|
Simon Szécsényi
Simon Szécsényi (; died c. 29 January 1412), was a Hungarian baron and military leader, who was a staunch supporter of King Sigismund of Luxembourg since the 1380s. Joining a magnate conspiracy in 1401, he played a key role in the arrest of the king, but later was pardoned and retained his political influence until his death. Family Simon was born into the influential Szécsényi family as one of the three sons of Kónya Szécsényi, Ban of Croatia and Elizabeth Haschendorfer, a daughter of Austrian noble Wulfing Haschendorfer from Haschendorf/Hasfalva (today part of Neckenmarkt in Austria). His brothers were Frank, also a baron and his closest political ally, and Nicholas I. The Szécsényi family originated from the Kacsics clan. Simon's grandfather was Thomas I Szécsényi, who rose to prominence during King Charles I's war against the oligarchs and received numerous grants of land thereafter. Indicating the social status of his family, Simon Szécsényi married Elizab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judge Royal
The judge royal, also justiciar,Rady 2000, p. 49. chief justiceSegeš 2002, p. 202. or Lord Chief JusticeFallenbüchl 1988, p. 145. (,Fallenbüchl 1988, p. 72. ,Zsoldos 2011, p. 26. , ), was the second-highest judge, preceded only by the Palatine (Kingdom of Hungary), palatine, in the Kingdom of Hungary between around 1127 and 1884. After 1884, the judge royal was only a symbolic function, but it was only in 1918 — with the end of Habsburgs in the Kingdom of Hungary (the kingdom continued formally until 1946) — that the function ceased officially. There remain significant problems in the translation of the title of this officer. In Latin, the title translates as 'Judge of the Royal Court', which lacks specificity. In Hungarian, he is 'Judge of the Country', with 'country' in this sense meaning 'political community', being thus broadly analogous to the German 'Land'. English has no obvious translation for Landesrichter, which is the direct German translation of országbíró. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis I Of Hungary
Louis I, also Louis the Great (; ; ) or Louis the Hungarian (; 5 March 132610 September 1382), was King of Hungary and Croatia from 1342 and King of Poland from 1370. He was the first child of Charles I of Hungary and his wife, Elizabeth of Poland, to survive infancy. A 1338 treaty between his father and Casimir III of Poland, Louis's maternal uncle, confirmed Louis's right to inherit the Kingdom of Poland if his uncle died without a son. In exchange, Louis was obliged to assist his uncle to reoccupy the lands that Poland had lost in previous decades. He bore the title Duke of Transylvania between 1339 and 1342 but did not administer the province. Louis was of age when he succeeded his father in 1342, but his deeply religious mother exerted a powerful influence on him. He inherited a centralized kingdom and a rich treasury from his father. During the first years of his reign, Louis launched a crusade against the Lithuanians and restored royal power in Croatia; his troops ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voivode Of Transylvania
The Voivode of Transylvania (;Fallenbüchl 1988, p. 77. ;Zsoldos 2011, p. 36. ; ) was the highest-ranking official in Transylvania within the Kingdom of Hungary from the 12th century to the 16th century. Appointed by the King of Hungary, monarchs, the voivodesthemselves also the heads or ''ispáns'' of Fehér County (former), Fehér Countywere the superiors of the ''ispáns'' of all the other County (Kingdom of Hungary), counties in the province. They had wide-ranging administrative, military and judicial powers, but their jurisdiction never covered the whole province. The Transylvanian Saxons, Saxon and Székelys, Székely communitiesorganized into their own districts or "Seat (territorial-administrative unit), seats" from the 13th centurywere independent of the voivodes. The kings also exempted some Transylvanian towns and villages from their authority over the centuries. Even so, the Voivodeship of Transylvania "was the largest single administrative entity"Je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borač Fortress
Borač (Serbian Cyrillic: Борач), also known as Borač na Kršu is a medieval town and fortress. The remains of the Borač fortress lie on top of a rocky hill 10km northwest of Knić and are protected as a Immovable Cultural Heritage of Great Importance (Serbia), cultural monument of great importance. History Archeological findings confirm that the area of Borač hills has been inhabited for thousands of years. The first fort was built by the Ancient Rome, Romans, who used it as an observation post of an important Roman road. Although the town of Borač existed as a center of a Serbian ''župa'', or a district since 12th century, the fortification was first mentioned in the records from 1389 as a residence of Princess Milica of Serbia, princess Milica after the death of her husband, prince Lazar of Serbia in Battle of Kosovo earlier that year. Despot Stefan Lazarevic promulgated a charter to the people of Dubrovnik in Borač in 1405. In that period, it was one of the most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
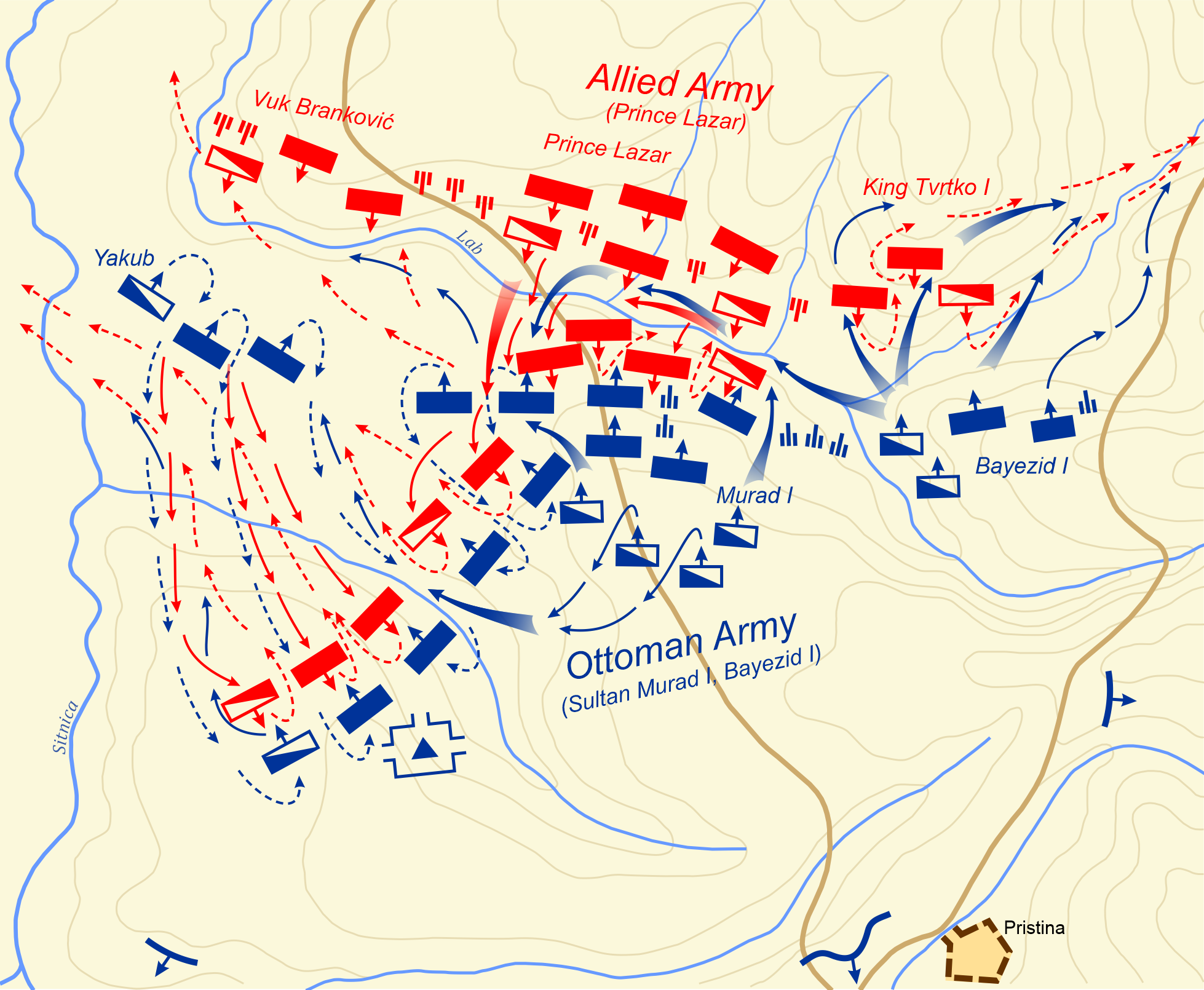
Battle Of Kosovo
The Battle of Kosovo took place on 15 June 1389 between an army led by the Serbian Prince Lazar Hrebeljanović and an invading army of the Ottoman Empire under the command of Sultan Murad I. It was one of the largest battles of the Late Middle Ages. The battle was fought on the Kosovo field in the territory ruled by Serbian nobleman Vuk Branković, in what is today Kosovo, about northwest of the modern city of Pristina. The army under Prince Lazar consisted mostly of his own troops, a contingent led by Branković, and a contingent sent from Bosnia by King Tvrtko I, commanded by Vlatko Vuković. Additionally, Lazar was also supported by a Christian coalition from various European ethnic groups. Prince Lazar was the ruler of Moravian Serbia and the most powerful among the Serbian regional lords of the time, while Branković ruled the District of Branković and other areas, recognizing Lazar as his overlord. Reliable historical accounts of the battle are scarce. The bulk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moravian Serbia
Moravian Serbia (), the Principality of Moravian Serbia () or the Realm of Prince Lazar was the largest and most powerful Serbian principality to emerge from the ruins of the Serbian Empire (1371). Moravian Serbia was named after Morava, the main river of the region. The independent principality in the region of Morava was established in 1371, and attained its largest extent in 1379 through the military and political activities of its first ruler, prince Lazar Hrebeljanović. In 1402 it was raised to the Serbian Despotate, which would exist until 1459. History Lazar Hrebeljanović was born in around 1329 in the fortress of Prilepac, near the town of Novo Brdo in the region of Kosovo, Kingdom of Serbia. Lazar was a courtier at the court of Serbian Tsar Stefan Uroš Dušan, and at the court of Dušan's successor, Tsar Stefan Uroš V (r. 1356–1371). Uroš's reign was characterized by the weakening of the central authority and the gradual disintegration of the Serbian Empir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trencsén County
Trencsén county (Latin: ''comitatus Trentsiniensis / Trenchiniensis''; Hungarian language, Hungarian: ''Trencsén (vár)megye''; Slovak language, Slovak: ''Trenčiansky komitát / Trenčianska stolica / Trenčianska župa''; ) was an administrative county (Comitatus (Kingdom of Hungary), comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now in western Slovakia. Geography Trencsén county shared borders with the Cisleithania, Austrian lands Moravia, Galicia (Central Europe), Galicia, and Silesia, and the Hungarian counties Árva (county), Árva, Turóc (county), Turóc and Nyitra county, Nyitra. The county's territory was a strip in the extreme northwestern edge of present-day Slovakia, i.e. the territory between the Czech Republic, Czech border, the town of Nové Mesto nad Váhom, Vágújhely, the Turóc county, the Árva county and the Poland, Polish border. The river Váh, Vág flowed through the county. Its area was 4,456 km2 around 1910. Capitals The capital of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ispán
The ispánRady 2000, p. 19.''Stephen Werbőczy: The Customary Law of the Renowned Kingdom of Hungary in Three Parts (1517)'', p. 450. or countEngel 2001, p. 40.Curta 2006, p. 355. (, , and ),Kirschbaum 2007, p. 315. deriving from title of župan, was the leader of a castle district (a fortress and the royal lands attached to it) in the Kingdom of Hungary from the early 11th century. Most of them were also heads of the basic administrative units of the kingdom, called County (Kingdom of Hungary), counties, and from the 13th century the latter function became dominant. The ''ispáns'' were appointed and dismissed by either the king of Hungary, monarchs or a high-ranking royal official responsible for the administration of a larger territorial unit within the kingdom. They fulfilled administrative, judicial and military functions in one or more counties. Heads of counties were often represented locally by their deputies, the vice-ispánsRady 2000, p. 41. (,Nemes 1989, p. 21. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hont County
Hont County was an administrative county (Comitatus (Kingdom of Hungary), comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Most of its territory is now part of Slovakia, while a smaller southern portion is part of Hungary. Today, in Slovakia Hont is the informal designation of the corresponding territory and an official tourist region. Geography Hont county shared borders with the counties Bars county, Bars, Zólyom county, Zólyom, Nógrád County (former), Nógrád, Pest-Pilis-Solt-Kiskun and Esztergom County, Esztergom. It was situated between Banská Štiavnica, Selmecbánya and the Danube river, but the territory around the town of Krupina, Korpona was added only at the end of the 19th century. The rivers Korpona and Ipeľ, Ipoly were the central rivers that flowed through the county. Its area was 2633 km2 around 1910. Capitals The capitals of the county were the Hont Castle together with Hídvég (present-day Ipeľské Predmostie), then from the 16th century onwards there wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Börzsöny
Börzsöny (; or ''Novohradské hory'', New City Mountains) is a mountain range in Northern Hungary. Its tallest peak is the Csóványos with . It is the westernmost member of the North Hungarian Mountains, which belongs to the Inner Western Carpathians Divisions of the Carpathians are a categorization of the Carpathian mountains system. Below is a detailed overview of the major subdivisions and ranges of the Carpathian Mountains. The Carpathians are a "subsystem" of a bigger Alps-Himalaya S .... The varied landscape offers good hiking opportunities. A large part of the Börzsöny is national park. From the top of Csóványos we can see one of the country's most beautiful panorama on the Danube Bend, Danube Bend (''Dunakanyar''). Geography The mountain is structurally divided into four parts: High Börzsöny, Northern Börzsöny, Western Börzsöny and Southern Börzsöny. High Börzsöny Here are the highest peaks of Börzsöny: the Csóványos (938 m), Magos-f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banate Of Severin
The Banate of Severin or Banate of Szörény (; ; ; , ; , ) was a Hungarian political, military and administrative unit with a special role in the initially anti- Bulgarian, latterly anti- Ottoman defensive system of the medieval Kingdom of Hungary. It was founded by Prince Béla in 1228. Territory The Banate of Severin was a march (or a border province) of the medieval Kingdom of Hungary between the Lower Danube and the Olt River (in present-day Oltenia in Romania). A charter of grant, issued on 2 June 1247 to the Knights Hospitallers, mentioned the Olt as its eastern border. The Knights received the "Land of Severin" ''(Terra de Zeurino)'', along with the nearby mountains, from Béla IV of Hungary. The king had described the same region as a "deserted and depopulated" land in a letter to Pope Gregory IX on 7 June 1238. Modern scholars assume that either the Hungarian conquest of the territory or confrontations between Bulgaria and Hungary had forced the local population t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |