|
Shri Shivraj Ashtak
Shri Shivraj Ashtak is an Indian Marathi-language historical drama film series created by Digpal Lanjekar. The franchise started off with an eight-part film series written and directed by Lanjekar based on Maratha Empire. The first film ''Farzand'' released on 1 June 2018 and was followed by 5 films: ''Fatteshikast'' (2019), '' Pawankhind'' (2022), ''Sher Shivraj'' (2022), '' Subhedar'' (2023), ''Shivrayancha Chhava'' (2024). All five films starred Chinmay Mandlekar and Mrinal Kulkarni. Feature films Overview ''Farzand'' (2018) The story begins with the fall of Tanaji Malusare, in capturing Kondana fort near Pune from a Mughal garrison in 1670. Three years later, when Shivaji Maharaj's coronation to be held, Shivaji Maharaj wishes that he is crowned only when his kingdom and his people have peace and security. Panhala fort is still under the command of a cruel general, Beshak Khan, of the Adil Shah of Bijapur, whose forces harass the peasantry. The previous attempt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digpal Lanjekar
Digpal Lanjekar is an Indian film director and writer who is known for the ''Shri Shivraj Ashtak'' film included ''Farzand'' (2018), ''Fatteshikast'' (2019), '' Pawankhind'' (2022), ''Sher Shivraj'' (2022). He continued the series with '' Subhedar'' was released on 25 August 2023. He planned the film titled "''Bhadrakali''" team up with Prasad Oak Prasad Prabhakar Oak (Marathi pronunciation: Help:IPA/Marathi, ɾəsaːd̪ oːk born 17 February 1975) is an actor. He has received several awards including two Filmfare Awards Marathi and a National Film Award. In 2007, he participated in ... based on Sarsenapati tarabai Dabhade Umabai. Filmography ''All films are in Marathi, unless mentioned.'' References External links * Marathi film directors Indian film directors Living people Year of birth missing (living people) {{Screen-writer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
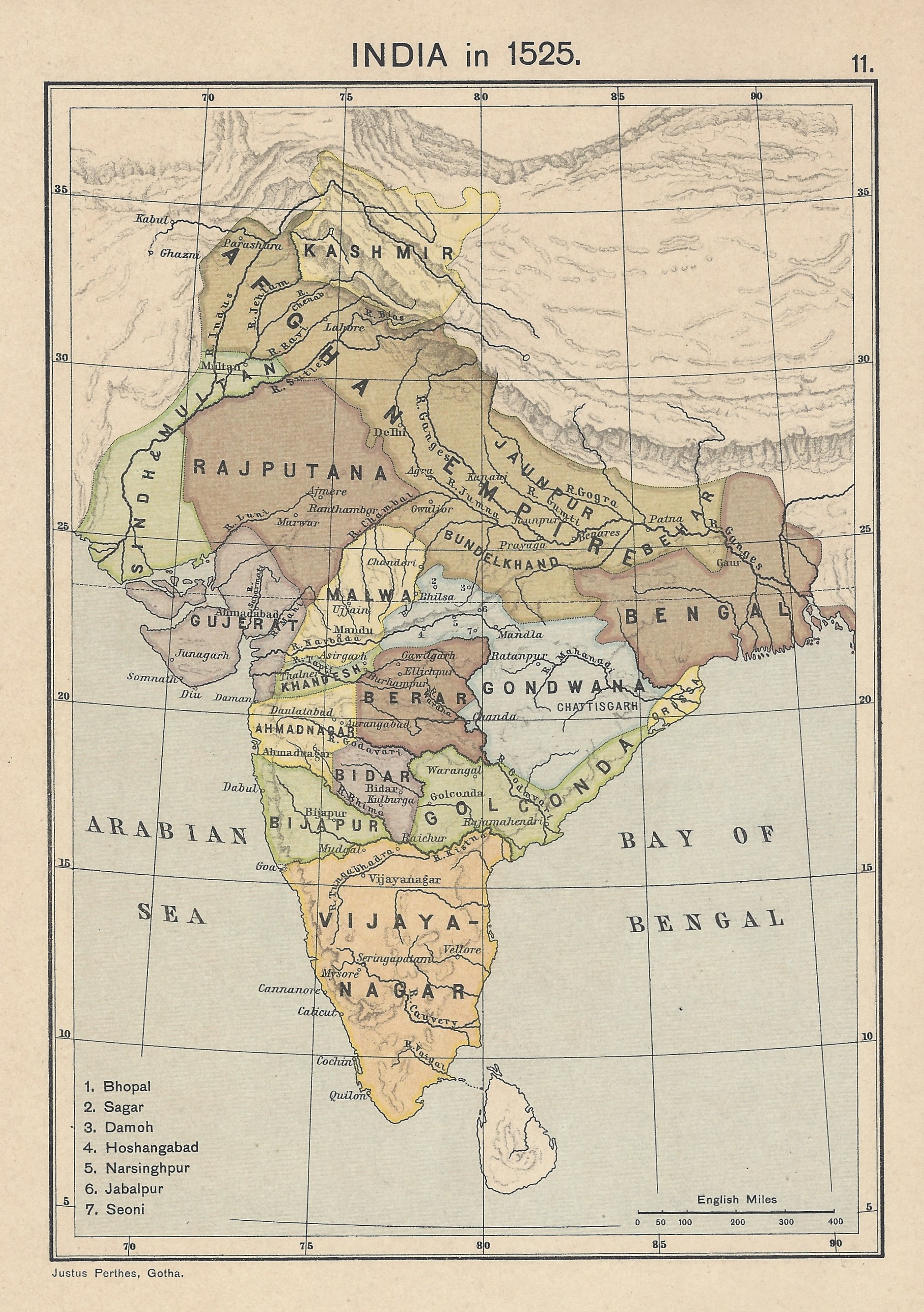
Bijapur
Bijapur (officially Vijayapura) is the district headquarters of Bijapur district of the Karnataka state of India. It is also the headquarters for Bijapur Taluk. Bijapur city is well known for its historical monuments of architectural importance built during the rule of the Adil Shahi dynasty. It is also well known for the popular Karnataka premier league team, the Bijapur Bulls. Bijapur is located northwest of the state capital Bangalore and about from Mumbai and north east of the city of Belgaum. The city was established in the 10th–11th centuries during the time of Kalyani Chalukyas and was known as ''Vijayapura'' (city of victory). The city was passed to Yadavas after Chalukya's demise. In 1347, the area was conquered by the Bahmani Sultanate. After the split of the Bahmani Sultanate, the Bijapur Sultanate ruled from the city. Relics of the Sultanates' rule can be found in the city, including the Bijapur Fort, Bara Kaman, Jama Masjid, and Gol Gumbaz. Bijapur, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subedar
Subedar ( ) is a military rank in the militaries of South Asia roughly equivalent to that of a warrant officer. Historically classed in the British Indian Army as a Viceroy's commissioned officer, the rank was retained in the Indian Army and Pakistan Army after independence. The rank of subedar is classed as a junior commissioned officer rank in India and Pakistan. History ''Subedar'' or ''subadar'' was the second-highest rank of Indian officers in the military forces of British India, ranking below "British Commissioned Officers" and above "Local Non-Commissioned Officers". Indian officers were promoted to this rank on the basis of both lengths of service and individual merit. Under British rule, a Risaldar was the cavalry equivalent of a Subedar. Subedar and Risaldar were both ranked senior to a Jemadar and junior to a Subedar Major or a Risaldar Major in an infantry/cavalry regiment of the Indian Army. Both Subedars and Risaldars wore two stars as rank insignia. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afzal Khan (general)
Afzal Khan (died 20 November 1659) was a general of the Adil Shahi dynasty of Bijapur Sultanate of in Deccan Plateau, Deccan India. He played an important role in the southern expansion of the Bijapur Sultanate by subjugating the Nayaka dynasties, Nayaka chiefs who had taken control of the former Vijayanagara Empire, Vijayanagara territory. In 1659, the Bijapur government sent Afzal Khan to subjugate Shivaji, a former vassal who had rebelled against the Bijapur government. He was killed at a truce negotiation meeting with Shivaji, and his army was defeated at the Battle of Pratapgad. Victory over the Nayakas Amid the decline of the Vijayanagara Empire, the Bijapur government campaigned against the Nayaka dynasties, Nayaka chiefs who had taken control of the former Vijayanagara territory. One of these chiefs was Virabhadra, the Nayakas of Keladi, Nayaka of Ikkeri. Kenge Nayaka (or Keng Nayak), the chief of Basavapattana and a discontented tributary of Virabhadra, helped the B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Pavan Khind
The battle of Pavan Khind ( ) was a rearguard last stand that took place on 13 July 1660, at a mountain pass in the vicinity of fort Vishalgad, near the city of Kolhapur by the Maratha general Baji Prabhu Deshpande and Shambhu Singh Jadhav against Siddi Masud of the Bijapur Sultanate. The engagement ended with the destruction of the Maratha forces, and a tactical victory for the Bijapur Sultanate that failed to achieve a strategic victory. In popular culture * The battle was depicted in episodes of '' Raja Shivchatrapati'' * In 2022, a Marathi-language film depicting the battle is titled '' Pawankhind'' directed by Digpal Lanjekar starring Chinmay Mandlekar as Shivaji and Ajay Purkar as Baji Prabhu Deshpande released on 21 January. See also * Battle of Kolhapur * Third Battle of Panipat The Third Battle of Panipat took place on 14 January 1761 between the Maratha Empire and the invading army of the Durrani Empire. The battle took place in and around the city of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adilshah
The Sultanate of Bijapur was an early modern kingdom in the western Deccan and South India, ruled by the Muslim Adil Shahi (or Adilshahi) dynasty. Bijapur had been a ''taraf'' (province) of the Bahmani Kingdom prior to its independence in 1490 and before the kingdom's political decline in the last quarter of the 15th century. It was one of the Deccan sultanates, the collective name of the kingdom's five successor states. The Sultanate of Bijapur was one of the most powerful states on the Indian Subcontinent at its peak, second to the Mughal Empire which conquered it in 1686 under Aurangzeb. After emigrating to the Bahmani Sultanate, Yusuf Adil Shah rose through the ranks to be appointed governor of the province of Bijapur. In 1490, he created a ''de facto'' independent Bijapur state which became formally independent with the Bahmani collapse in 1518. The Bijapur Sultanate's borders changed considerably throughout its history. Its northern boundary remained relatively stable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siddi Masud
Siddi Masud or Siddi Masood was a general in the Adilshahi sultanate and he was the son-in-law of famous general Siddi Jauhar. He went on to become the Wazir of Bijapur Sultanate during Sikandar Adil Shah's reign. Early life and Siege of Panhala Not much is known about his early life. He was the son in law of Siddi Jauhar. He was present at the siege of Panhalgad by Siddi Jauhar. He led the pursuing Adilshahi forces against the Maratha rearguard led by Baji Prabhu Deshpande and Bandal Sena in the Battle of Pavankhind. Later on he was defeated by Marathas at the base of Vishalgadh and retreated to safer location. Later life and Promotion as a Wazir He rose through the ranks in a tumultuous period in a weak Adilshahi's reign. He was the leader of the Deccan faction in the Adilshahi court against the Pathani faction led Bahlolkhan. He was able to subdue his Pathani rivals even though the internal feuds went on. He rose to the position of Wazir sometime around 1676 acting as a reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baji Prabhu Deshpande
Baji Prabhu Deshpande ( 1615 – 13 July 1660) was a general of the Maratha Army. He is known for his role in the Battle of Pavan Khind at Ghod Khind, where he sacrificed his life defending Shivaji Maharaj from incoming Adil Shahi forces of Siddi Johar. He also was a landlord or ''Vatandar'' in the Maval region. Early life Baji Prabhu was born around 1615 in a Chandraseniya Kayastha Prabhu family. Earlier he worked under Krishnaji Bandal of Rohida near Bhor. After Shivaji Maharaj defeated Krishnaji at Rohida and captured the fort, many commanders along with Baji Prabhu joined Shivaji Maharaj. Battle of Pavan Khind Shivaji Maharaj continued to push into the Bijapur territory, after defeating Afzal Khan and the rout of the Bijapur army at Pratapgad. Within a few days, the Marathas captured Panhala fort (near the city of Kolhapur). Meanwhile, another Maratha force, led by Netaji Palkar, pushed towards Bijapur. Bijapur forces repulsed this attack, forcing Shivaji Maharaj, som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to the southeast and Chhattisgarh to the east, Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh to the north, and the Indian union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the northwest. Maharashtra is the second-most populous state in India, the third most populous country subdivision in South Asia and the fourth-most populous in the world. The state is divided into 6 divisions and 36 districts. Mumbai is the capital of Maharashtra due to its historical significance as a major trading port and its status as India's financial hub, housing key institutions and a diverse economy. Additionally, Mumbai's well-developed infrastructure and cultural diversity make it a suitable administrative center for the state, and the most populous urban are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kolhapur
Kolhapur () is a city on the banks of the Panchganga River in the southern part of the Indian state of Maharashtra. Kolhapur is one of the most significant cities in South Maharashtra and has been a hub of historical, religious, and cultural activities for centuries. It is famous for its unique food culture, including its signature Kolhapuri cuisine. The city is situated in the western part of Maharashtra and is often referred to as "Dakshin Kashi" or "Mahateerth". It boasts a rich history, which has given it various other names, including Kollagiri, Kolladigiripattan and Kollpur, all meaning "valley" Around 2 CE Kolhapur's name was 'Kuntal'. Kolhapur is known as Dakshin Kashi''' or Kashi of the South because of its spiritual history and the antiquity of its shrine Mahalaxmi, better known as Ambabai. The region is known for the production of the famous handcrafted and braided leather slippers called Kolhapuri chappal, which received the Geographical Indication designatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vishalgad
Vishalgad (also called Vishalgarh, Khelna or Khilna) was a jagir during the Maratha Empire and then later part of the Deccan States Agency of the British Raj. Fort A fort had existed at Vishalgad for a long period. During the Bahmani rule it belonged to the Shirke clan. During that period it was known by the name , khelna. The Maratha emperor Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj had escaped to it after being besieged at Panhala Fort in 1660 and in 1844 it was one of the forts of Kolhapur State that initiated a rebellion against a regent called Daji Krishna Pandit who had been installed by the British to govern the state in 1843 at a time when the natural heir to the throne was underage. He took direction from a political agent of the East India Company and among their actions were reforms to the tax of land. These reforms caused much resentment and, despite Kolhapur having refrained from involvement in the previous Anglo-Maratha Wars, a revolt against the British began in 1844. The r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Last Stand
A last stand, or final stand, is a military situation in which a body of troops holds a defensive position in the face of overwhelming and virtually insurmountable odds. Troops may make a last stand due to a sense of duty; because they are defending a tactically crucial point; to buy time to enable a trapped army, person, or group of people to escape; due to fear of execution if captured; or to protect their ruler or leader. Last stands loom large in history, as the heroism and sacrifice of the defenders exert a large pull on the public's imagination. Some last stands have become a celebrated part of a fighting force's or a country's history, especially if the defenders accomplished their goals (or, in rare cases, defeated their attackers). Tactical significance A "last stand" is a last resort tactic, and is chosen because the defending force realizes or believes the benefits of fighting outweigh the benefits of retreat or surrender. This usually arises from strategic or mora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |