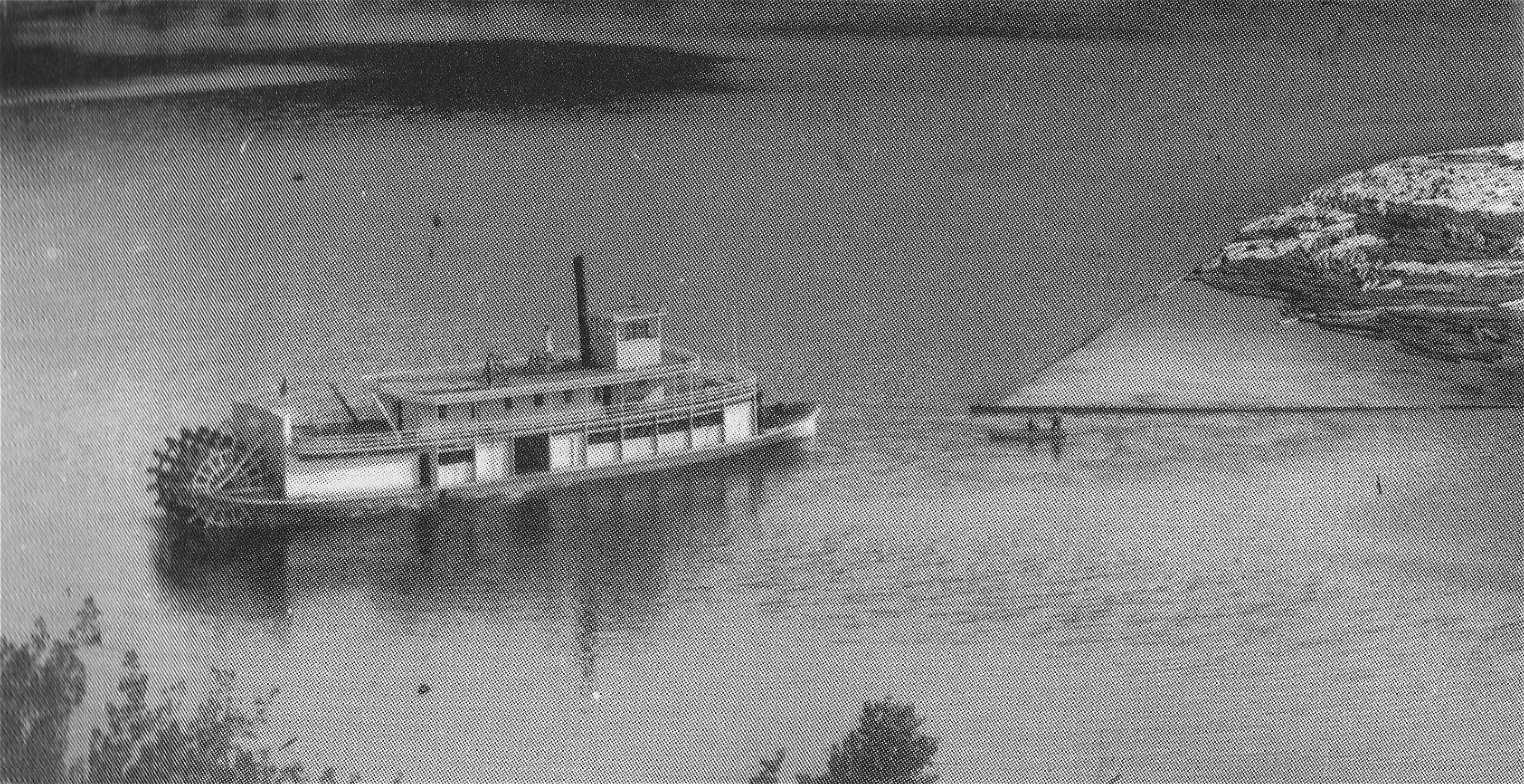|
Shuswap Lake
Shuswap Lake (pronounced /ˈʃuːʃwɑːp/) is a lake located in the southern interior of British Columbia, Canada that drains via the Little Shuswap River into Little Shuswap Lake. Little Shuswap Lake is the source of the South Thompson River, a branch of the Thompson River, a tributary of the Fraser River. It is at the heart of a region known as the Columbia Shuswap or "the Shuswap", noted for its recreational lakeshore communities including the city of Salmon Arm. The name "Shuswap" is derived from the Shuswap or Secwepemc First Nations people, the most northern of the Interior Salish peoples, whose territory includes the Shuswap. The Shuswap call themselves /ʃǝxwépmǝx/ in their own language, which is called /ʃǝxwepmǝxtʃín/. Geography The central interior plateau of British Columbia drained by the Fraser and Okanagan rivers is part of the Shuswap terrane in British Columbia and northern Washington state. It is dissected by numerous elongated, glacially- over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, forests, lakes, mountains, inland deserts and grassy plains. British Columbia borders the province of Alberta to the east; the territories of Yukon and Northwest Territories to the north; the U.S. states of Washington (state), Washington, Idaho and Montana to the south, and Alaska to the northwest. With an estimated population of over 5.7million as of 2025, it is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, third-most populous province. The capital of British Columbia is Victoria, British Columbia, Victoria, while the province's largest city is Vancouver. Vancouver and its suburbs together make up List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada, the third-largest metropolit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinook Salmon
The Chinook salmon (''Oncorhynchus tshawytscha'') is the largest and most valuable species of Oncorhynchus, Pacific salmon. Its common name is derived from the Chinookan peoples. Other vernacular names for the species include king salmon, quinnat salmon, spring salmon, blackmouth, and tyee salmon. The scientific species name is based on the Russian common name ''chavycha'' (чавыча). Chinook are anadromous fish native to the North Pacific Ocean and the river systems of western North America, ranging from California to Alaska, as well as Asian rivers ranging from northern Japan to the Palyavaam River in Arctic northeast Siberia. They have been introduced to other parts of the world, including New Zealand and Patagonia. Introduced Chinook salmon are thriving in Lake Michigan and Michigan's western rivers. A large Chinook is a prized and sought-after catch for a sporting angler. The flesh of the salmon is also highly valued for its dietary nutritional content, which includes h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicamous
Sicamous () is a district municipality in the Shuswap Country region of south central British Columbia. The place is adjacent to the narrows, which is the confluence of Mara Lake into Shuswap Lake. At the BC Highway 97A intersection on BC Highway 1, the locality is by road about west of Revelstoke, east of Kamloops, and north of Vernon. First Nations and fur traders The Secwepemc (Shuswap) First Nations have long inhabited the shores of Shuswap and Mara lakes, evidenced by the presence of pit-houses dating back over 3,200 years. An annual potlach was held at the mouth of the Eagle River. In the 1840s, an encampment existed west of the narrows on the slopes later called CPR hill. From the early 1820s, they brought furs to trade at the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) fort at Kamloops. By the 1840s, an HBC outpost opened at the mouth of the Eagle River. For centuries, the river had provided an abundance of salmon, which also created a trade in dried fish. A trail on the north si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monashees
The Monashee Mountains are a mountain range lying mostly in British Columbia, Canada, extending into the U.S. state of Washington. They stretch from north to south and from east to west. They are a sub-range of the Columbia Mountains. The highest summit is Mount Monashee, which reaches . The name is from the Scottish Gaelic ''monadh'' and ''sìth,'' meaning "moor" and "peace". Geography The Monashee Mountains are limited on the east by the Columbia River and Arrow Lakes, beyond which lie the Selkirk Mountains. They are limited on the west by the upper North Thompson River and the Interior Plateau. The northern end of the range is Canoe Mountain at the south end of the Robson Valley, near of the town of Valemount, British Columbia. The southern extremity of the range is in Washington State, where the Kettle River Range reaches the confluence of the Kettle River and the Columbia, and reaches west to the southern extremity of the Okanagan Highland (spelled Okanogan Highland in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eagle Pass (British Columbia)
Eagle Pass (elevation ) is a mountain pass through the Gold Range of the Monashee Mountains in British Columbia, Canada. It divides the Columbia River drainage basin from that of the Fraser River (via the Shuswap Lakes and the Thompson River). Eagle Pass was chosen as the route of the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR), and later the Trans-Canada Highway The Trans-Canada Highway (Canadian French, French: ; abbreviated as the TCH or T-Can) is a transcontinental federal–provincial highway system that travels through all ten provinces of Canada, from the Pacific Ocean on the west coast to the A ..., over the Monashees. The line over the Eagle Pass was the last section of the CPR to be completed; the last spike was driven at a location known as Craigellachie in 1885. The pass was discovered by Walter Moberly in his role as Assistant Surveyor General of British Columbia in 1865. The nearest city to Eagle Pass is Revelstoke, 20 kilometres to the east. See also * Eagle River ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmon Arm
Salmon Arm is a city in the Columbia Shuswap Regional District of the Southern Interior of the Canadian province of British Columbia that has a population of 19,432 (2021). Salmon Arm was voted the best community in British Columbia in 2019. Salmon Arm was incorporated as a municipal district on May 15, 2005. The city of Salmon Arm separated from the district in 1912, but was downgraded to a village in 1958. The city of Salmon Arm once again reunited with the District Municipality in 1970. Salmon Arm once again became a city in 2005, and is now the location of the head offices of the Columbia-Shuswap Regional District. It is a tourist town in the summer, connected to all 4 arms of Shuswap Lake, with many beaches, numerous golf courses, camping facilities, and house boat rentals. Salmon Arm is home to the longest wooden freshwater wharf in North America. Etymology Salmon Arm takes its name from its place along Shuswap Lake. The lake has four "arms": Shuswap Arm in the west, Seym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmon River (Shuswap Lake)
The Salmon River is a river in the Shuswap region of British Columbia, Canada. The river arises in the mountains between Kamloops and Kelowna. It flows west to Salmon Lake, then issues northeastward and descends into a broad valley near Westwold. It then runs east along the route of Highway 97 past the town of Falkland before turning north again through the Silver Creek area to flow into the Salmon Arm of Shuswap Lake at Salmon Arm. For several kilometres upstream and downstream of Westwold the river runs through a deep gravel bed; in this section it has no surface flow except during freshet in any year that is not exceptionally wet. This presents a barrier to migratory fish. The river takes its name from the numerous salmon that spawned in the river prior to 1914, the year of the Hell's Gate Slide. Since then the salmon run has been very small, and salmon fishing is prohibited. See also *List of rivers of British Columbia The following is a partial list of rivers of Bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adams Lake
Adams Lake is a deep, cold-water lake in south-central British Columbia, which separates the Thompson Country, Thompson and Shuswap Country, Shuswap regions and the Thompson–Nicola Regional District, Thompson–Nicola and Columbia–Shuswap Regional District, Columbia–Shuswap regional districts. The upper reaches lie in the northern Monashee Mountains, while the lower end penetrates the Shuswap Highland. The southern end is by road about northeast of Kamloops. Name origin On Archibald MacDonald's 1827 map, the river is called "Choo-chooach". On S. Black's 1835 map, the lake is unnamed. First Nations in Canada, First Nations Chief Sel-howt-kin, who lived on the lakeshore, became a Roman Catholic. When John Nobili, Father Nobli baptized him, he received the name Adam. Chief Adam (sometimes spelled Atahm) was a prominent Secwepemc chief in the mid-nineteenth century. By most accounts, the lake is named after him. Adam died in the 1862 Pacific Northwest smallpox epidemic, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arm (geography)
In geography, an arm is a narrow extension, inlet, or smaller reach (geography), reach, of water flowing out from a much larger body of water, such as an ocean, a sea, or a lake. Although different geographically, a sound (geography), sound or bay may also be called an arm, or vice versa. Both the tributary and distributary of a river are sometimes called an "arm". By extension, a ''canal arm'' is a subsidiary branch of a canal or inland waterway. A number of place names are derived from this term, such as Salmon Arm, Indian Arm and Alice Arm. See also *Anabranch *River *Channel (geography), Channel *Indian Arm *Alice Arm *Gulf of Bothnia *Lake George (other), Lake George References {{DEFAULTSORT:Arm (Geography) Coastal and oceanic landforms Bodies of water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fjord
In physical geography, a fjord (also spelled fiord in New Zealand English; ) is a long, narrow sea inlet with steep sides or cliffs, created by a glacier. Fjords exist on the coasts of Antarctica, the Arctic, and surrounding landmasses of the northern and southern hemispheres. Norway's coastline is estimated to be long with its nearly 1,200 fjords, but only long excluding the fjords. Formation A true fjord is formed when a glacier cuts a U-shaped valley by ice segregation and abrasion of the surrounding bedrock. According to the standard model, glaciers formed in pre-glacial valleys with a gently sloping valley floor. The work of the glacier then left an overdeepened U-shaped valley that ends abruptly at a valley or trough end. Such valleys are fjords when flooded by the ocean. Thresholds above sea level create freshwater lakes. Glacial melting is accompanied by the rebounding of Earth's crust as the ice load and eroded sediment is removed (also called isostasy or gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overdeepening
Overdeepening is a characteristic of Depression (geology), basins and valleys eroded by glaciers. An overdeepened valley profile is often eroded to depths which are hundreds of metres below the lowest continuous surface line (the thalweg) along a valley or watercourse. This phenomenon is observed under modern day glaciers, in salt-water fjords and fresh-water lakes remaining after glaciers melt, as well as in tunnel valleys which are partially or totally filled with sediment. When the Channel (geography), channel produced by a glacier is filled with debris, the subsurface Geomorphology, geomorphic structure is found to be erosionally cut into bedrock and subsequently filled by sediments. These overdeepened cuts into bedrock structures can reach a depth of several hundred metres below the valley floor. Overdeepened fjords and lakes have significant economic value as harbours and fisheries. Overdeepened basins and valleys filled with sediment (termed tunnel valleys) are of particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |