|
Siegfried Kasche
Siegfried Kasche (18 June 1903 – 7 June 1947) was a German Nazi Party politician who served as the ambassador of Nazi Germany to the Independent State of Croatia where he was complicit in the atrocities committed against Serbs, Jews and other ethnic groups. He was also an SA-''Obergruppenführer'' in the ''Sturmabteilung'' (SA), a Nazi paramilitary organization. He headed the SA agricultural settlement program to replace native populations in the occupied Polish territories with SA settlers. Kasche was proposed as the head of the '' Reichskommissariat Moskowien'' but, due to German military reversals, the ''Reichskommissariat'' was never established. Following the end of the Second World War, he was put on trial in Croatia, convicted of war crimes and hanged. Early life Kasche was born in Strausberg, the son of a physician. After graduating from the Victoria '' Gymnasium'' (today, the ), he attended cadet school in Potsdam and the '' Preußische Hauptkadettenanstalt'' milita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalitarianism, totalitarian dictatorship. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", referred to the Nazi claim that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which the Nazis referred to as the Thousand-Year Reich, ended in May 1945, after 12 years, when the Allies of World War II, Allies defeated Germany and entered the capital, Berlin, End of World War II in Europe, ending World War II in Europe. After Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany in 1933, the Nazi Party began to eliminate political opposition and consolidate power. A 1934 German referendum confirmed Hitler as sole ''Führer'' (leader). Power was centralised in Hitler's person, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freikorps
(, "Free Corps" or "Volunteer Corps") were irregular German and other European paramilitary volunteer units that existed from the 18th to the early 20th centuries. They effectively fought as mercenaries or private military companies, regardless of their own nationality. In German-speaking countries, the first so-called ("free regiments", ''Freie Regimenter'') were formed in the 18th century from native volunteers, enemy renegades, and deserters. These sometimes exotically equipped units served as infantry and cavalry (or, more rarely, as artillery); sometimes in just company strength and sometimes in formations of up to several thousand strong. There were also various mixed formations or legions. The Prussian included infantry, jäger, dragoons and hussars. The French '' Volontaires de Saxe'' combined uhlans and dragoons. In the aftermath of World War I and during the German Revolution of 1918–19, , consisting partially of World War I veterans, were raised as para ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichskommissariat Moskowien
Reichskommissariat Moskowien (RKM; ) was the civilian occupation-regime that Nazi Germany intended to establish in central and northern European Russia during World War II, one of several similar ''Reichskommissariate''. It was also known initially as the Reichskommissariat Rußland (), but was later renamed as part of German policies of partitioning the Russian state. Siegfried Kasche was the projected ''Reichskomissar'', but due to the Wehrmacht's failure to occupy the territories intended to form the ''Reichskommissariat'', it remained on paper only. Territorial planning The administrative capital was tentatively proposed as Moscow, the historical and political center of the Russian state. As the German armies were approaching the Soviet capital in the Operation Typhoon in the autumn of 1941, Hitler determined that Moscow, like Leningrad and Kiev, would be levelled and its 4 million inhabitants killed, to destroy it as a potential center of Bolshevist resistance. For this p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
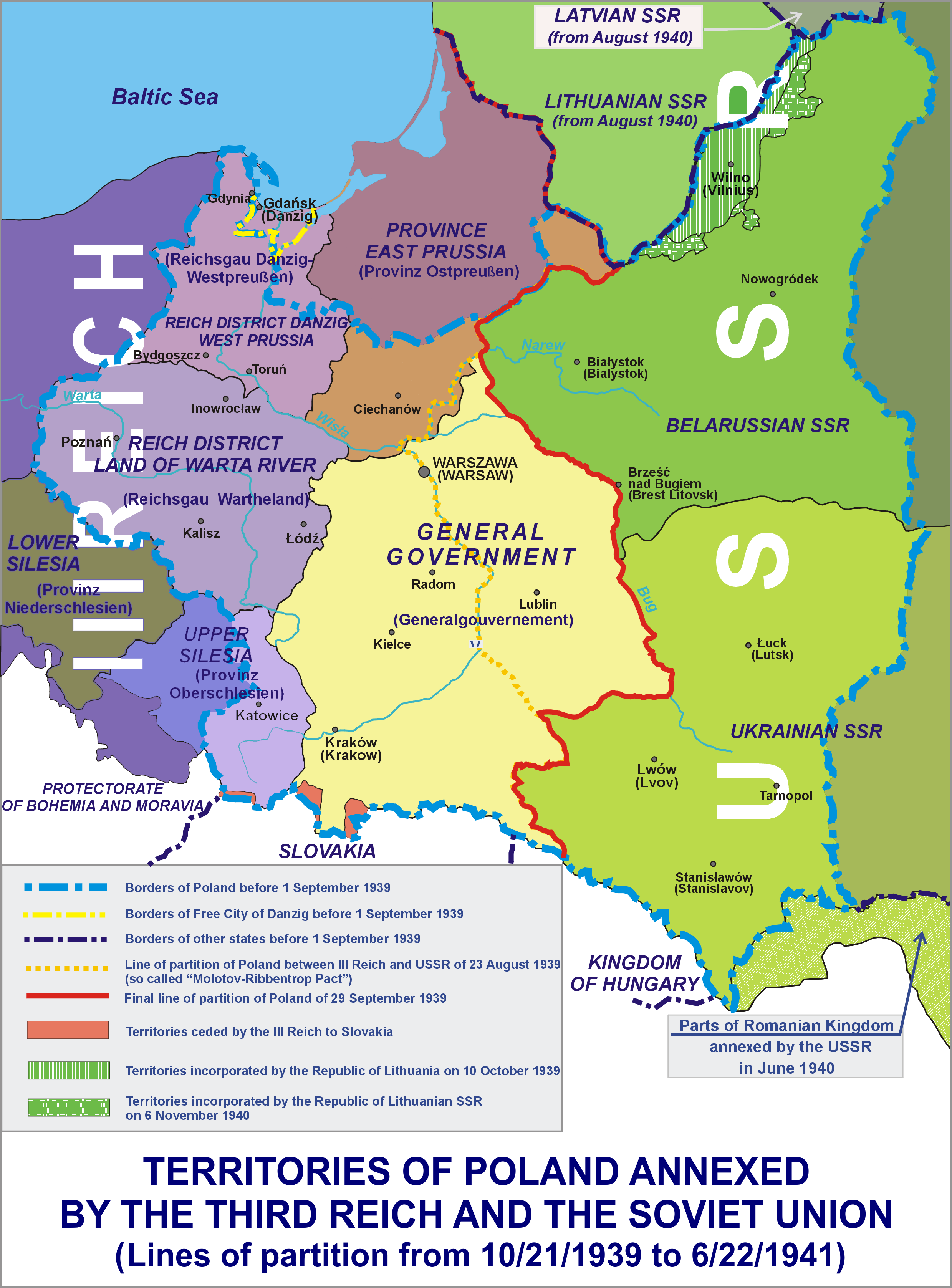
Polish Areas Annexed By Nazi Germany
Following the Invasion of Poland at the beginning of World War II, nearly a quarter of the entire territory of the Second Polish Republic was Areas annexed by Nazi Germany, annexed by Nazi Germany and placed directly under the German civil administration. The rest of Nazi-occupied Poland was renamed as the General Government district. The annexation was part of the Partition of Poland#"Fourth Partition", "fourth partition of Poland" by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union, outlined months before the invasion, in the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact.Maly Rocznik Statystyczny (wrzesien 1939 – czerwiec 1941), Ministerstwo Informacji i Documentacji, London 1941, p.5, as cited in Piotr Eberhardt, Political Migrations in Poland, 1939–1948, Warsaw 2006, p.4 Some smaller territories were incorporated directly into the existing Gau (administrative division), Gaue Gau East Prussia, East Prussia and Gau Silesia, Silesia, while the bulk of the land was used to create new ''Reichsgaue'' Reichsg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramilitary
A paramilitary is a military that is not a part of a country's official or legitimate armed forces. The Oxford English Dictionary traces the use of the term "paramilitary" as far back as 1934. Overview Though a paramilitary is, by definition, not a military, it is usually equivalent to a light infantry or special forces in terms of strength, firepower, and organizational structure. Paramilitaries use combat-capable kit/equipment (such as Internal security vehicle, internal security/SWAT vehicles), or even actual military equipment (such as Long gun, long guns and Armoured personnel carrier, armored personnel carriers; usually military surplus resources), skills (such as battlefield medicine and bomb disposal), and tactics (such as urban warfare and close-quarters combat) that are compatible with their purpose, often combining them with skills from other relevant fields such as law enforcement, coast guard, or search and rescue. A paramilitary may fall under the command of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sturmabteilung
The (; SA; or 'Storm Troopers') was the original paramilitary organisation under Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party of Germany. It played a significant role in Adolf Hitler's rise to power, Hitler's rise to power in the 1920s and early 1930s. Its primary purposes were providing protection for Nazi rallies and assemblies, disrupting the meetings of opposing parties, fighting against the paramilitary units of the opposing parties, especially the ''Roter Frontkämpferbund'' of the Communist Party of Germany (KPD) and the ''Reichsbanner Schwarz-Rot-Gold'' of the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD), and intimidating Romani people, Romani, trade unionists, and especially Jews. The SA were colloquially called Brownshirts () because of the colour of their Uniforms and insignia of the Sturmabteilung, uniform's shirts, similar to Benito Mussolini's Blackshirts. The official uniform of the SA was a brown shirt with a brown tie. The color came about because a large shipment of Paul von ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obergruppenführer
(, ) was a paramilitary rank in Nazi Germany that was first created in 1932 as a rank of the ''Sturmabteilung'' (SA) and adopted by the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) one year later. Until April 1942, it was the highest commissioned SS rank after only . Translated as "senior group leader", the rank of was senior to '' Gruppenführer''. A similarly named rank of existed in the SA from 1929 to 1930 and as a title until 1933. In April 1942, the new rank of was created which was above and below . Creation and history The rank of was created in 1932 by Ernst Röhm and was intended as a seniormost rank of the Nazi stormtroopers for use by Röhm and his top SA generals. In its initial concept, the rank was intended to be held by members of the ''Oberste SA-Führung'' (Supreme SA Command) and also by veteran commanders of certain ''SA-Gruppen'' (SA groups). Some of the early promotions to the rank included Ernst Röhm, Viktor Lutze, Edmund Heines, August Schneidhuber, and Frit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, religion, and community are highly interrelated, as Judaism is their ethnic religion, though it is not practiced by all ethnic Jews. Despite this, religious Jews regard Gerim, converts to Judaism as members of the Jewish nation, pursuant to the Conversion to Judaism, long-standing conversion process. The Israelites emerged from the pre-existing Canaanite peoples to establish Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Israel and Kingdom of Judah, Judah in the Southern Levant during the Iron Age.John Day (Old Testament scholar), John Day (2005), ''In Search of Pre-Exilic Israel'', Bloomsbury Publishing, pp. 47.5 [48] 'In this sense, the emergence of ancient Israel is viewed not as the cause of the demise of Canaanite culture but as its upshot'. Originally, J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Southeastern Europe who share a common Serbian Cultural heritage, ancestry, Culture of Serbia, culture, History of Serbia, history, and Serbian language, language. They primarily live in Serbia, Kosovo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Montenegro as well as in North Macedonia, Slovenia, Germany and Austria. They also constitute a significant diaspora with several communities across Europe, the Americas and Oceania. The Serbs share many cultural traits with the rest of the peoples of Southeast Europe. They are predominantly Eastern Orthodoxy, Eastern Orthodox Christians by religion. The Serbian language, Serbian language (a standardized version of Serbo-Croatian) is official in Serbia, co-official in Kosovo and Bosnia and Herzegovina, and is spoken by the plurality in Montenegro. Ethnology The identity of Serbs is rooted in Eastern Orthodoxy and traditions. In the 19th century, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambassador
An ambassador is an official envoy, especially a high-ranking diplomat who represents a state and is usually accredited to another sovereign state or to an international organization as the resident representative of their own government or sovereign or appointed for a special and often temporary diplomatic assignment. The word is also used informally for people who are known, without national appointment, to represent certain professions, activities, and fields of endeavor, such as sales. An ambassador is the ranking government representative stationed in a foreign capital or country. The host country typically allows the ambassador control of specific territory called an embassy (which may include an official residence and an office, chancery (diplomacy), chancery, located together or separately, generally in the host nation's capital), whose territory, staff, and vehicles are generally afforded diplomatic immunity in the host country. Under the Vienna Convention on Diplomati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Cross
The Baltic Cross (German: Das ''Baltenkreuz'') was a military decoration of the German Weimar Republic. It was created in 1919 by the Baltic National Committee (''Baltischer Nationalausschuss''), the political representation of German-Baltic population of southern Livonia and Courland (roughly equivalent to parts of modern Latvia). The Cross was awarded to officers, NCOs and men of the Baltic Landeswehr and voluntary groups who had fought in the Baltic states during 1918–19 for at least three months against the Bolshevik armies. Ceremonies are known from July 1919. The Baltic National Committee in Jelgava, in Courland (now in Latvia) issued numbered warrants for the award. A total of 21,839 Baltic Crosses were awarded. The Cross was accepted as a state-approved decoration of the German Reich on 16 May 1933 and was allowed to be worn. State approval was continued by the Federal Republic of Germany. The Baltic Cross is a black oxidised metal cross superimposed with a gilt cros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Cross
The Iron Cross (, , abbreviated EK) was a military decoration in the Kingdom of Prussia, the German Empire (1871–1918), and Nazi Germany (1933–1945). The design, a black cross pattée with a white or silver outline, was derived from the insignia of the medieval Teutonic Order and borne by its knights from the 13th century. As well as being a military medal, it has also been used as an emblem by the Prussian Army, the Imperial German Army, and the of the Weimar Republic, while the ''Balkenkreuz'' (bar cross) variant was used by the ''Wehrmacht''. The Iron Cross is now the emblem of the , the modern German armed forces. King Frederick William III of Prussia established the Iron Cross award on 17 March 1813 during the Napoleonic Wars (EK 1813). The award was backdated to the birthday (10 March) of his late wife, Louise of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, Queen Louise, who was the first person to receive it (posthumously). The Iron Cross was also awarded during the Franco-Prussian War ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |