|
Shōryū-ji
Shōryū-ji (青龍寺 ''kana:'' しょうりゅうじ) is a Shingon Buddhist Temple located in Tosa, Kōchi, Japan. It is the 36th temple of the Shikoku Pilgrimage. The Honzon of worship at Shōryū-ji is Acala. History According to the temple records, the temple was founded by Kukai during the Kōnin era (810-824). Following his travels to China, upon returning to Japan with the knowledge that Kukai's teacher Huiguo had bestowed upon him, Kukai grasped his vajra, prayed that he had arrived in a land he was destined to, and threw it eastwards. Kukai sensed that the vajra he had thrown was inside a pine tree of the mountain Shōryū-ji is located on, and reported to Emperor Saga. During the 6th year of the Kounin era (815), remembering his master's teachings, Kukai founded the construction of Shoryu-ji, which shared the same name as his masters temple in Chang-an, Qinglong Temple (青龍寺). The Honzon Acala was chosen due to an experience Kukai had during a storm while ret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
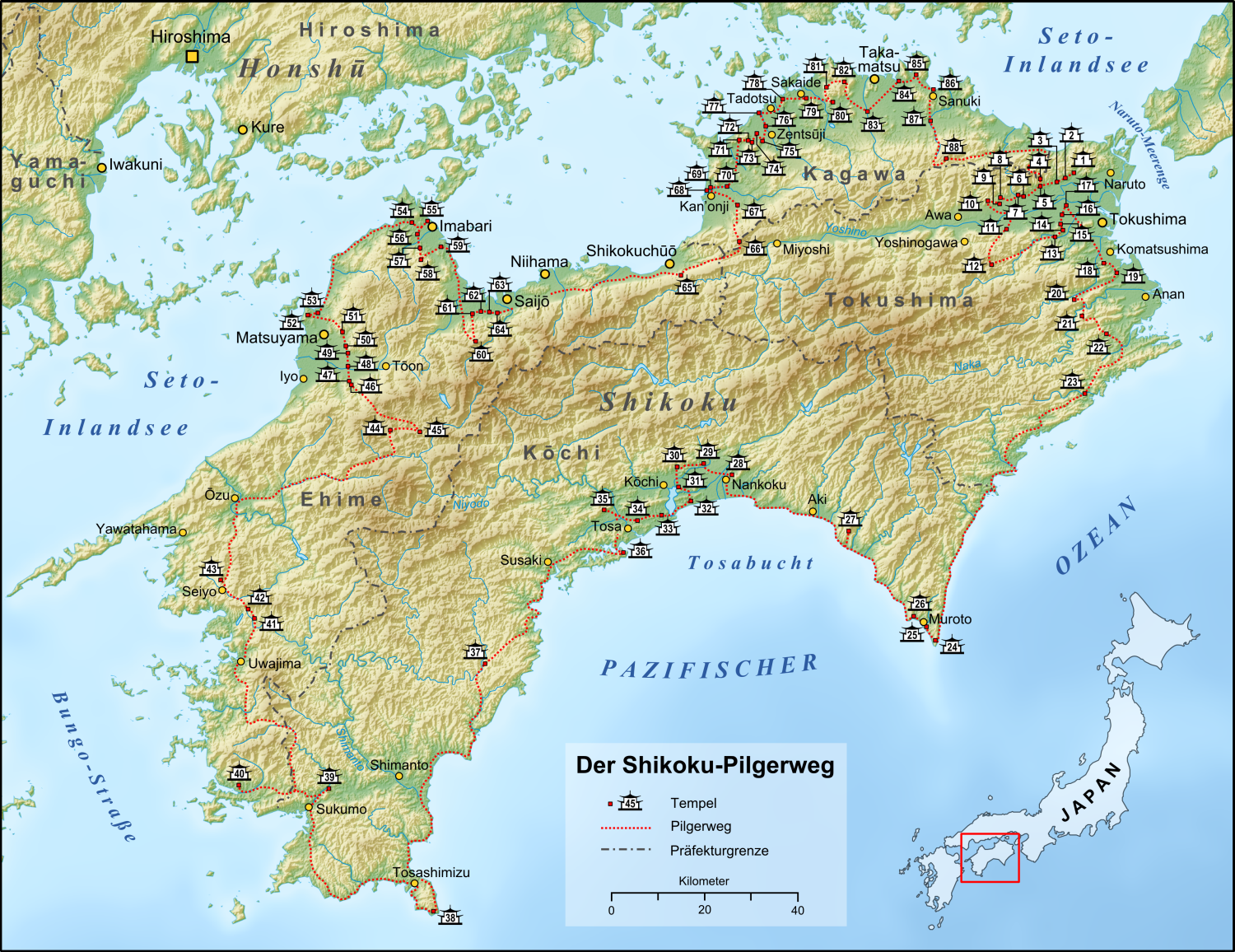
Shikoku Pilgrimage
The or is a multi-site pilgrimage of 88 temples associated with the Buddhist monk Kūkai (''Kōbō Daishi'') on the island of Shikoku, Japan. A popular and distinctive feature of the island's cultural landscape, and with a long history, large numbers of pilgrims, known as , still undertake the journey for a variety of ascetic, pious, and tourism-related purposes. The pilgrimage is traditionally completed on foot, but modern pilgrims use cars, taxis, buses, bicycles, or motorcycles, and often augment their travels with public transportation. The standard walking course is approximately long and can take anywhere from 30 to 60 days to complete. In addition to the 88 "official" temples of the pilgrimage, there are 20 ''bekkaku'' (別格) temples, which are officially associated with the Shikoku Pilgrimage (and hundreds more ''bangai'' (番外) temples, simply meaning "outside the numbers," which are not considered part of the official 88). To complete the pilgrimage, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tosa, Kōchi
file:仁淀川河口大橋.jpg, 270px, Niyodo River in Tosa file:Tosa city center area Aerial photograph.2014.jpg, 270px, Aerial view of Tosa city center is a Cities of Japan, city located in Kōchi Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 26,427 in 12,671 households and a population density of 290 persons per km2. The total area of the city is . The city of Tosa should not be confused with the historical Tosa Province, which covered all of modern-day Kōchi Prefecture. Geography Tosa is located in central Kōchi Prefecture on the southern coast of the island of Shikoku, and faces the Shikoku Mountains to the north and Pacific Ocean to the south. The Niyodo River flows through the Takaoka Plain in the town, where rice is grown. Surrounding municipalities Kōchi Prefecture *Hidaka, Kōchi, Hidaka *Ino, Kōchi, Ino *Kōchi (city) *Kōchi, Kōchi, Kōchi *Sakawa, Kōchi, Sakawa *Susaki, Kōchi, Susaki Climate Tosa has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen ''Cf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kōchi Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located on the island of Shikoku. Kōchi Prefecture has a population of 669,516 (1 April 2023) and has a geographic area of 7,103 km2 (2,742 sq mi). Kōchi Prefecture borders Ehime Prefecture to the northwest and Tokushima Prefecture to the northeast. Kōchi is the capital and largest city of Kōchi Prefecture, with other major cities including Nankoku, Shimanto, and Kōnan. Kōchi Prefecture is located on Japan's Pacific coast surrounding a large bay in the south of Shikoku, with the southernmost point of the island located at Cape Ashizuri in Tosashimizu. Kōchi Prefecture is home to Kōchi Castle, considered the most intact Japanese castle, and the Shimanto River, one of the few undammed rivers in Japan. History Antiquity Before the Ritsuryō System In the Kujiki, first recorded governments in Kōchi Prefecture were Hata (in the west) and Tosa (in the center). Hata was established first, so it is thought that it had more influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Saga
was the 52nd emperor of Japan, Emperor Saga, Saganoyamanoe Imperial Mausoleum, Imperial Household Agency according to the traditional order of succession. Saga's reign lasted from 809 to 823. Traditional narrative Saga was the second son of Emperor Kanmu and Fujiwara no Otomuro. Brown and Ishida, p. 280. His personal name was . Saga was an "accomplished calligrapher" able to compose in Chinese who held the first imperial poetry competitions (). According to legend, he was the first Japanese emperor to drink tea. Saga is traditionally venerated at his tomb; the Imperial Household Agency designates , in Ukyō-ku, Kyoto, as the location of Saga's mausoleum. Events of Saga's life * 806 Saga became the crown prince at age 21. * June 17, 809 (): In the 4th year of Emperor Heizei's reign, he fell ill and abdicated; and the succession (''senso'') was received by Kanmu's second son Saga, the eldest son having become a Buddhist priest. Shortly thereafter, Emperor Saga is said to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist Temples In Japan
Buddhist temples or monasteries are (along with Shinto shrines) the most numerous, famous, and important religious buildings in Japan.The term "Shinto shrine" is used in contrast to "Buddhist temple" to mirror the distinction made in Japanese between Shinto and Buddhist religious structures. In Japanese the first are called , the second . The shogunates or leaders of Japan have made it a priority to update and rebuild Buddhist temples since the Azuchi–Momoyama period, Momoyama period (late 16th century). The Japanese language, Japanese word for a Buddhist monastery is (kanji, ''kun'' reading), and the same kanji also has the pronunciation ''ji'' (''on'' reading), so temple names frequently end in ''-dera'' (rendaku, voiced) or ''-ji''. Another ending, , is normally used to refer to minor temples. Examples of temple names that have these suffixes are Kiyomizu-dera, Enryaku-ji and Kōtoku-in. Etymology The Japanese word for a Buddhist temple, , was anciently also written phonetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shōhō
was a after '' Kan'ei'' and before '' Keian''. This period spanned the years from December 1644 through February 1648. The reigning emperor was .Titsingh, Isaac. (1834) ''Annales des empereurs du japon'', p. 412./ref> Change of era * 1644 : The era name was changed to Shōhō to mark the enthronement of the new emperor Go-Kōmyō. The previous era ended and a new one commenced in ''Kan'ei'' 21, on the 16th day of the 12th month.Hall, John Whitney. ''The Cambridge History of Japan.'' p. xx. Events of the ''Shōhō'' era * 1644 (''Shōhō 1''): The third major map of Japan was ordered by the Tokugawa Shogunate—the first having been completed in '' Keichō'' 10—at a scale of 1:432,000 (based on maps of the provinces drawn to a scale of 1:21,600).Traganeou, Jilly. (2004). ''The Tokaido Road: Traveling and Representation in Edo and Meiji Japan'', p. 230. * May 18, 1645 (''Shōhō 2, 23rd day of the 4th month''): The Shōgun was elevated the court role of . * June 13, 1645 ('' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamauchi Tadayoshi
Yamauchi or Yamanouchi (やまうち or やまのうち, lit. "inside mountains") is a Japanese surname. Either name is written in kanji as 山内 while Yamanouchi can also be written as 山ノ内. Notable people with the surname include: * Yamanouchi Toyoshige, 15th feudal lord of the Tosa domain * Yamauchi Kazutoyo, first feudal lord of the Tosa domain *Kenji Yamanouchi, eponymous founder of Yamanouchi Pharmaceutical Co., now part of Astellas Pharma * Don Yamauchi, American chef *Edwin M. Yamauchi, historian and biblical scholar * Fusajiro Yamauchi, founder of Nintendo **Sekiryo Yamauchi (born Sekiryo Kaneda), second president of Nintendo, son-in-law of Fusajiro Yamauchi **Hiroshi Yamauchi, third president of Nintendo, grandson of Fusajiro Yamauchi * Goiti Yamauchi, Japanese-Brazilian mixed martial artist *Kazunori Yamauchi, creator of the ''Gran Turismo'' videogame series *Mara Yamauchi, British long-distance runner *, Japanese rower *, Japanese long-distance runner *Wakako Yama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tosa Domain
The was a Han (Japan), feudal domain under the Tokugawa shogunate of Edo period Japan, controlling all of Tosa Province in what is now Kōchi Prefecture on the island of Shikoku. It was centered around Kōchi Castle, and was ruled throughout its history by the ''tozama daimyō'' Yamauchi clan. Many people from the domain played important roles in events of the late Edo period including Nakahama Manjirō, Sakamoto Ryōma, Yui Mitsue, Gotō Shōjirō, Itagaki Taisuke, Nakae Chōmin, and Takechi Hanpeita. Tosa Domain was renamed during the early Meiji period until it was dissolved in the abolition of the han system in 1871 and became Kōchi Prefecture. History At the end of the Sengoku period, the Chōsokabe clan ruled Tosa Province. The Chōsokabe had briefly controlled the entire island of Shikoku under Chōsokabe Motochika from 1583 until he was defeated by Toyotomi Hideyoshi in the Invasion of Shikoku (1585), Invasion of Shikoku in 1585. Motochika fought for Hideyoshi in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edo Period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characterized by prolonged peace and stability, urbanization and economic growth, strict social order, Isolationism, isolationist foreign policies, and popular enjoyment of Japanese art, arts and Culture of Japan, culture. In 1600, Tokugawa Ieyasu prevailed at the Battle of Sekigahara and established hegemony over most of Japan, and in 1603 was given the title ''shogun'' by Emperor Go-Yōzei. Ieyasu resigned two years later in favor of his son Tokugawa Hidetada, Hidetada, but maintained power, and defeated the primary rival to his authority, Toyotomi Hideyori, at the Siege of Osaka in 1615 before his death the next year. Peace generally prevailed from this point on, making samurai largely redundant. Tokugawa sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinglong Temple (Xi'an)
Qinglong Temple (), also known as Shifo Temple (), is a Buddhist temple located in Xi'an, Shaanxi, China. In the mid-Tang dynasty (618–907), Huiguo taught Vajrayana at the temple, his Japanese disciple Kūkai introduced it to Japan, since then, Qinglong Temple became the cradle of Vajrayana of both Chinese and Japanese Buddhism. Qinglong Temple was completely damaged in 1086 during the Northern Song dynasty (960–1127) and gradually it became unknown to public, the nascent version was completed in the 1980s with Tang dynasty architectural style. History Sui dynasty Qinglong Temple traces its origins to the former Linggan Temple (), which was established in 582, at the dawn of Sui dynasty (581–618). Tang dynasty In 662, namely the 2nd year of Longshuo period of Emperor Gaozong of Tang dynasty (618–907), Princess Chengyang was sick, monk Falang () prayed to Buddha to bless the princess. When she recovered from her illness, she established the Guanyin Temple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huiguo
Huiguo () (746–805) was a Buddhist monk of Tang China who studied and taught Chinese Esoteric Buddhism, a Vajrayana tradition recently imported from India. Later Huiguo would become the teacher of Kūkai, founder of Shingon Buddhism, a prominent school of Buddhism in Japan. Biography Huiguo was one of two Buddhist masters at Ximing Temple, the other being the Indian monk Prajñā. Huiguo began his study of Buddhism as a śrāmaṇera at age 9 under a senior disciple of Amoghavajra, a monk of the tantric tradition, eventually becoming a direct disciple. By age 22 in 766 CE, Huiguo was ordained as a monk and extensively studied the Womb Realm and Diamond Realm mandalas before being fully initiated into Vajrayana that same year by Amoghavajra. Succession In time, Huiguo's prominence attracted students from Korea, Central Asia and even Java Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
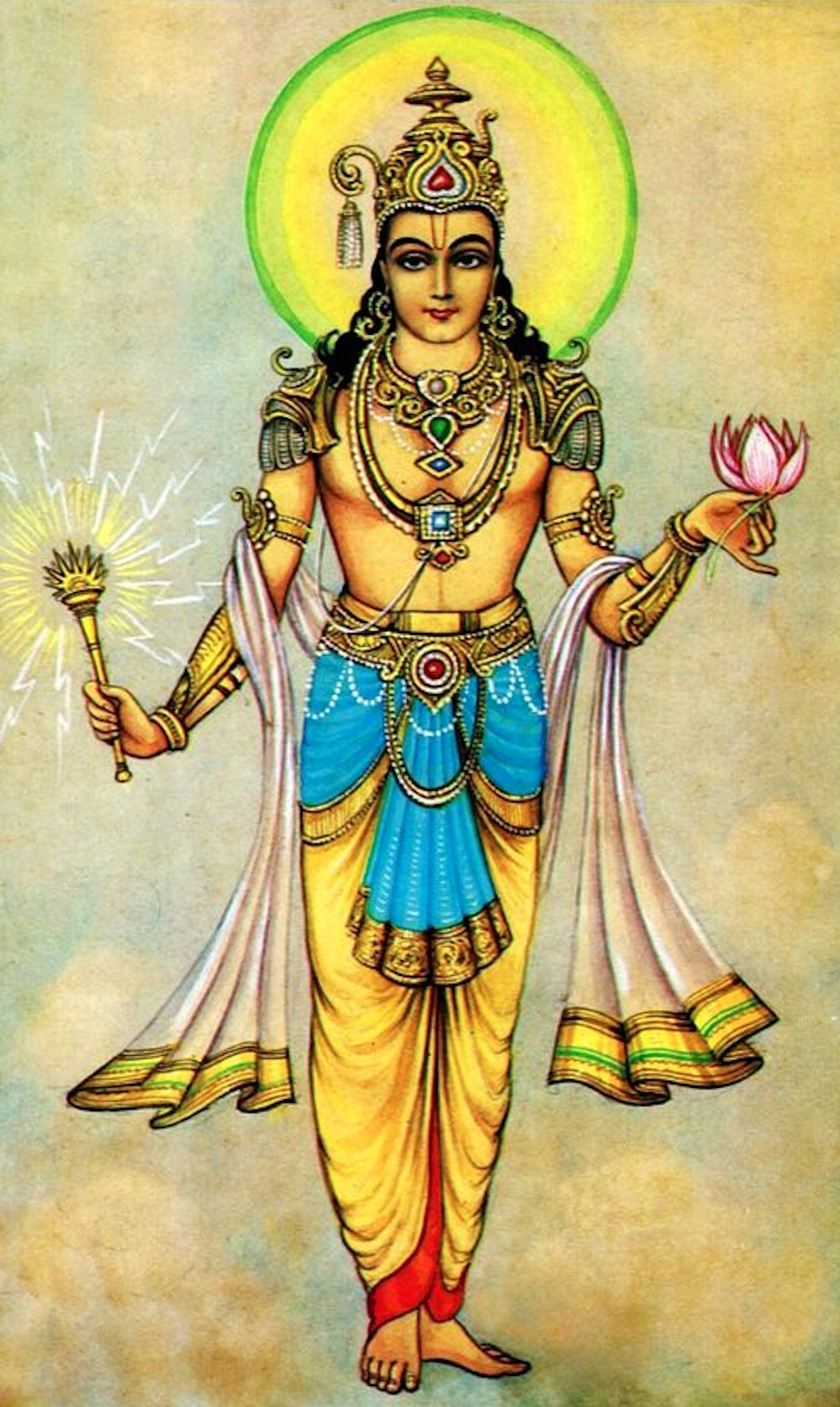
Vajra
The Vajra (, , ), is a legendary and ritualistic tool, symbolizing the properties of a diamond (indestructibility) and a thunderbolt (irresistible force). It is also described as a "ritual weapon". The use of the bell and vajra together as symbolic and ritual tools is found in all schools of Tibetan Buddhism. The vajra is a round, symmetrical metal scepter with two ribbed spherical heads. The ribs may meet in a ball-shaped top, or they may be separate and end in sharp points. The vajra is considered inseparable from the bell, and both are sold in dharma stores only in matching sets. The bell is also metal with a ribbed spherical head. The bell also depicts the face of Dhatvisvari, a female buddha and the consort of Akshobhya. The vajra has also been associated as the weapon of Indra, the Vedic king of the Deva (Hinduism), devas and Svarga, heaven. It is used symbolically by the dharma, dharmic traditions of Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism, often to represent firmness of spir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |