically, groundwater is thought of as water flowing through shallow aquifers, but, in the technical sense, it can also contain soil mois ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halite
Halite ( ), commonly known as rock salt, is a type of salt, the mineral (natural) form of sodium chloride ( Na Cl). Halite forms isometric crystals. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, pink, red, orange, yellow or gray depending on inclusion of other materials, impurities, and structural or isotopic abnormalities in the crystals. It commonly occurs with other evaporite deposit minerals such as several of the sulfates, halides, and borates. The name ''halite'' is derived from the Ancient Greek word for "salt", ἅλς (''háls''). Occurrence Halite dominantly occurs within sedimentary rocks where it has formed from the evaporation of seawater or salty lake water. Vast beds of sedimentary evaporite minerals, including halite, can result from the drying up of enclosed lakes and restricted seas. Such salt beds may be hundreds of meters thick and underlie broad areas. Halite occurs at the surface today in playas in reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |