|
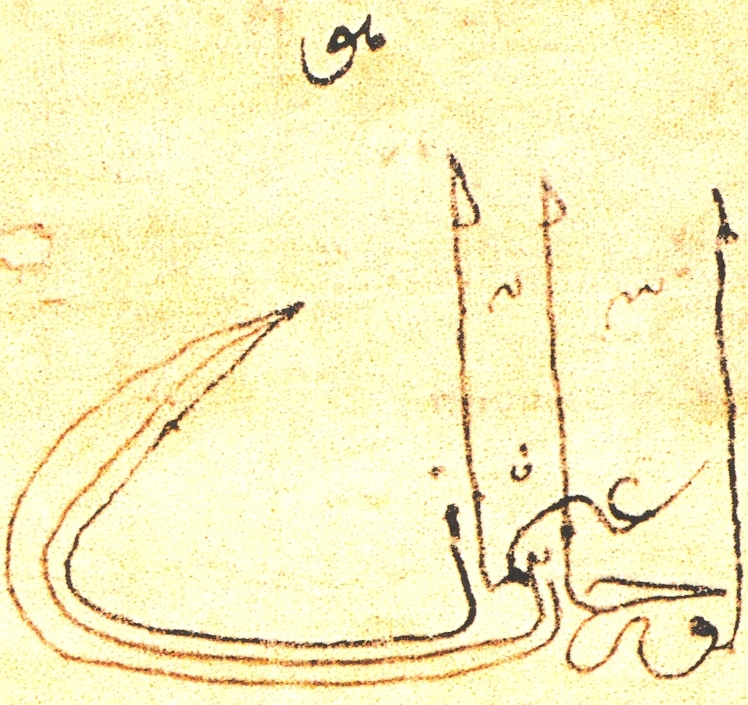
Signum Manus
''Signum manus'' (transl. ''sign of the hand'', sometimes also known as ''Chrismon'') refers to the Middle Ages, medieval European practice of Signature, signing a document or charter with a special type of monogram or royal cypher. The practice is documented from at least the Merovingian period (ca. 5th century) until the 14th century in the Frankish Empire and its successors. History The term ''Chrismon'' was introduced in Neo-Latin specifically as a term for the Chi Rho monogram. As this symbol was used in Merovingian documents at the starting point of what would diversify into the tradition of "cross-signatures", German scholarship of the 18th century extended use of the term ''Chrismon'' to the entire field. In medievalist paleography and ''Diplomatik'' (''ars diplomaticae'', i.e. the study of :wikt:diploma#Latin, documents or charters), the study of these signatures or sigils was known as ''Chrismologia'' or ''Chrismenlehre'', while the study of Christian cross variants, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signum Manus Of Charlemagne
Signum is Latin for "sign" and may refer to: Brands and companies * Integra Signum, a (defunct) Swiss railroad signaling company ** Integra-Signum, a train protection system * Opel Signum, an Opel car model * Signum Biosciences, a company based in New Jersey * Signum (typeface), a 1955 typeface designed by Georg Trump for the Weber Typefoundry Media * ''Signum'' (magazine), a German literary magazine * Signum (musical group), a trance music group * Signum (''Nanoha''), a character from the ''Magical Girl Lyrical Nanoha'' series * Signum Quartet, a string quartet based in Cologne, Germany * Signum Records, a classical music record label in the UK Other uses * Signum, part of Roman naming conventions * Signum, an alternative name for some Roman Republic army units * Signum (anatomy), a part of the female Lepidoptera genitalia * Signum function or sign function in mathematics * Signum manus ''Signum manus'' (transl. ''sign of the hand'', sometimes also known as ''Chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theology Of The Cross
The theology of the Cross (, ) or staurology (from Greek , and ''- logy'': ) is a term coined by the German theologian Martin Luther to refer to theology that posits "the cross" (that is, divine self-revelation) as the only source of knowledge concerning who God is and how God saves. It is contrasted with the "theology of glory" (), which places greater emphasis on human abilities and human reason. Catholic understanding Paragraph 2015 of the Catechism of the Catholic Church describes the way of perfection as passing by way of the Cross. There is no holiness without renunciation and spiritual battle. Spiritual progress entails the ascesis and mortification that gradually leads to living in the peace and joy of the beatitudes. As defined by Luther The term was used very rarely by Luther. He first used the term, and explicitly defined it in contrast to the theology of glory, in the Heidelberg Disputation of 1518. During this debate, he represented the Augustinians and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monograms
A monogram is a motif (visual arts), motif made by overlapping or combining two or more letters or other graphemes to form one symbol. Monograms are often made by combining the initials of an individual or a company, used as recognizable symbols or logos. A series of uncombined initials is properly referred to as a cypher (e.g. a royal cypher) and is not a monogram. Many of today's monograms are embroidered on items for the home like towels, bedding, robes etc. History Monograms first appeared on coins, as early as 350 BC. The earliest known examples are of the names of Greek cities which issued the coins, often the first two letters of the city's name. For example, the monogram of Achaea (ancient region), Achaea consisted of the letters alpha (Α) and chi (letter), chi (Χ) joined together. Monograms have been used as signatures by artists and Artisan, craft workers on paintings, sculptures and pieces of furniture, especially when guilds enforced measures against unauthor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tughra
A tughra (; ) is a calligraphy, calligraphic monogram, Seal (emblem), seal or signature of a sultan that was affixed to all official documents and correspondence. Inspired by the Tamga, tamgha, it was also carved on his seal and stamped on the coins minted during his reign. Very elaborate decorated versions were created for important documents that were also works of art in the tradition of Ottoman illumination, such as the example of Suleiman the Magnificent in the gallery below. The tughra was designed at the beginning of the sultan's reign and drawn by the court calligrapher or ''nisanci, nişancı'' on written documents. The first tughra examples are from the 14th century. Tughras served a purpose similar to the cartouche in ancient Egypt or the Royal Cypher of British monarchs. Every Ottoman sultan had his own individual tughra. Etymology There are two main schools of thought on the origins of the word tughra. The first sees it derived from a Turkic languages, Turkic secret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Cypher
In modern heraldry, a royal cypher is a monogram or monogram-like device of a country's reigning Monarch, sovereign, typically consisting of the initials of the monarch's name and title, sometimes interwoven and often surmounted by a Crown (heraldry), crown. Such a cypher as used by an emperor or empress is called an imperial cypher. Royal cyphers appear on some government buildings, impressed upon royal and state documents, and are used by Ministry (government department), governmental departments. They may also appear on other governmental structures built under a particular ruler. Commonwealth realms The use of a royal cypher in the Commonwealth realms originated in the United Kingdom, where the public use of the royal initials dates at least from the early Tudor period, and was simply the initial of the sovereign with, after Henry VIII of England, Henry VIII's reign, the addition of the letter 'R' for or (Latin for "king" and "queen" respectively). The letter 'I' for was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rota (papal Signature)
The ''rota'' is one of the symbols used by the pope to authenticate documents such as papal bulls. It is a cross inscribed in two concentric circles. Pope Leo IX was the first pope to use it. The four inner quadrants contain: " ''Petrus''", " ''Paulus''", the pope's name, and the pope's ordinal number. The pope's autograph or motto is sometimes inscribed between the concentric circles. A ''rota'' was also used by monarchs for the authentication of documents and diplomas. See also * ''Signum manus'' * Tughra A tughra (; ) is a calligraphy, calligraphic monogram, Seal (emblem), seal or signature of a sultan that was affixed to all official documents and correspondence. Inspired by the Tamga, tamgha, it was also carved on his seal and stamped on the co ... * Khelrtva Notes References External links Examples of the rota Documents of the Catholic Church Seals (insignia) {{RC-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christogram
A Christogram () is a monogram or combination of letters that forms an abbreviation for the name of Jesus Christ, traditionally used as a Christian symbolism, religious symbol within the Christian Church. One of the oldest Christograms is the Chi-Rho (☧). It consists of the superimposed Greek letters Chi (letter), chi and Rho (letter), rho , which are the first two letters of the Greek , 'Christ'. It was displayed on the military standard used by Constantine I in 312 AD. The IX monogram () is a similar form, using the initials of the name , 'Jesus (the) Christ', as is the IH monogram, ΙΗ monogram (), using the first two letters of the name , 'JESUS' in uppercase. There were a very considerable number of variants of "Christograms" or monograms of Christ in use during the medieval period, with the boundary between specific monograms and mere scribal abbreviations somewhat fluid. The name ''Jesus'', spelt in Greek capitals, has the abbreviations ''IHS'' (also written ''JHS, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis The Pious
Louis the Pious (; ; ; 16 April 778 – 20 June 840), also called the Fair and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and Holy Roman Emperor, co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aquitaine from 781. As the only surviving son of Charlemagne and Hildegard (queen), Hildegard, he became the sole ruler of the Franks after his father's death in 814, a position that he held until his death except from November 833 to March 834, when he was deposed. During his reign in Aquitaine, Louis was charged with the defence of the empire's southwestern frontier. He Siege of Barcelona (801), conquered Barcelona from the Emirate of Córdoba in 801 and asserted Frankish authority over Pamplona and the Basques south of the Pyrenees in 812. As emperor, he included his adult sons, Lothair I, Lothair, Pepin I of Aquitaine, Pepin and Louis the German, Louis, in the government and sought to establish a suitable division of the realm among them. The first decade of his reig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian Empire from 800, holding these titles until his death in 814. He united most of Western Europe, Western and Central Europe, and was the first recognised emperor to rule from the west after the fall of the Western Roman Empire approximately three centuries earlier. Charlemagne's reign was marked by political and social changes that had lasting influence on Europe throughout the Middle Ages. A member of the Frankish Carolingian dynasty, Charlemagne was the eldest son of Pepin the Short and Bertrada of Laon. With his brother, Carloman I, he became king of the Franks in 768 following Pepin's death and became the sole ruler three years later. Charlemagne continued his father's policy of protecting the papacy and became its chief defender, remo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clovis II
Clovis II (633 – 657) was King of the Franks in Neustria and Burgundy, having succeeded his father Dagobert I in 639. His brother Sigebert III had been King of Austrasia since 634. He was initially under the regency of his mother Nanthild until her death in her early thirties in 642. Nanthild's death allowed Clovis to fall under the influence of the secular magnates, who reduced the royal power in their own favour; first Aega and then Erchinoald. The Burgundian mayor of the palace Flaochad used him to lure his rival, Willebad, to a battle in Autun, in which Willebad was killed. Background Clovis married Balthild, an Anglo-Saxon sold into slavery in Gaul. She had been owned by the Neustrian mayor of the palace, Erchinoald, but then attracted the interest of the king. They had three sons, who all became kings after his death. The eldest, Chlothar, succeeded him and his second eldest, Childeric, was placed on the Austrasian throne and eventually also succeeded in N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlothar II
Chlothar II, sometimes called "the Young" ( French: le Jeune), (May/June 584 – 18 October 629) was king of the Franks, ruling Neustria (584–629), Burgundy (613–629) and Austrasia (613–623). The son of Chilperic I and his third wife, Fredegund, he started his reign as an infant under the regency of his mother, who was in an uneasy alliance with Chlothar's uncle King Guntram of Burgundy, who died in 592. Chlothar took power upon the death of his mother in 597; though rich, his realm was one of the smallest portions of Francia. He continued his mother's feud with Queen Brunhilda with equal viciousness and bloodshed, finally achieving her execution by dismemberment in 613, after winning the battle that enabled Chlothar to unite Francia under his rule. Like his father, he built up his territories by seizing lands after the deaths of other kings. His reign was long by contemporary standards, but saw the continuing erosion of royal power to the French nobility and the church ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Gregory III
Pope Gregory III (; died 28 November 741) was the bishop of Rome from 11 February 731 to his death on 28 November 741. His pontificate, like that of his predecessor, was disturbed by Byzantine iconoclasm and the advance of the Lombards, in which he invoked the intervention of Charles Martel, although ultimately in vain. He was the last pope to seek the consent of the Byzantine exarch of Ravenna for his election, the last pope of Syrian origin, and the last pope born outside Europe until the election of Pope Francis 1,272 years later in 2013. Election Gregory was the son of a Syrian Christian named Ioannes, Yohannan or John. He was elected pope by popular acclamation on 11 February 731, but was not formally consecrated as bishop of Rome until 18 March, after having received the approval of the Byzantine exarch of Ravenna. He was the last pope to seek the exarch's ratification of a papal election. Anti-iconoclasm Immediately upon his accession, Gregory appealed to Emperor Leo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |