|
Short-circuits
A short circuit (sometimes abbreviated to short or s/c) is an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path with no or very low electrical impedance. This results in an excessive current flowing through the circuit. The opposite of a short circuit is an open circuit, which is an infinite resistance (or very high impedance) between two nodes. Definition A short circuit is an abnormal connection between two nodes of an electric circuit intended to be at different voltages. This results in an electric current limited only by the Thévenin equivalent resistance of the rest of the network which can cause circuit damage, overheating, fire or explosion. Although usually the result of a fault, there are cases where short circuits are caused intentionally, for example, for the purpose of voltage-sensing crowbar circuit protectors. In circuit analysis, a ''short circuit'' is defined as a connection between two nodes that forces them to be at the same v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overheating (electricity)
Overheating is a phenomenon of rising temperatures in an electrical circuit. Overheating causes damage to the circuit components and can cause fire, explosion, and injury. Damage caused by overheating is usually irreversible; the only way to repair it is to replace some components. Causes When overheating, the temperature of the part rises above the operating temperature. Overheating can take place: * if heat is produced in more than expected amount (such as in cases of short-circuits, or applying more voltage than rated), or * if heat dissipation is poor, so that normally produced waste heat does not drain away properly. Overheating may be caused from any accidental fault of the circuit (such as short-circuit or spark-gap), or may be caused from a wrong design or manufacture (such as the lack of a proper heat dissipation system). Due to accumulation of heat, the system reaches an equilibrium of heat accumulation vs. dissipation at a much higher temperature than expected. Preventi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossed Wires
In electronics, crosstalk (XT) is a phenomenon by which a signal transmitted on one circuit or channel of a transmission system creates an undesired effect in another circuit or channel. Crosstalk is usually caused by undesired capacitive, inductive, or conductive coupling from one circuit or channel to another. Where the electric, magnetic, or traveling fields of two electric signals overlap, the electromagnetic interference created causes crosstalk. For example, crosstalk can comprise magnetic fields that induce a smaller signal in neighboring wires. In electrical circuits sharing a common signal return path, electrical impedance in the return path creates between the signals, resulting in crosstalk. Crosstalk is a significant issue in structured cabling, audio electronics, integrated circuit design, wireless communication and other communications systems. In cabling In structured cabling, crosstalk refers to electromagnetic interference from one unshielded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Resistance
The electrical resistance of an object is a measure of its opposition to the flow of electric current. Its reciprocal quantity is , measuring the ease with which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with mechanical friction. The SI unit of electrical resistance is the ohm (), while electrical conductance is measured in siemens (S) (formerly called the 'mho' and then represented by ). The resistance of an object depends in large part on the material it is made of. Objects made of electrical insulators like rubber tend to have very high resistance and low conductance, while objects made of electrical conductors like metals tend to have very low resistance and high conductance. This relationship is quantified by resistivity or conductivity. The nature of a material is not the only factor in resistance and conductance, however; it also depends on the size and shape of an object because these properties are extensive rather tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault Current
In an electric power system, a fault is a defect that results in abnormality of electric current. A fault current is any abnormal electric current. For example, a short circuit in which a live wire touches a neutral or ground wire is a fault. An open-circuit fault occurs if a circuit is interrupted by a failure of a current-carrying wire (phase or neutral) or a blown fuse or circuit breaker. In a "ground fault" or "earth fault", current flows into the earth. In three-phase systems, a fault may involve one or more phases and ground, or may occur only between phases. In a polyphase system, a fault may affect all phases equally, which is a "symmetric fault". If only some phases are affected, the resulting "asymmetric fault" becomes more complicated to analyse. The analysis of these types of faults is often simplified by using methods such as symmetrical components. The prospective short-circuit current of a predictable fault can be calculated for most situations. In power systems, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
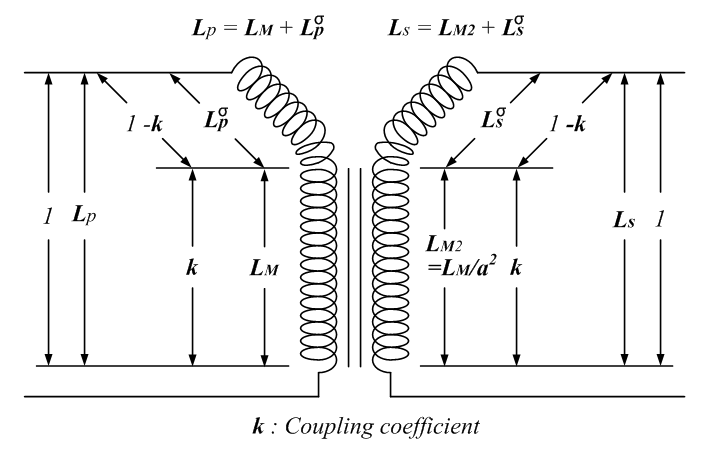
Leakage Inductance
Leakage inductance derives from the electrical property of an imperfectly coupled transformer whereby each Electromagnetic coil, winding behaves as a self-inductance in series and parallel circuits, series with the winding's respective Electrical resistance and conductance, ohmic resistance constant. These four winding constants also interact with the transformer's mutual inductance. The winding leakage inductance is due to leakage flux not linking with all turns of each imperfectly coupled winding. Leakage reactance is usually the most important element of a power system transformer due to power factor, voltage drop, reactive power consumption and Fault (power engineering), fault current considerations. Leakage inductance depends on the geometry of the core and the windings. Voltage drop across the inductive reactance, leakage reactance results in often undesirable supply regulation with varying transformer load. But it can also be useful for Harmonics (electrical power), harmonic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground And Neutral
In electrical engineering, ground (or earth) and neutral are circuit conductors used in alternating current (AC) electrical systems. The neutral conductor carries alternating current (in tandem with one or more ''phase '' conductors) during normal operation of the circuit. By contrast, a ground conductor is not intended to carry current for normal operation, but instead connects exposed conductive parts (such as equipment enclosures or conduits enclosing wiring) to Earth (the ground), and only carries significant current in the event of a circuit fault that would otherwise energize exposed conductive parts and present a shock hazard. In such case the intention is for the fault current to be large enough to trigger a circuit protective device that will either de-energize the circuit, or provide a warning. To limit the effects of leakage current from higher-voltage systems, the neutral conductor is often connected to earth ground at the point of supply. Significant voltage unin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyphase System
A polyphase system (the term coined by Silvanus Thompson) is a means of distributing alternating-current (AC) electrical power that utilizes more than one AC phase, which refers to the phase offset value (in degrees) between AC in multiple conducting wires; ''phases'' may also refer to the corresponding terminals and conductors, as in color codes. Polyphase systems have two or more energized electrical conductors carrying alternating currents with a defined phase between the voltage waves in each conductor. Early systems used 4 wire two-phase with a 90° phase angle, but modern systems almost universally use three-phase voltage, with a phase angle of 120° (or 2π/3 radians). Polyphase systems are particularly useful for transmitting power to electric motors which rely on alternating current to rotate. Three-phase power is used for industrial applications and for power transmission. Compared to a single-phase, two-wire system, a three-phase three-wire system transmits thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mains Electricity
Mains electricity, utility power, grid power, domestic power, wall power, household current, or, in some parts of Canada, hydro, is a general-purpose Alternating current, alternating-current (AC) electric power supply. It is the form of electrical power that is delivered to homes and businesses through the electrical grid in many parts of the world. People use this electricity to power everyday items (such as domestic appliances, televisions and lamps) by plugging them into a wall outlet. The voltage and utility frequency, frequency of electric power differs between regions. In much of the world, a voltage (nominally) of 230 volts and frequency of 50 Hz is used. In North America, the most common combination is 120 V and a frequency of 60 Hz. Other combinations exist, for example, 230 V at 60 Hz. Travellers' portable appliances may be inoperative or damaged by foreign electrical supplies. Non-interchangeable AC power plugs and sockets, plugs and sock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Insulation
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations. Common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others. The presence of either a positive or negative electric charge produces an electric field. The motion of electric charges is an electric current and produces a magnetic field. In most applications, Coulomb's law determines the force acting on an electric charge. Electric potential is the work done to move an electric charge from one point to another within an electric field, typically measured in volts. Electricity plays a central role in many modern technologies, serving in electric power where electric current is used to energise equipment, and in electronics dealing wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base (chemistry)
In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word "base": '' Arrhenius bases'', '' Brønsted bases'', and '' Lewis bases''. All definitions agree that bases are substances that react with acid An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...s, as originally proposed by Guillaume-François Rouelle, G.-F. Rouelle in the mid-18th century. In 1884, Svante Arrhenius proposed that a base is a substance which dissociates in aqueous solution to form hydroxide ions OH−. These ions can react with Hydron (chemistry), hydrogen ions (H+ according to Arrhenius) from the dissociation of acids to form water in an acid–base reaction. A base was therefore a metal hydroxide such as NaOH or Calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2. Such aqueous hydroxide solutions were also described by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid. The first category of acids are the proton donors, or Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acids. In the special case of aqueous solutions, proton donors form the hydronium ion H3O+ and are known as Acid–base reaction#Arrhenius theory, Arrhenius acids. Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted, Brønsted and Martin Lowry, Lowry generalized the Arrhenius theory to include non-aqueous solvents. A Brønsted–Lowry or Arrhenius acid usually contains a hydrogen atom bonded to a chemical structure that is still energetically favorable after loss of H+. Aqueous Arrhenius acids have characteristic properties that provide a practical description of an acid. Acids form aqueous solutions with a sour taste, can turn blue litmus red, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solvent like water. Upon dissolving, the substance separates into cations and anions, which disperse uniformly throughout the solvent. Solid-state electrolytes also exist. In medicine and sometimes in chemistry, the term electrolyte refers to the substance that is dissolved. Electrically, such a solution is neutral. If an electric potential is applied to such a solution, the cations of the solution are drawn to the electrode that has an abundance of electrons, while the anions are drawn to the electrode that has a deficit of electrons. The movement of anions and cations in opposite directions within the solution amounts to a current. Some gases, such as hydrogen chloride (HCl), under conditions of high temperature or low pressure can also functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |