|
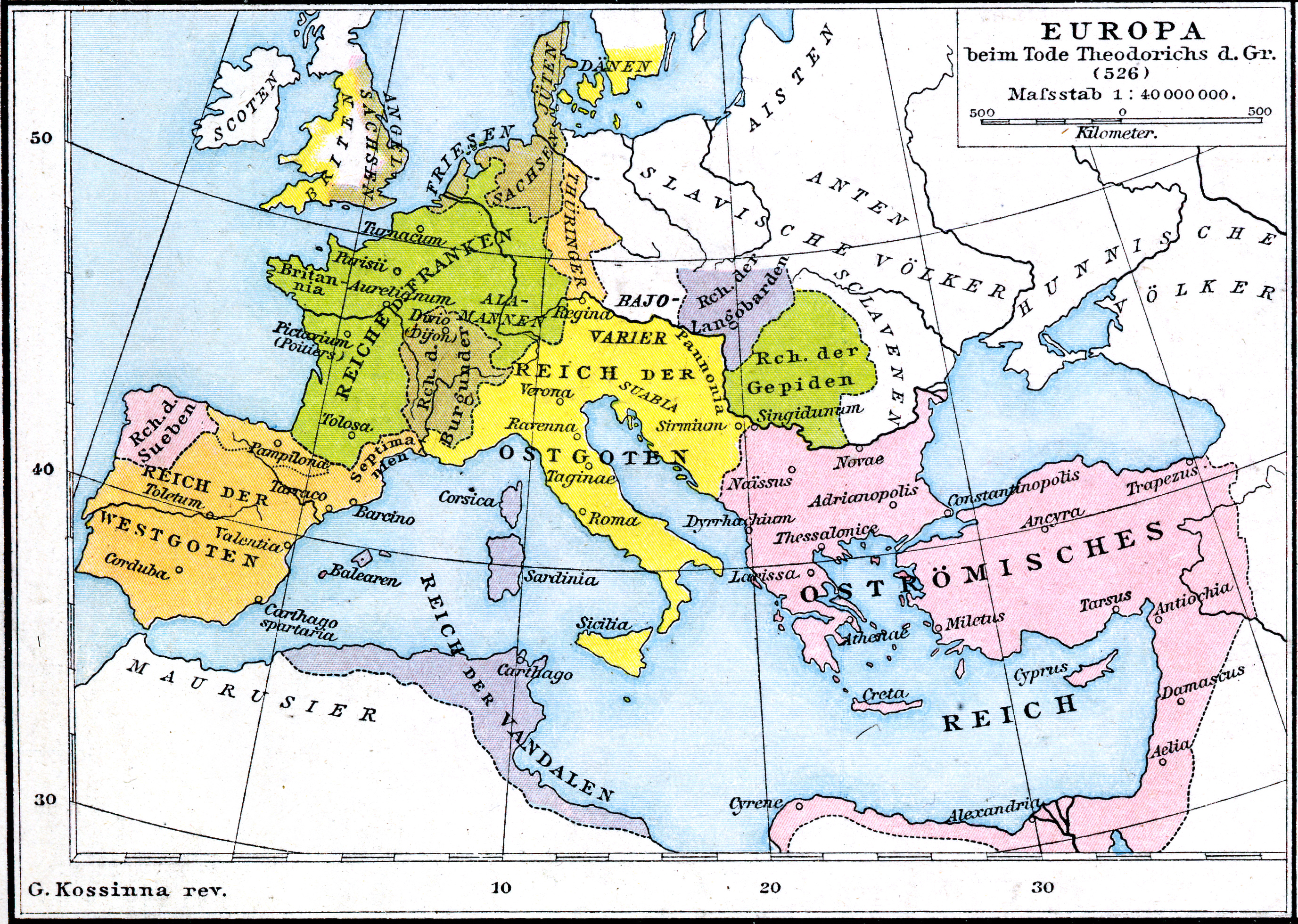
Siege Of Arles (507–508)
The siege of Arles between 507 and 508 was a battle between the Franks and Burgundians, who wanted to occupy Provence, and the Visigothic Kingdom, who had the support of the Ostrogothic Kingdom. Background After the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, the Franks created their own kingdom under the Merovingian dynasty, and wanted to expel the Visigoths from Gaul for their Arianism. Aided by the Catholic clergy and the Gallic populations dominated by the Arian Visigoths and Burgundians, Clovis I decided to attack the Kingdom of the Burgundians in 500. After the severe defeat at the Battle of Dijon, Gundobad left the city and fled south, pursued by Clovis and Godegisel, leaving Lyons and Vienne to Clovis. He finally waited for him at Avignon, where he was besieged and signed peace in return for paying tribute and yielding Vienne to his brother. But he was finally defeated and killed by his rival, when he attacked the capital in 502. Siege Probably in the autumn of 507, when re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arles
Arles ( , , ; ; Classical ) is a coastal city and Communes of France, commune in the South of France, a Subprefectures in France, subprefecture in the Bouches-du-Rhône Departments of France, department of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France, region, in the former Provinces of France, province of Provence. A large part of the Camargue, the largest wetlands in France, is located within the territory of the commune, which is the List of French communes by surface area, largest in Metropolitan France in terms of geographic territory. In non-metropolitan France, Maripasoula in French Guiana is the largest French commune in general. The commune's land area is roughly similar to that of Singapore. The city has a long history, and was of considerable importance in the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis. The Arles, Roman and Romanesque Monuments, Roman and Romanesque Monuments of Arles were listed as UNESCO World Heritage Sites in 1981 for their testimony to the his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arian
Arianism (, ) is a Christological doctrine which rejects the traditional notion of the Trinity and considers Jesus to be a creation of God, and therefore distinct from God. It is named after its major proponent, Arius (). It is considered heretical by most modern mainstream branches of Christianity. It is held by a minority of modern denominations, although some of these denominations hold related doctrines such as Socinianism, and some shy away from use of the term Arian due to the term's historically negative connotations. Modern denominations sometimes connected to the teaching include Jehovah's Witnesses, some individual churches within the Churches of Christ (including the movement's founder Barton W. Stone), as well as some Hebrew Roots Christians and Messianic Jews (although many Messianic Jews also follow Nicene Christianity). It is first attributed to Arius (), a Christian presbyter who preached and studied in Alexandria, Egypt, although it developed out of vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodoric The Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal, was king of the Ostrogoths (475–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy between 493 and 526, regent of the Visigoths (511–526), and a patrician (ancient Rome)#Late Roman and Byzantine period, patrician of the Byzantine Empire#Loss of the Western Roman Empire, Eastern Roman Empire. As ruler of the combined Gothic realms, Theodoric controlled an empire stretching from the Atlantic Ocean to the Adriatic Sea. Though Theodoric himself only used the title 'king' (''rex''), some scholars characterize him as a Roman Emperor#Later assertions to the title, Western Roman emperor in all but name, since he ruled a large part of the former Western Roman Empire described as a ''Res Publica'', had received the former Western imperial regalia from Constantinople in 497 which he used, was referred to by the imperial title ''princeps'' by the Italian aristocracy and exercised imper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septimania
Septimania is a historical region in modern-day southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of '' Gallia Narbonensis'' that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septimania was ceded to their king, Theodoric II. During the Early Middle Ages, the region was variously known as Gallia Narbonensis, Gallia, or Narbonensis. The territory of Septimania roughly corresponds with the modern French former administrative region of Languedoc-Roussillon that merged into the new administrative region of Occitanie. In the Visigothic Kingdom, which became centred on Toledo by the end of the reign of Leovigild, Septimania was both an administrative province of the central royal government and an ecclesiastical province whose metropolitan was the Archbishop of Narbonne. Originally, the Goths may have maintained their hold on the Albigeois, but if so it was conquered by the time of Chilperic I. There is archaeological evidence that some enclaves of Visi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avignon
Avignon (, , ; or , ; ) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Vaucluse department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region of southeastern France. Located on the left bank of the river Rhône, the Communes of France, commune had a population of 93,671 as of the census results of 2017, with about 16,000 (estimate from Avignon's municipal services) living in the ancient town centre enclosed by its Walls of Avignon, medieval walls. It is Functional area (France), France's 35th-largest metropolitan area according to INSEE with 337,039 inhabitants (2020), and France's 13th-largest urban unit with 459,533 inhabitants (2020). Its urban area was the fastest-growing in France from 1999 until 2010 with an increase of 76% of its population and an area increase of 136%. The Communauté d'agglomération du Grand Avignon, a cooperation structure of 16 communes, had 197,102 inhabitants in 2022. Between 1309 and 1377, during the Avignon Papacy, seven successive popes resided in Avi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vienne, Isère
Vienne (; ) is a town in southeastern France, located south of Lyon, at the confluence of the Gère and the Rhône. It is the fourth-largest commune in the Isère department, of which it is a subprefecture alongside La Tour-du-Pin. Vienne was a major centre of the Roman Empire under the Latin name ''Vienna''. Vienne was the capital of the Allobroges, a Gallic people, before its conquest by the Romans. Transformed into a Roman colony in 47 BC under Julius Caesar, it became a major urban centre, ideally located along the Rhône, then a major axis of communication. Emperor Augustus banished Herod the Great's son, the ethnarch Herod Archelaus to Vienne in 6 AD. As Vienne was a Roman provincial capital, remains of Roman constructions are still widespread across it. The city was also an important early bishopric in Christian Gaul. Its most famous bishop was Avitus of Vienne. At the Council of Vienne, which was convened there in October 1311, Pope Clement V abolished the or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyons
Lyon (Franco-Provençal: ''Liyon'') is a city in France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, to the northwest of the French Alps, southeast of Paris, north of Marseille, southwest of Geneva, Switzerland, northeast of Saint-Étienne. The City of Lyon is the List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, third-largest city in France with a population of 522,250 at the Jan. 2021 census within its small municipal territory of , but together with its suburbs and exurbs the Lyon Functional area (France), metropolitan area had a population of 2,308,818 that same year, the second largest in France. Lyon and 58 suburban municipalities have formed since 2015 the Lyon Metropolis, Metropolis of Lyon, a directly elected metropolitan authority now in charge of most urban issues, with a population of 1,424,069 in 2021. Lyon is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes Regions of France, region and seat of the Departmental co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Godegisel
Godegisel (? – 501) was a Burgundian sub-king and son of the Burgundian king Gondioc. Godegisel was the educator and uncle of Clotilde, wife of the Frankish king Clovis I. Beginning in 463 he was a sub-king of Kingdom of the Burgundians. With the help of Clovis, Godegisel attempted to become the king of all the Kingdom of the Burgundians by eliminating his brother Gundobad. Gundobad had previously seized the rest of the kingdom after the assassination of their brother Chilperic II, the father of Clotilde. With the promise of annual tribute and territorial cessions, Clovis agreed to aid Godegisel, and in 500 (or 501) Clovis entered the Burgundian territory, compelling Gundobad to march against the invaders and request his brother's aid. When the armies arrived outside of Dijon, Gundobad found himself fighting both the Franks and his brother. Defeated, Gundobad fled to Avignon, while Godigisel retired to Vienne. Clovis followed Gundobad to Avignon and began besieging it, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dijon
Dijon (, ; ; in Burgundian language (Oïl), Burgundian: ''Digion'') is a city in and the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Côte-d'Or Departments of France, department and of the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté Regions of France, region in eastern France. the Communes of France, commune had a population of 156,920. The earliest archaeological finds within the city limits of Dijon date to the Neolithic Period (geology), period. Dijon later became a Roman Empire, Roman settlement named ''Divio'', located on the road between Lyon and Paris. The province was home to the Duke of Burgundy, Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th centuries, and Dijon became a place of tremendous wealth and power, one of the great European centres of art, learning, and science. The city has retained varied architectural styles from many of the main periods of the past millennium, including Capetian, Gothic architecture, Gothic, and Renaissance architecture, Renaissance. Many still-i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gundobad
Gundobad (; ; 452 – 516) was King of the Burgundians (473–516), succeeding his father Gundioc of Burgundy. Previous to this, he had been a patrician of the moribund Western Roman Empire in 472–473, three years before its collapse, succeeding his uncle Ricimer. He is perhaps best known today as the probable issuer of the '' Lex Burgundionum'' legal codes, which synthesized Roman law with ancient Germanic customs. He was the husband of Caretene. Early life Gundobad seized the title of Patrician when his uncle Ricimer, who had been the power behind the throne for the Western Empire, died on 18 August 472. According to John of Antioch, Gundobad had previously executed the deposed emperor Anthemius on his uncle's orders. Once in power, Gundobad elevated the current , Glycerius, to the position of Roman emperor in the West. However, not long after this, Gundobad left for Burgundy where his father, Gundioc, had died; the exact date is unclear, with authorities stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |