|
Shikimic Acid
Shikimic acid, more commonly known as its anionic form shikimate, is a cyclohexene, a cyclitol and a cyclohexanecarboxylic acid. It is an important biochemical metabolite in plants and microorganisms. Its name comes from the Japanese flower ''shikimi'' (, the Japanese star anise, ''Illicium anisatum''), from which it was first isolated in 1885 by Johan Fredrik Eykman. The elucidation of its structure was made nearly 50 years later. Biosynthesis Phosphoenolpyruvate and erythrose-4-phosphate condense to form 3-deoxy-D-arabinoheptulosonate-7-phosphate (DAHP), in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme DAHP synthase. DAHP is then transformed to 3-dehydroquinate (DHQ), in a reaction catalyzed by DHQ synthase. Although this reaction requires nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) as a cofactor, the enzymic mechanism regenerates it, resulting in the net use of no NAD. : DHQ is dehydrated to 3-dehydroshikimic acid by the enzyme 3-dehydroquinate dehydratase, which is reduced to sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclohexene
Cyclohexene is a hydrocarbon with the formula . It is a cycloalkene. At room temperature, cyclohexene is a colorless liquid with a sharp odor. Among its uses, it is an chemical intermediate, intermediate in the commercial synthesis of nylon. Production and uses Cyclohexene is produced by the partial hydrogenation of benzene, a process developed by the Asahi Chemical company. The main product of the process is cyclohexane because cyclohexene is more easily hydrogenated than benzene. In the laboratory, it can be prepared by dehydration reaction, dehydration of cyclohexanol. : Reactions and uses Benzene is converted to cyclohexylbenzene by acid-catalyzed alkylation with cyclohexene. Cyclohexylbenzene is a precursor to both phenol and cyclohexanone. Hydration of cyclohexene gives cyclohexanol, which can be dehydrogenation, dehydrogenated to give cyclohexanone, a precursor to caprolactam. The oxidative cleavage of cyclohexene gives adipic acid. Hydrogen peroxide is used as the oxid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a Cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NADPH as a reducing agent ('hydrogen source'). NADPH is the redox, reduced form, whereas NADP is the redox, oxidized form. NADP is used by all forms of cellular life. NADP is essential for life because it is needed for cellular respiration. NADP differs from NAD+, NAD by the presence of an additional phosphate group on the 2' position of the ribose ring that carries the adenine Moiety (chemistry), moiety. This extra phosphate is added by NAD+ kinase, NAD+ kinase and removed by NADP+ phosphatase. Biosynthesis NADP In general, NADP+ is synthesized before NADPH is. Such a reaction usually starts with NAD+, NAD+ from either the de-novo or the salvage pathway, with NAD+ kinase, NAD+ kinase adding the extra phosphate g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavonoid
Flavonoids (or bioflavonoids; from the Latin word ''flavus'', meaning yellow, their color in nature) are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans. Chemically, flavonoids have the general structure of a 15-carbon skeleton, which consists of two phenyl rings (A and B) and a Heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic ring (C, the ring containing the embedded oxygen). This carbon structure can be abbreviated C6-C3-C6. According to the IUPAC nomenclature, they can be classified into: *flavonoids or bioflavonoids *isoflavonoids, derived from 3-phenylchromone, chromen-4-one (3-phenyl-1,4-benzopyran, benzopyrone) structure *neoflavonoids, derived from 4-phenylcoumarin (4-phenyl-1,2-benzopyran, benzopyrone) structure The three flavonoid classes above are all ketone-containing compounds and as such, anthoxanthins (flavones and flavonols). This class was the first to be termed bioflavonoids. The terms flavonoid and bioflavo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
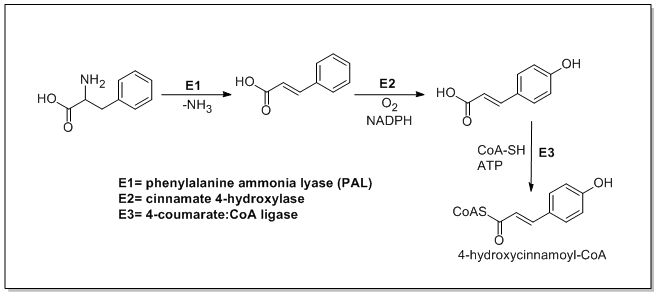
Phenylpropanoid Biosynthesis
The biosynthesis of phenylpropanoids involves a number of enzymes. From amino acids to cinnamates In plants, all phenylpropanoids are derived from the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL, a.k.a. phenylalanine/tyrosine ammonia-lyase) is an enzyme that transforms L-phenylalanine and tyrosine into trans-cinnamic acid and p-coumaric acid, ''p''-coumaric acid, respectively. Trans-cinnamate 4-monooxygenase (cinnamate 4-hydroxylase) is the enzyme that transforms trans-cinnamate into 4-hydroxycinnamate (''p''-coumaric acid). 4-Coumarate-CoA ligase is the enzyme that transforms 4-coumarate (''p''-coumaric acid) into 4-coumaroyl-CoA. Enzymes associated with biosynthesis of hydroxycinnamic acids * Cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD), an enzyme that transforms cinnamyl alcohol into cinnamaldehyde * Sinapine esterase, an enzyme that transforms sinapoylcholine into sinapate (sinapic acid) and choline * Trans-cinnamate 2-monooxygenase, an enzyme that tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituent, substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of alanine. This essential amino acid is classified as neutral, and chemical polarity, nonpolar because of the inert and hydrophobic nature of the benzyl side chain. The chirality (chemistry)#Naming conventions, L-isomer is used to biochemically form proteins coded for by DNA. Phenylalanine is a precursor for tyrosine, the monoamine neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), and the biological pigment melanin. It is Genetic code, encoded by the messenger RNA codons UUU and UUC. Phenylalanine is found naturally in the milk of mammals. It is used in the manufacture of food and drink products and sold as a nutritional supplement as it is a direct precursor to the neuromodulation, neuromodulator phe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylketonuria
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an inborn error of metabolism that results in decreased metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine. Untreated PKU can lead to intellectual disability, seizures, behavioral problems, and mental disorders. It may also result in a musty smell and lighter skin. A baby born to a mother who has poorly treated PKU may have heart problems, a small head, and low birth weight. Phenylketonuria is an inherited genetic disorder. It is caused by mutations in the '' PAH'' gene, which can result in inefficient or nonfunctional phenylalanine hydroxylase, an enzyme responsible for the metabolism of excess phenylalanine. This results in the buildup of dietary phenylalanine to potentially toxic levels. It is autosomal recessive, meaning that both copies of the gene must be mutated for the condition to develop. The two main types are classic PKU and variant PKU, depending on whether any enzyme function remains. Those with one copy of a mutated gene typically do not ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Essential Amino Acid
An essential amino acid, or indispensable amino acid, is an amino acid that cannot be synthesized from scratch by the organism fast enough to supply its demand, and must therefore come from the diet. Of the 21 amino acids common to all life forms, the nine amino acids humans cannot synthesize are valine, isoleucine, leucine, methionine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, threonine, histidine, and lysine. Six other amino acids are considered conditionally essential in the human diet, meaning their synthesis can be limited under special pathophysiological conditions, such as prematurity in the infant or individuals in severe catabolic distress. These six are arginine, cysteine, glycine, glutamine, proline, and tyrosine. Six amino acids are non-essential (dispensable) in humans, meaning they can be synthesized in sufficient quantities in the body. These six are alanine, aspartic acid, asparagine, glutamic acid, serine, and selenocysteine (considered the 21st amino acid). Pyrr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromatic beta carbon substituent. Tryptophan is also a precursor to the neurotransmitter serotonin, the hormone melatonin, and vitamin B3 (niacin). It is encoded by the codon UGG. Like other amino acids, tryptophan is a zwitterion at physiological pH where the amino group is protonated (–; pKa = 9.39) and the carboxylic acid is deprotonated ( –COO−; pKa = 2.38). Humans and many animals cannot synthesize tryptophan: they need to obtain it through their diet, making it an essential amino acid. Tryptophan is named after the digestive enzymes trypsin, which were used in its first isolation from casein proteins. It was assigned the one-letter symbol W based on the double ring being visually suggestive to the bulky letter. Function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Greek ''tyrós'', meaning ''cheese'', as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheese. It is called tyrosyl when referred to as a functional group or side chain. While tyrosine is generally classified as a hydrophobic amino acid, it is more hydrophilic than phenylalanine. It is encoded by the codons UAC and UAU in messenger RNA. The one-letter symbol Y was assigned to tyrosine for being alphabetically nearest of those letters available. Note that T was assigned to the structurally simpler threonine, U was avoided for its similarity with V for valine, W was assigned to tryptophan, while X was reserved for undetermined or atypical amino acids. The mnemonic t''Y''rosine was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituent, substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of alanine. This essential amino acid is classified as neutral, and chemical polarity, nonpolar because of the inert and hydrophobic nature of the benzyl side chain. The chirality (chemistry)#Naming conventions, L-isomer is used to biochemically form proteins coded for by DNA. Phenylalanine is a precursor for tyrosine, the monoamine neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), and the biological pigment melanin. It is Genetic code, encoded by the messenger RNA codons UUU and UUC. Phenylalanine is found naturally in the milk of mammals. It is used in the manufacture of food and drink products and sold as a nutritional supplement as it is a direct precursor to the neuromodulation, neuromodulator phe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromatic Amino Acid
An aromatic amino acid is an amino acid that includes an aromaticity, aromatic ring. Among the 20 standard amino acids, histidine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, tyrosine, are classified as aromatic. Properties and function Optical properties Aromatic amino acids, excepting histidine, absorb Ultraviolet, ultraviolet light above and beyond 250 nm and will fluorescence, fluoresce under these conditions. This characteristic is used in quantitative analysis, notably in determining the concentrations of these amino acids in solution. Most proteins Absorption spectroscopy, absorb at 280 nm due to the presence of tyrosine and tryptophan. Of the aromatic amino acids, tryptophan has the highest extinction coefficient; its absorption maximum occurs at 280 nm. The absorption maximum of tyrosine occurs at 274 nm. Role in protein structure and function Aromatic amino acids stabilize folded structures of many proteins. Aromatic residues are found predominantly sequestered within the cores o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alga
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular microalgae, such as cyanobacteria, '' Chlorella'', and diatoms, to multicellular macroalgae such as kelp or brown algae which may grow up to in length. Most algae are aquatic organisms and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem, and phloem that are found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds. In contrast, the most complex freshwater forms are the Charophyta, a division of green algae which includes, for example, ''Spirogyra'' and stoneworts. Algae that are carried passively by water are plankton, specifically phytoplankton. Algae constitute a polyphyletic group because they do not include a common ancestor, and although eukaryotic algae with chlorophyll-bearing plastids seem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |