|
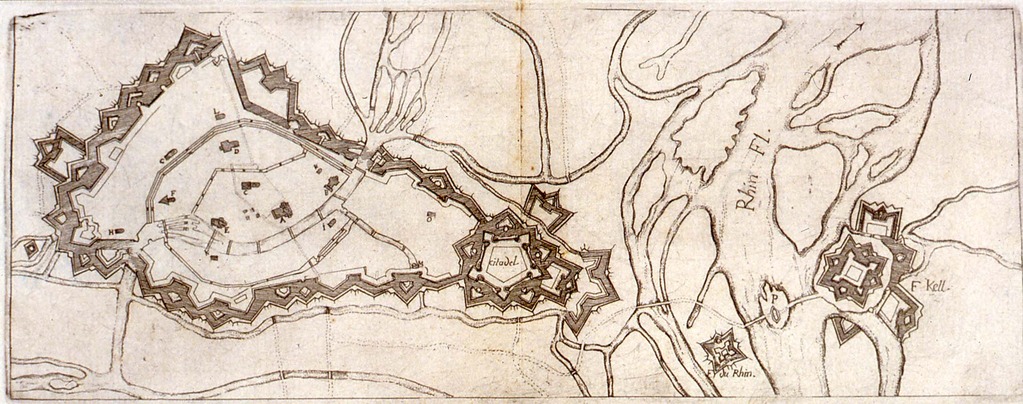
Siege Of Kehl (1796–1797)
The siege of Kehl lasted from 26 October 1796 to 9 January 1797. Habsburg and Duchy of Württemberg, Württemberg regulars numbering 40,000, under the command of Maximilian Anton Karl, Count Baillet de Latour, besieged and captured the French-controlled fortifications at the village of Kehl in the German state of Baden-Durlach. The fortifications at Kehl represented an important bridgehead crossing the Rhine to Strasbourg, an Alsace, Alsatian city and a French Revolutionary stronghold. This battle was part of the Rhine Campaign of 1796, in the French Revolutionary Wars, French Revolutionary War of the First Coalition. In the 1790s, the Rhine was wild, unpredictable, and difficult to cross, in some places more than four times wider than it is in the twenty-first century, even under non-flood conditions. Its channels and tributaries wound through marsh and meadow and created islands of trees and vegetation that were alternately submerged by floods or exposed during the dry seasons. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhine Campaign Of 1796
In the Rhine campaign of 1796 (June 1796 to February 1797), two First Coalition armies under the overall command of Archduke Charles, Duke of Teschen, Archduke Charles outmaneuvered and defeated two First French Republic, French Republican armies. This was the last campaign of the War of the First Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. The French military strategy against Austria called for a three-pronged invasion to surround Vienna, ideally capturing the city and forcing the Holy Roman emperor, Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor, Francis II, to surrender and accept French Revolutionary territorial integrity. The French assembled the Army of Sambre and Meuse commanded by Jean-Baptiste Jourdan against the Austrian Army of the Lower Rhine in the north. The Army of the Rhine and Moselle, led by Jean Victor Marie Moreau, opposed the Austrian Army of the Upper Rhine in the south. A third army, the Army of Italy (France), Army of Italy, commanded by Napoleon Bonaparte, app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Victor Marie Moreau
Jean Victor Marie Moreau (, 14 February 1763 – 2 September 1813) was a French general who helped Napoleon Bonaparte rise to power, but later became his chief military and political rival and was banished to the United States. He is among the foremost French generals in military history. Biography Rise to fame Moreau was born at Morlaix in Brittany. His father was a successful lawyer, and instead of allowing Moreau to enter the army, as he attempted to do, insisted on Moreau studying law at the University of Rennes. Young Moreau showed no inclination for law, but reveled in the freedom of student life. Instead of taking his degree, he continued to live with the students as their hero and leader, and formed them into a sort of army, which he commanded as their provost. When 1789 came, he commanded the students in the daily affrays which took place at Rennes between the young noblesse and the populace. In 1791, Moreau was elected a lieutenant colonel of the volunteers of Ill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Schliengen
At the Battle of Schliengen (24 October 1796), the French Army of the Rhine and Moselle under the command of Jean Victor Marie Moreau, Jean-Victor Moreau and the Austrian army under the command of Archduke Charles, Duke of Teschen, Archduke Charles of Austria both claimed victories. The village of Schliengen lies in the present-day Districts of Germany, Kreis Lörrach (district), Lörrach close to the border of present-day Baden-Württemberg (Germany), the Haut-Rhin (France), and the Canton of Basel-Stadt (Switzerland). During the French Revolutionary Wars, Schliengen was a strategically important location for the armies of both French First Republic, Republican France and Austrian monarchy, Habsburg Austria. Control of the area gave either combatant access to southwestern German states and important Rhine crossings. On 20 October Moreau retreated from Freiburg im Breisgau and established his army along a ridge of hills. The severe condition of the roads prevented Archduke Char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archduke Charles, Duke Of Teschen
Archduke Charles Louis John Joseph Lawrence of Austria, Duke of Teschen (; 5 September 177130 April 1847) was an Austrian field marshal, the third son of Emperor Leopold II and his wife, Maria Luisa of Spain. He was also the younger brother of Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor. He was epileptic, but achieved respect both as a commander and as a reformer of the Austrian army. He was considered one of Napoleon's most formidable opponents and one of the greatest generals of the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. He began his career fighting the revolutionary armies of France. Early in the wars of the First Coalition, he saw victory at Neerwinden in 1793, before being defeated at Wattignies in 1793 and Fleurus in 1794. In 1796, as chief of all Austrian forces on the Rhine, Charles defeated Jean-Baptiste Jourdan at Amberg, Würzburg and Limburg, and then won victories at Wetzlar, Emmendingen and Schliengen that forced Jean Victor Marie Moreau to withdraw across the Rhine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basel
Basel ( ; ), also known as Basle ( ), ; ; ; . is a city in northwestern Switzerland on the river Rhine (at the transition from the High Rhine, High to the Upper Rhine). Basel is Switzerland's List of cities in Switzerland, third-most-populous city (after Zurich and Geneva), with 177,595 inhabitants within the city municipality limits. The official language of Basel is Swiss Standard German and the main spoken language is the local Basel German dialect. Basel is commonly considered to be the cultural capital of Switzerland and the city is famous for its many Museums in Basel, museums, including the Kunstmuseum Basel, Kunstmuseum, which is the first collection of art accessible to the public in the world (1661) and the largest museum of Swiss art, art in Switzerland, the Fondation Beyeler (located in Riehen), the Museum Tinguely and the Museum of Contemporary Art (Basel), Museum of Contemporary Art, which is the first public museum of contemporary art in Europe. Forty museums ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hüningen
Huningue (; ; ) is a Communes of France, commune in the Haut-Rhin Departments of France, department of France. Huningue is a northern suburb of the Swiss city of Basel. It also borders Germany (Weil am Rhein, a suburb of Basel located in Germany). The main square of the town is the Place Abbatucci, named after the Corsican-born French general Jean Charles Abbatucci who unsuccessfully defended it in 1796 against the Austrians and died here. Huningue is noted for its pisciculture and is a major producer of fish eggs. History Huningue was first mentioned in a document in 826. Huningue was wrested from the Holy Roman Empire by the duke of Lauenburg in 1634 by the Treaty of Westphalia, and subsequently passed by purchase to Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV. Louis XIV tasked Vauban with the construction of Huningue Fortress, built by Jacques Tarade, Tarade from 1679 to 1681 together with a bridge across the Rhine. Construction of the fortress required the displacement of the population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Kehl (1796)
During the Battle of Kehl (23–24 June 1796), a First French Republic, Republican French force under the direction of Jean Charles Abbatucci mounted an amphibious crossing of the Rhine River against a defending force of soldiers from the Swabian Circle. In this action of the War of the First Coalition, the French drove the Swabians from their positions in Kehl and subsequently controlled the bridgehead on both sides of the Rhine. Although separated politically and geographically, the fates of Kehl, a village on the eastern shore of the Rhine in Baden-Durlach, and those of the Alsace, Alsatian city of Strasbourg, on the western shore, were united by the presence of bridges and a series of gates, fortifications and Barrage (dam), barrage dams that allowed passage across the river. In the 1790s, the Rhine was wild, unpredictable, and difficult to cross, in some places more than four or more times wider than it is in the twenty-first century, even under non-flood conditions. Its c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Polish Succession
The War of the Polish Succession (; 1733–35) was a major European conflict sparked by a civil war in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth over the succession to Augustus II the Strong, which the other European powers widened in pursuit of their own national interests. France and Spain, the two Bourbon powers, tested the power of the Austrian Habsburgs in Western Europe, as did the Kingdom of Prussia, whilst Saxony and Russia mobilized to support the eventual victor. The fighting in Poland–Lithuania resulted in the accession of Augustus III, who in addition to Russia and Saxony, was politically supported by the Habsburgs. The war's major military campaigns and battles occurred outside the borders of Poland–Lithuania. The Bourbons, supported by Charles Emmanuel III of Sardinia, moved against isolated Habsburg territories. In the Rhineland, France successfully took the Duchy of Lorraine, and in Italy, Spain regained control over the kingdoms of Naples and Sicily lost i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Kehl (1733)
The siege of Kehl (14–28 October 1733) was one of the opening moves of the French Rhineland campaign in the War of the Polish Succession, at the fortress town of Kehl in the upper Rhine River valley in the Holy Roman Empire. A large French army under the command of the Duke of Berwick besieged and captured the fortress, which was lightly garrisoned and in poor condition. Context On the death of Augustus II on 1 February 1733, the Polish throne was claimed by both his son, Augustus III, and by Stanislas I, father in law of Louis XV. Whilst a body double ostensibly left Brest by sea, Stanilas crossed Germany incognito and arrived at Warsaw on 8 September. On 12 September Stanislas was elected king of Poland by the diet. On his election Russia and Austria (backing Augustus III) invaded Poland. By 22 September Stanislas, who did not have a proper army, had to take refuge in Danzig (now known as Gdańsk), there to await the French help he had been promised. On 5 October, A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict fought between 1701 and 1714. The immediate cause was the death of the childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700, which led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between supporters of the French House of Bourbon, Bourbons and the Austrian House of Habsburg, Habsburgs. Charles had named as his heir Philip V of Spain, Philip of Anjou, a grandson of Louis XIV of France, whose claim was backed by Kingdom of France, France and most of Habsburg Spain, Spain. His Habsburg rival, Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor, Archduke Charles, was supported by the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Grand Alliance, whose primary members included Habsburg monarchy, Austria, the Dutch Republic, and Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain. Significant related conflicts include the Great Northern War (1700–1721) and Queen Anne's War (1702–1713). Although by 1701 Spain was no longer the predominant European power, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Kehl (1703)
The 1703 siege of Kehl was a military action of the War of the Spanish Succession, in which French and Spanish forces under the command of the Duc de Villars captured the fortress of the Holy Roman Empire at Kehl, opposite Strasbourg on the Rhine River The Rhine ( ) is one of the major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Swiss-Austrian border. From Lake Cons .... Siege operations began on 20 February 1703, following Villars's early departure from winter quarters. The fortress, defended by 3,500 troops of Louis William, the Margrave of Baden-Baden, capitulated on 10 March. References Battles of the War of the Spanish Succession Sieges involving France Sieges involving the Holy Roman Empire Conflicts in 1703 Sieges of the War of the Spanish Succession Military history of Baden-Württemberg {{France-battle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |