|
Shortland, New South Wales
Shortland is a suburb of Newcastle, New South Wales, Australia, located from Newcastle's central business district. It is part of the City of Newcastle local government area. The Awabakal and Worimi peoples are acknowledged by City of Newcastle as the descendants of the traditional custodians of the land situated within the Newcastle local government area, including wetlands, rivers creeks and coastal environments. It is known that their heritage and cultural ties to Newcastle date back tens of thousands of years. Shortland was named after Lt. John Shortland, master's mate of the ''Sirius'', the escorting vessel to the First Fleet. The area is restricted in development growth due to surrounding wetlands. Education There are two primary schools in Shortland, Shortland Public School and Our Lady of Victories Catholic School, both located on Sandgate Road. Shortland Pre-School is located next to Shortland Public School on Sandgate Road. Margaret Jurd College, a Ministry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newcastle, New South Wales
Newcastle ( ; Awabakal: ) is a metropolitan area and the second most populated city in the state of New South Wales, Australia. It includes the Newcastle and Lake Macquarie local government areas, and is the hub of the Greater Newcastle area, which includes most parts of the local government areas of City of Newcastle, City of Lake Macquarie, City of Cessnock, City of Maitland and Port Stephens Council. Located at the mouth of the Hunter River, it is the predominant city within the Hunter Region. Famous for its coal, Newcastle is the largest coal exporting harbour in the world, exporting 159.9 million tonnes of coal in 2017. Beyond the city, the Hunter Region possesses large coal deposits. Geologically, the area is located in the central-eastern part of the Sydney Basin. History Aboriginal history Newcastle and the lower Hunter Region were traditionally occupied by the Awabakal and Worimi Aboriginal people, who called the area Malubimba. Based on Aboriginal lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Awabakal
The Awabakal people , are those Aboriginal Australians who identify with or are descended from the Awabakal tribe and its clans, Indigenous to the coastal area of what is now known as the Hunter Region of New South Wales. Their traditional territory spread from Wollombi in the west, to the Lower Hunter River near Newcastle and Lake Macquarie in the north. The name Kuringgai, also written Guringai, has often been used as a collective denominator of the Awabakal and several other tribes in this belt, but Norman Tindale has challenged it as an arbitrary coinage devised by ethnologist John Fraser in 1892. For Tindale, Kuringgai was synonymous with Awabakal. Arthur Capell however asserted that there was indeed evidence for a distinct Kuringgai language, which, in Tindale's schema, would imply they were a distinct people from the Awabakal. Name In their language, ''awaba'' was the word for Lake Macquarie, meaning flat or plain surface, and by extension referred to the peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NSW TrainLink
NSW TrainLink is a train and coach operator in Australia, providing services throughout New South Wales and the Australian Capital Territory, along with limited interstate services into Victoria, Queensland and South Australia. Its primary intercity and regional services are spread throughout five major rail lines, operating out of Sydney's Central railway station. NSW TrainLink was formed on 1 July 2013 when RailCorp was restructured and CountryLink was merged with the intercity services of CityRail. History In May 2012, the Minister for Transport announced a restructure of RailCorp. On 1 July 2013, NSW TrainLink took over (a) the operation of regional rail and coach services previously operated by CountryLink; (b) non-metropolitan Sydney services previously operated by CityRail; and (c) responsibility for the Main Northern railway line from Berowra railway station to Newcastle station, the Main Western railway line from Emu Plains railway station to Bathurst railwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warabrook Railway Station
Warabrook railway station is located on the Main Northern line in New South Wales, Australia. It serves the western Newcastle suburb of Warabrook and the University of Newcastle, opening on 23 October 1995. NSWrail.net Platforms & services Warabrook has one island platform with two faces. It is serviced by Hunter Line services travelling from Newcastle to[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandgate Railway Station, New South Wales
Sandgate railway station is located on the Main Northern line in New South Wales, Australia. It serves the western Newcastle suburb of Sandgate, opening in 1881 as Grant's Creek. A one kilometre branch diverged behind the station in a north-westerly direction for Sandgate Cemetery. This closed on 13 October 1985. Following the completion of the Sandgate Flyover in November 2006, Sandgate station is flanked by two coal lines on either side. Australian Rail Track Corporation 24 November 2006 Platforms & services Sandgate has two side platforms. It is serviced by[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
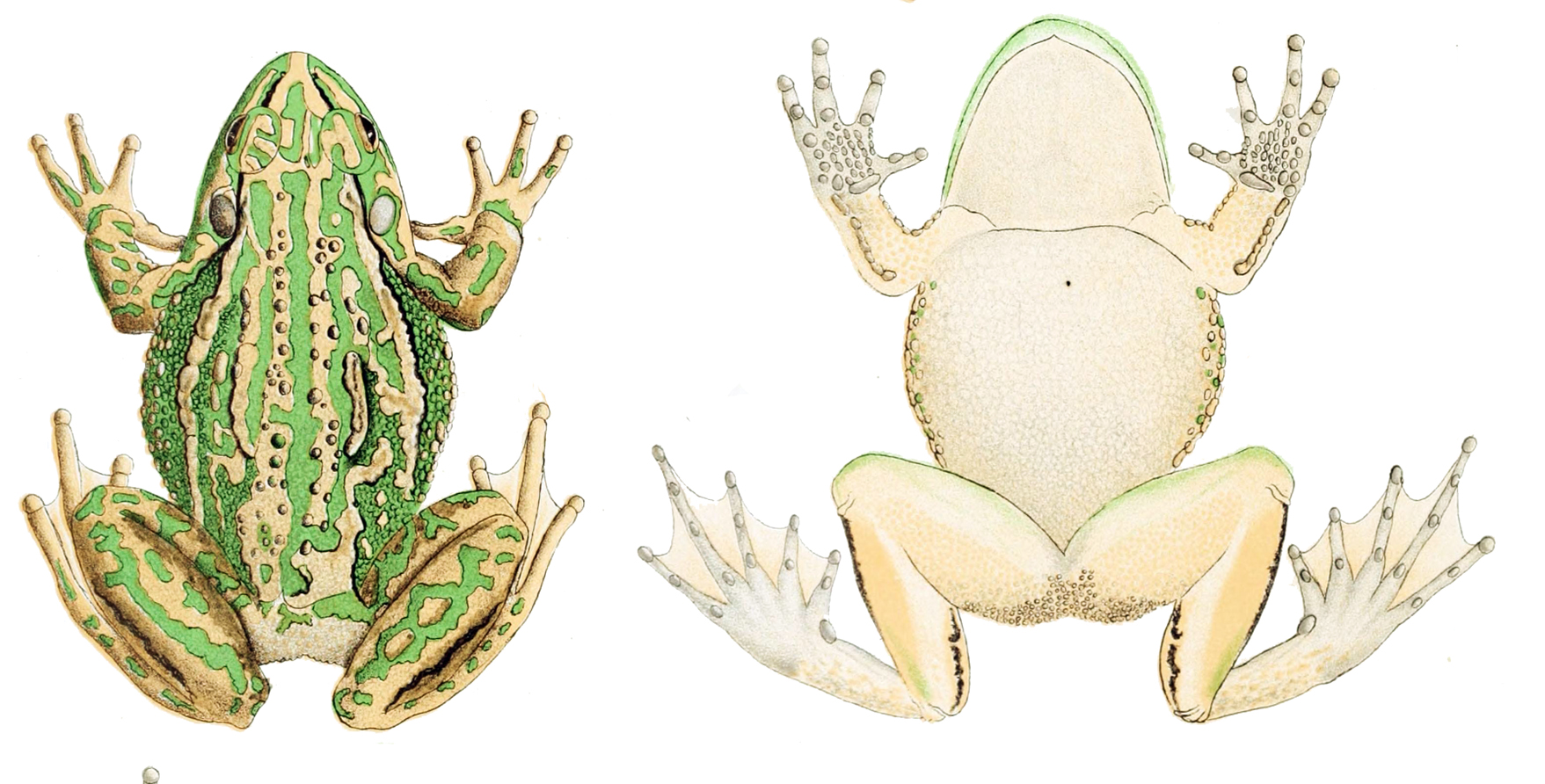
Green And Golden Bell Frog
The green and golden bell frog (''Ranoidea aurea''), also named the green bell frog, green and golden swamp frog and green frog, is a species of ground-dwelling tree frog native to eastern Australia. Despite its classification and climbing abilities, it does not live in trees and spends almost all of its time close to ground level. It can reach up to in length, making it one of Australia's largest frogs. Coloured gold and green, the frogs are voracious eaters of insects, but will also eat larger prey, such as worms and mice. They are mainly diurnal, although this is mostly to warm in the sun. They tend to be less active in winter except in warmer or wetter periods, and breed in the warmer months. Males reach maturity after around 9 months, while for the larger females, this does not occur until they are two years old. The frogs can engage in cannibalism, and males frequently attack and injure one another if they infringe on one another's space. Many populations, particularly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newcastle Inner City Bypass
Newcastle Inner City Bypass is a road in Newcastle, New South Wales, Newcastle and City of Lake Macquarie, Lake Macquarie, New South Wales, Australia. Originally cobbled together from a collection of arterial roads, it has been slowly upgraded and lengthened in sections over the years to a motorway-standard bypass through the inner western suburbs of Newcastle. Route The road is divided into five sections. The southernmost section is the West Charlestown, New South Wales, Charlestown Bypass, which is a freeway standard road that was opened to traffic in 2003. The second section leads up the ridge and consists of parts of Charlestown Road and Lookout Road, which were widened into a divided dual carriageway non-freeway configuration during the 1980s. The third section is a planned freeway diverging from Lookout Road near the intersection of McCaffrey Drive, skirting around the west of the John Hunter Hospital and passing over Newcastle Road to join the fourth section, bypassing Je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yowie
Yowie is one of several names for an Australian folklore entity that is reputed to live in the Outback. The creature has its roots in Aboriginal oral history. In parts of Queensland, they are known as ''quinkin'' (or as a type of quinkin), and as ''joogabinna'', in parts of New South Wales they are called ''Ghindaring'', ''jurrawarra'', ''myngawin'', ''puttikan'', ''doolaga'', ''gulaga'' and ''thoolagal''. Other names include ''yaroma'', ''noocoonah'', ''wawee'', ''pangkarlangu'', ''jimbra'' and ''tjangara''. Yowie-type creatures are common in Aboriginal Australian legends, particularly in the eastern Australian states. Description The yowie is usually described as a hairy and ape-like creature standing upright at between and . The yowie's feet are described as much larger than a human's, but alleged yowie tracks are inconsistent in shape and toe number, and the descriptions of yowie foot and footprints provided by yowie witnesses are even more varied than those of Bigfoot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunter Estuary Wetlands
The Hunter Estuary Wetlands comprise a group of associated wetlands at and near the mouth of the Hunter River in the city of Newcastle, New South Wales, Australia. Some 30 km2 of the wetlands has been recognised as being of international importance by designation under the Ramsar Convention. It was listed on 21 February 1984 as Ramsar site 287. A larger area of the wetlands has been identified by BirdLife International as an Important Bird Area (IBA). The wetlands are recognised as the most important area in New South Wales for waders, or shorebirds. Description Ramsar site The Ramsar site comprises the Kooragang Nature Reserve and the nearby Shortland Wetlands, which are connected by a wildlife corridor that includes the Hunter River and Ironbark Creek. Kooragang Island is an artificial, estuarine island liable to flooding at high tide. Its habitats include mangroves, brackish and freshwater swamps, saltmarsh, ''Casuarina'' forest, mudflats, beaches and rock walls. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramsar Convention
The Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance Especially as Waterfowl Habitat is an international treaty for the conservation and sustainable use of Ramsar site, Ramsar sites (wetlands). It is also known as the Convention on Wetlands. It is named after the city of Ramsar, Mazandaran, Ramsar in Iran, where the convention was signed in 1971. Every three years, representatives of the contracting parties meet as the Ramsar Convention#Conference of the Contracting Parties, Conference of the Contracting Parties (COP), the policy-making organ of the wetland conservation, convention which adopts decisions (resolutions and recommendations) to administer the work of the convention and improve the way in which the parties are able to implement its objectives. COP12 was held in Punta del Este, Uruguay, in 2015. COP13 was held in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, in October 2018. List of wetlands of international importance The list of wetlands of international importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Newcastle (Australia)
The University of Newcastle (UON), informally known as Newcastle University, is a public university in Newcastle, New South Wales, Australia. Established in 1965, it has a primary campus in the Newcastle suburb of Callaghan. The university also operates campuses in Ourimbah, Port Macquarie, Singapore, Newcastle CBD and Sydney CBD. Historically, the University of Newcastle Medical School has implemented the problem-based learning system for its undergraduate Bachelor of Medicine program – a system later mandated for use by the Australian Medical Council throughout Australia. It pioneered use of the Undergraduate Medicine and Health Sciences Admission Test (UMAT) in the early 1990s. UMAT has since been accepted widely by different medical schools across Australia as an additional selection criteria. The University of Newcastle is a member of the Australian Technology Network, Universities Australia and the Association to Advance Collegiate Schools of Business. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Fleet
The First Fleet was a fleet of 11 ships that brought the first European and African settlers to Australia. It was made up of two Royal Navy vessels, three store ships and six convict transports. On 13 May 1787 the fleet under the command of Captain Arthur Phillip, with over 1400 people ( convicts, marines, sailors, civil officers and free settlers), left from Portsmouth, England and took a journey of over and over 250 days to eventually arrive in Botany Bay, New South Wales, where a penal colony would become the first European settlement in Australia. History Lord Sandwich, together with the President of the Royal Society, Sir Joseph Banks, the eminent scientist who had accompanied Lieutenant James Cook on his 1770 voyage, was advocating establishment of a British colony in Botany Bay, New South Wales. Banks accepted an offer of assistance from the American Loyalist James Matra in July 1783. Under Banks's guidance, he rapidly produced "A Proposal for Establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)