|
Siberion
''Siberion'' is an extinct genus of lobopodian from the Sinsk biota of Russia. Its anatomy, including the proboscis-like organ projecting from the face and prominent grasping first pair of appendages, suggests that xenusians like this organism may have been phylogenetically related to anomalocaridids, like ''Anomalocaris ''Anomalocaris'' (from Ancient Greek , meaning "unlike", and , meaning "shrimp", with the intended meaning "unlike other shrimp") is an extinct genus of radiodont, an order of early-diverging stem-group marine arthropods. It is best known fro ...''. Only two incomplete specimens are known, and the probability of finding more is low, as the Sinsk Algal Lens has been nearly destroyed by commercial fossil collectors. Morphology It is similar to other siberiids, however it is distinguished by the shape of its “tail” and body. The holotype preserves most of the body, however the appendages and head are incomplete. Its body is annulated, and while the hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
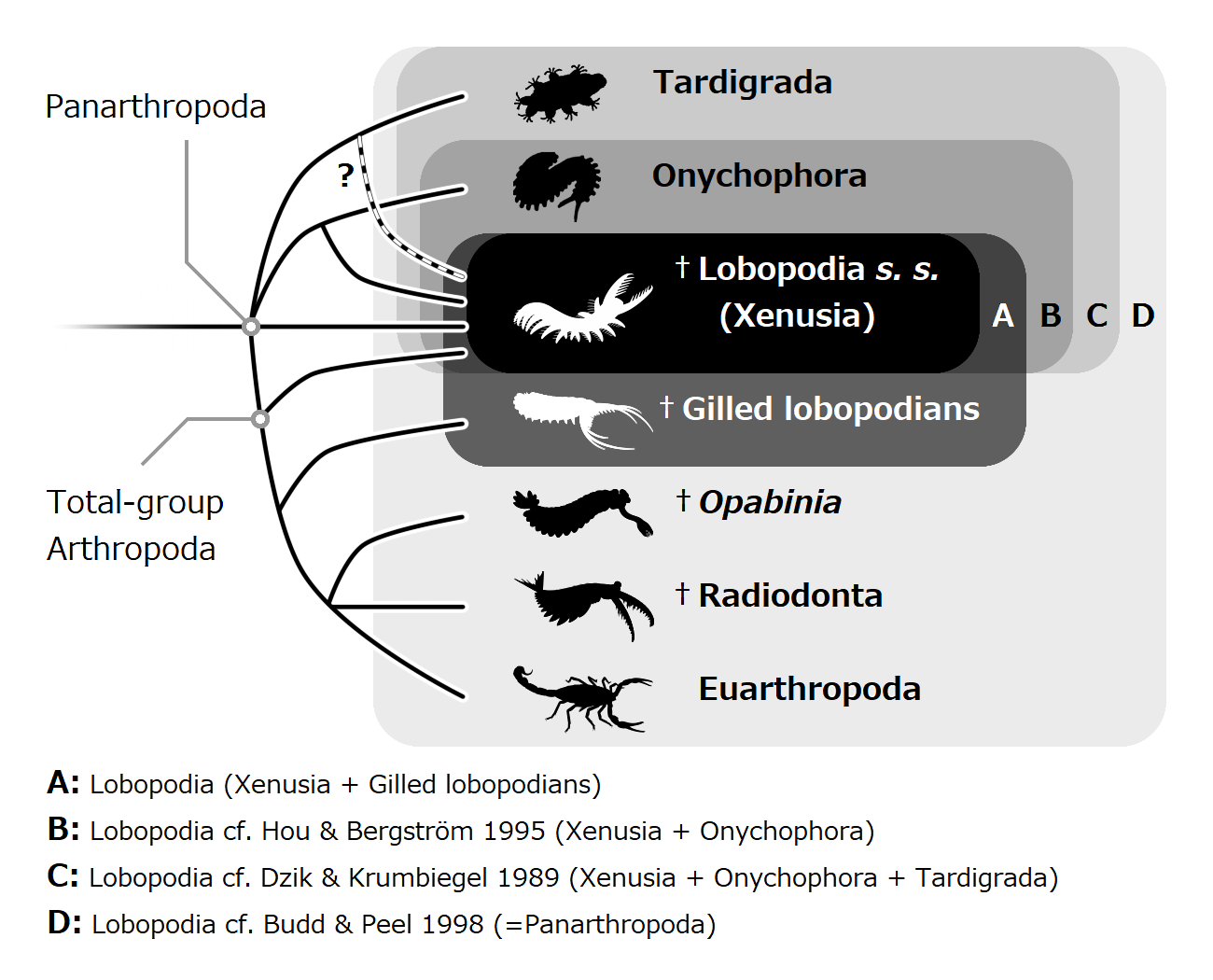
Lobopodian
Lobopodians are members of the informal group Lobopodia (), or the formally erected phylum Lobopoda Cavalier-Smith (1998). They are panarthropods with stubby legs called lobopods, a term which may also be used as a common name of this group as well. While the definition of lobopodians may differ between literatures, it usually refers to a group of soft-bodied, marine worm-like fossil panarthropods such as ''Aysheaia'' and ''Hallucigenia''. However, other genera like ''Kerygmachela'' and ''Pambdelurion'' (which have features similar to other groups) are often referred to as “gilled lobopodians”. The oldest near-complete fossil lobopodians date to the Lower Cambrian; some are also known from Ordovician, Silurian and Carboniferous Lagerstätten. Some bear toughened claws, plates or spines, which are commonly preserved as small carbonaceous fossil, carbonaceous or Small Shelly Fossils, mineralized microfossils in Cambrian strata. The grouping is considered to be paraphyletic, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lobopodia
Lobopodians are members of the informal group Lobopodia (), or the formally erected phylum Lobopoda Cavalier-Smith (1998). They are panarthropods with stubby legs called lobopods, a term which may also be used as a common name of this group as well. While the definition of lobopodians may differ between literatures, it usually refers to a group of soft-bodied, marine worm-like fossil panarthropods such as '' Aysheaia'' and '' Hallucigenia''. However, other genera like '' Kerygmachela'' and '' Pambdelurion'' (which have features similar to other groups) are often referred to as “gilled lobopodians”. The oldest near-complete fossil lobopodians date to the Lower Cambrian; some are also known from Ordovician, Silurian and Carboniferous Lagerstätten. Some bear toughened claws, plates or spines, which are commonly preserved as carbonaceous or mineralized microfossils in Cambrian strata. The grouping is considered to be paraphyletic, as the three living panarthropod groups (A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberiida
Siberiidae is a family of Cambrian lobopodians, sometimes called "jianshanopodians" or "giant lobopodians". Morphology Siberiids often reach large sizes, achieving as much as 22 cm, or even over 30 cm in length as seen in ''Jianshanopodia''. Cephalon The anterior of the Cephalon (arthropod head), cephalon is blunt, prominent appendages equipped with Arthropod leg, endites protrude laterally from it. In the case of ''Megadictyon'' the appendages terminate with sclerotized spines. The bottom of the head exposes an oral opening surrounded by an array of layers of plates and teeth which has been compared to the oral cones of Radiodonta, radiodonts; the pharynx houses numerous pharyngeal teeth, and has been compared to that of Priapulida, priapulids. No eyes have been observed. Limbs Siberiids bear stout, unarthropodized, annulated limbs called lobopods. They bear gill-like papillae protruding dorsally from the series of annuli; These papillae were weakly sclerotized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinocaridida
DinocarididaGreek for ''deinos'' "terrible" and Latin for ''caris'' "crab" – sometimes informally spelt Dinocarida, but the second 'id' is linguistically correct – see is a proposed fossil taxon of basal arthropods, which flourished during the Cambrian period and survived up to Early Devonian. Characterized by a pair of frontal appendages and series of body flaps, the name of Dinocaridids (Greek for ''deinos'' "terrible" and Latin for ''caris'' "crab") refers to the suggested role of some of these members as the largest marine predators of their time. Dinocaridids are occasionally referred to as the 'AOPK group' by some literatures, as the group composed of Radiodonta (''Anomalocaris'' and relatives), Opabiniidae (''Opabinia'' and relatives), and the "gilled lobopodians" ''Pambdelurion'' and Kerygmachelidae. It is most likely paraphyletic, with Kerygmachelidae and ''Pambdelurion'' more basal than the clade compose of Opabiniidae, Radiodonta and other arthropods. Anatomy D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinsk Biota
The Sinsk Formation is a geologic formation in Central Siberia, Russia, exposed along the Lena River. It preserves fossils dating back to the Botomian stage of the Cambrian (corresponding to Cambrian Series 2). It notably contained the Sinsk Algal Lens, a Lagerstätte A Fossil-Lagerstätte (, from ''Lager'' 'storage, lair' '' Stätte'' 'place'; plural ''Lagerstätten'') is a sedimentary deposit that preserves an exceptionally high amount of palaeontological information. ''Konzentrat-Lagerstätten'' preserv ... which preserved some soft-bodied animals that would not typically be preserved as fossils. However, the Sinsk Algal Lens has largely been destroyed by commercial fossil collectors. Paleobiota After Ivantsov et al., 2005 Paleobiota See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Russia References External links * Geologic formations of Russia Cambrian Asia {{Cambrian-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Cambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period 486.85 Ma. Most of the continents lay in the southern hemisphere surrounded by the vast Panthalassa Ocean. The assembly of Gondwana during the Ediacaran and early Cambrian led to the development of new convergent plate boundaries and continental-margin arc magmatism along its margins that helped drive up global temperatures. Laurentia lay across the equator, separated from Gondwana by the opening Iapetus Ocean. The Cambrian marked a profound change in life on Earth; prior to the Period, the majority of living organisms were small, unicellular and poorly preserved. Complex, multicellular organisms gradually became more common during the Ediacaran, but it was not until the Cambrian that fossil diversity seems to rapidly in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animalia
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are motility, able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Animals form a clade, meaning that they arose from a single common ancestor. Over 1.5 million extant taxon, living animal species have been species description, described, of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates. It has been estimated there are as many as 7.77 million animal species on Earth. Animal body lengths range from to . They have complex ecologies and biological interaction, interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and recover. As a species' potential Range (biology), range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxon, Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the Fossil, fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. Over five billion species are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryotes globally, possibly many times more if microorganisms are included. Notable extinct animal species include Dinosaur, non-avian dinosaurs, Machairodontinae, saber-toothed cats, and mammoths. Through evolution, species arise through the process of specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. Phylogeneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders of Russia, land borders with fourteen countries. Russia is the List of European countries by population, most populous country in Europe and the List of countries and dependencies by population, ninth-most populous country in the world. It is a Urbanization by sovereign state, highly urbanised country, with sixteen of its urban areas having more than 1 million inhabitants. Moscow, the List of metropolitan areas in Europe, most populous metropolitan area in Europe, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, while Saint Petersburg is its second-largest city and Society and culture in Saint Petersburg, cultural centre. Human settlement on the territory of modern Russia dates back to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |