|
Shrewsbury Hoard
The Shrewsbury Hoard (also known as the Shropshire Hoard) is a hoard of 9,315 bronze Roman coins discovered by a metal detectorist in a field near Shrewsbury, Shropshire in August 2009. The coins were found in a large pottery storage jar that was buried in about AD 335. Discovery and excavation The coins were found buried in a brown pot in a plantation next to a public bridleway by Nic Davies only a month after he had started metal detecting as a hobby, and were his first find. Davies did not have permission from the landowner to metal detect on his land, not realising that it was a requirement, and when he located the hoard he dug up the pot himself, although he subsequently took it to show Peter Reavill, the Portable Antiquities Scheme Finds Liaison Officer for Herefordshire and Shropshire. Davies later led Reavill and Shropshire County Council archaeologists to the find site, and a small excavation was carried out. The excavation revealed that the pot had probably been place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Another View Of The Vessel And The Hoard (2)
*
{{disambiguation ...
Another or variant may refer to: * anOther or Another Magazine, culture and fashion magazine * ''Another'' (novel), a Japanese horror novel ** ''Another'' (film), a Japanese 2012 live-action film based on the novel * Another River, a river in the U.S. state of Alaska * A. N. Other, a pseudonym See also * Yet another * Indefinite pronoun * English determiners * Other (other) * Others (other) Others or The Others may refer to: Fictional characters * Others (''A Song of Ice and Fire''), supernatural creatures in the fictional world of George R. R. Martin's fantasy series ''A Song of Ice and Fire'' * Others (''Lost''), mysterious inh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constans
Flavius Julius Constans ( 323 – 350), sometimes called Constans I, was Roman emperor from 337 to 350. He held the imperial rank of ''caesar'' from 333, and was the youngest son of Constantine the Great. After his father's death, he was made '' augustus'' alongside his brothers in September 337. Constans was given the administration of the praetorian prefectures of Italy, Illyricum, and Africa. He defeated the Sarmatians in a campaign shortly afterwards. Quarrels over the sharing of power led to a civil war with his eldest brother and co-emperor Constantine II, who invaded Italy in 340 and was killed in battle with Constans's forces near Aquileia. Constans gained from him the praetorian prefecture of Gaul. Thereafter there were tensions with his remaining brother and co-''augustus'' Constantius II (), including over the exiled bishop Athanasius of Alexandria. In the following years he campaigned against the Franks, and in 343 he visited Roman Britain, the last legitim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2009 Archaeological Discoveries
9 (nine) is the natural number following and preceding . Evolution of the Arabic digit In the beginning, various Indians wrote a digit 9 similar in shape to the modern closing question mark without the bottom dot. The Kshatrapa, Andhra and Gupta started curving the bottom vertical line coming up with a -look-alike. The Nagari continued the bottom stroke to make a circle and enclose the 3-look-alike, in much the same way that the sign @ encircles a lowercase ''a''. As time went on, the enclosing circle became bigger and its line continued beyond the circle downwards, as the 3-look-alike became smaller. Soon, all that was left of the 3-look-alike was a squiggle. The Arabs simply connected that squiggle to the downward stroke at the middle and subsequent European change was purely cosmetic. While the shape of the glyph for the digit 9 has an ascender in most modern typefaces, in typefaces with text figures the character usually has a descender, as, for example, in . T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romano-British Objects In The British Museum
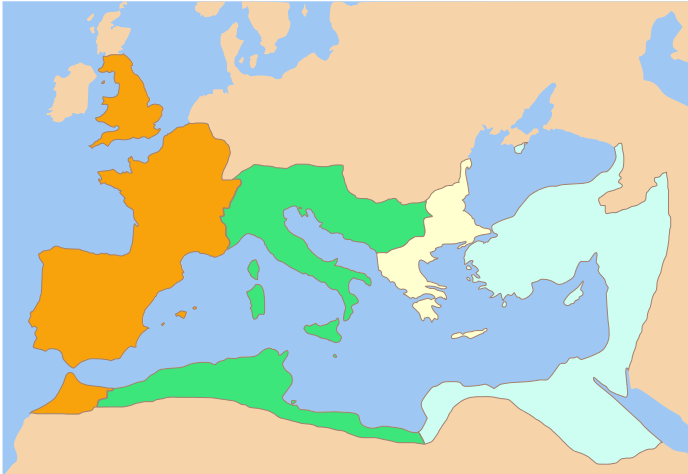
The Romano-British culture arose in Britain under the Roman Empire following the Roman conquest in AD 43 and the creation of the province of Britannia. It arose as a fusion of the imported Roman culture with that of the indigenous Britons, a people of Celtic language and custom. Scholars such as Christopher Snyder believe that during the 5th and 6th centuries – approximately from 410 when the Roman legions withdrew, to 597 when St Augustine of Canterbury arrived – southern Britain preserved an active sub-Roman culture that survived the attacks from the Anglo-Saxons and even used a vernacular Latin when writing. Arrival of the Romans Roman troops, mainly from nearby provinces, invaded in AD 43, in what is now part of England, during the reign of Emperor Claudius. Over the next few years the province of Britannia was formed, eventually including the whole of what later became England and Wales and parts of Scotland.Kinder, H. & Hilgemann W. ''The Penguin Atlas of World H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treasure Troves Of Roman Britain
Treasure (from la, thesaurus from Greek language ''thēsauros'', "treasure store") is a concentration of wealth — often originating from ancient history — that is considered lost and/or forgotten until rediscovered. Some jurisdictions legally define what constitutes treasure, such as in the British Treasure Act 1996. The phrase "blood and treasure" has been used to refer to the human and monetary costs associated with massive endeavours such as war that expend both. Searching for hidden treasure is a common theme in legend; treasure hunters do exist, and can seek lost wealth for a living. Burial Buried treasure is an important part of the popular mythos surrounding pirates. According to popular conception, pirates often buried their stolen fortunes in remote places, intending to return for them later (often with the use of treasure maps). There are three well-known stories that helped popularize the myth of buried pirate treasure: " The Gold-Bug" by Edgar A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treasure Troves In England
Treasure (from la, thesaurus from Greek language ''thēsauros'', "treasure store") is a concentration of wealth — often originating from ancient history — that is considered lost and/or forgotten until rediscovered. Some jurisdictions legally define what constitutes treasure, such as in the British Treasure Act 1996. The phrase "blood and treasure" has been used to refer to the human and monetary costs associated with massive endeavours such as war that expend both. Searching for hidden treasure is a common theme in legend; treasure hunters do exist, and can seek lost wealth for a living. Burial Buried treasure is an important part of the popular mythos surrounding pirates. According to popular conception, pirates often buried their stolen fortunes in remote places, intending to return for them later (often with the use of treasure maps). There are three well-known stories that helped popularize the myth of buried pirate treasure: "The Gold-Bug" by Edgar Allan Poe, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Hoards In Britain
The list of hoards in Britain comprises significant archaeological hoards of coins, jewellery, precious and scrap metal objects and other valuable items discovered in Great Britain ( England, Scotland and Wales). It includes both hoards that were buried with the intention of retrieval at a later date (personal hoards, founder's hoards, merchant's hoards, and hoards of loot), and also hoards of votive offerings which were not intended to be recovered at a later date, but excludes grave goods and single items found in isolation. The list is subdivided into sections according to archaeological and historical periods. Neolithic hoards Hoards dating to the Neolithic period, approximately 4000 to 2000 BC, comprise stone weapons and tools such as axeheads and arrowheads. Such hoards are very rare, and only a few are known from Britain. Bronze Age hoards A large number of hoards associated with the British Bronze Age, approximately 2700 BC to 8th century BC, have been foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrewsbury Museum And Art Gallery
Shrewsbury Museum and Art Gallery was founded in 1835 as the Museum of the Shropshire and North Wales Natural History and Antiquarian Society Society in Dogpole, Shrewsbury, England. In 1853 the collections were moved to Vaughan's Mansion on College Hill, which became known as the Shropshire and North Wales Museum. After 160 years and two subsequent homes the museum returned to Vaughan's Mansion and the Music Hall Complex after a major redevelopment of the site. History The Shrewsbury Museum and Art Gallery was founded in 1835 as the Museum of the Shropshire and North Wales Natural History and Antiquarian Society Society in Dogpole, Shrewsbury. In 1853 the collections were moved to Vaughan's Mansion on College Hill, which became known as the Shropshire and North Wales Museum. In 1877 the Society merged with newly formed Shropshire Archaeological Society to become Shropshire Archaeological and Natural History Society. That year the museum accepted a major collection of finds rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department For Culture, Media And Sport
, type = Department , logo = Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport logo.svg , logo_width = , logo_caption = , seal = , seal_width = , seal_caption = , picture = Government Offices Great George Street.jpg , picture_width = 200px , picture_caption = 100 Parliament Street – partly occupied by DCMS on the windowless fourth floor , formed = , preceding1 = Department for National Heritage , dissolved = , superseding = , jurisdiction = Government of the United Kingdom , headquarters = 100 Parliament Street,London SW1A 2BQ,England , employees = 3,020 , budget = £1.4 billion (current) & £1.3 billion (capital) for 2011–12 , minister1_name = Rt Hon Michelle Donelan MP , minister1_pfo = Secretary of State for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport , minister2_name = Matt Warman MP , minister2_pfo = Minister of State for Media, Data, and Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treasure Valuation Committee
The Treasure Valuation Committee (TVC) is an advisory non-departmental public body of the Department for Culture, Media and Sport (DCMS) based in London, which offers expert advice to the government on items of declared treasure in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland that museums there may wish to acquire from the Crown. The terms of reference of the TVC are laid down in the Treasure Act 1996 Code of Practice, which also details the principle of reward payments to finders and landowner for finds of Treasure which are acquired by museums. The TVC recommends to the Secretary of State the value of treasure finds which come before it, and also makes recommendations on the allocation of rewards and abatements of rewards where circumstances require. Minutes of its meetings are published on the website of the Portable Antiquities Scheme, after all of the cases discussed therein are concluded. The TVC meets at the British Museum but is independent of the museum. Members Members of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treasure Act 1996
The Treasure Act 1996 is a UK Act of Parliament, defining which objects are classified as treasure, legally obliging the finder to report their find. Provisions The Act is designed to deal with finds of treasure in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. It legally obliges finders of objects which constitute treasure (as defined in the Act) to report their find to their local coroner within 14 days. An inquest led by the coroner then determines whether the find constitutes treasure or not. If it is declared to be treasure then the finder must offer the item for sale to a museum at a price set by an independent board of antiquities experts known as the Treasure Valuation Committee. Only if a museum expresses no interest in the item, or is unable to purchase it, can the finder retain it. For the purposes of the Act, 'Treasure' is defined as being: *All coins from the same find, if it consists of two or more coins, and as long as they are at least 300 years old when found. If they con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inquests In England And Wales
Inquests in England and Wales are held into sudden or unexplained deaths and also into the circumstances of and discovery of a certain class of valuable artefacts known as "treasure trove". In England and Wales, inquests are the responsibility of a coroner, who operates under the jurisdiction of the Coroners and Justice Act 2009. In some circumstances where an inquest cannot view or hear all the evidence, it may be suspended and a public inquiry held with the consent of the Home Secretary. Where an inquest is needed There is a general duty upon every person to report a death to the coroner if an inquest is likely to be required. However, this duty is largely unenforceable in practice and the duty falls on the responsible registrar. The registrar must report a death where: *The deceased was not attended by a doctor during their last illness *The death occurred within 24 hours of admission to a hospital *The cause of death has not been certified by a doctor who saw the deceased af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




.jpg)