|
Shadow Effect (Genetics)
The shadow effect is a phenomenon seen in genetic studies that use noninvasive genetic data collection methods. It occurs when there are not enough loci and/or loci that have low variance of alleles within the population. As a result, researchers can capture two separate individuals and mistakenly label them as the same individual. This can create a negative bias in the data and portray a population as smaller and less genetically diverse than it is. This is most commonly seen in collection methods that rely on environmental DNA (eDNA) which is collected directly from the environment (such as feces or hair removed from the ground). The accuracy of non-invasive collection data can be increased by increasing the amount of loci being examined during the study. Background There are several types of rarefaction methods that can be used to estimate the size of a hard monitor species. The study of population size and density falls under demography, the study of populations of any kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian friar working in the 19th century in Brno, was the first to study genetics scientifically. Mendel studied "trait inheritance", patterns in the way traits are handed down from parents to offspring over time. He observed that organisms (pea plants) inherit traits by way of discrete "units of inheritance". This term, still used today, is a somewhat ambiguous definition of what is referred to as a gene. Phenotypic trait, Trait inheritance and Molecular genetics, molecular inheritance mechanisms of genes are still primary principles of genetics in the 21st century, but modern genetics has expanded to study the function and behavior of genes. Gene structure and function, variation, and distribution are studied within the context of the Cell (bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Diversity
Genetic diversity is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. It ranges widely, from the number of species to differences within species, and can be correlated to the span of survival for a species. It is distinguished from '' genetic variability'', which describes the tendency of genetic characteristics to vary. Genetic diversity serves as a way for populations to adapt to changing environments. With more variation, it is more likely that some individuals in a population will possess variations of alleles that are suited for the environment. Those individuals are more likely to survive to produce offspring bearing that allele. The population will continue for more generations because of the success of these individuals. The academic field of population genetics includes several hypotheses and theories regarding genetic diversity. The neutral theory of evolution proposes that diversity is the result of the accumulation of neutral substitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental DNA
Environmental DNA or eDNA is DNA that is collected from a variety of environmental samples such as soil, seawater, snow or air, rather than directly sampled from an individual organism. As various organisms interact with the environment, DNA is expelled and accumulates in their surroundings from various sources. Such eDNA can be DNA sequencing#High-throughput methods, sequenced by environmental omics to reveal facts about the species that are present in an ecosystem — even microscopic ones not otherwise apparent or detectable. In recent years, eDNA has been used as a tool to detect endangered wildlife that were otherwise unseen. In 2020, human health researchers began repurposing eDNA techniques to track the COVID-19 pandemic. Example sources of eDNA include, but are not limited to, feces, mucus, gametes, Moulting, shed skin, Carrion, carcasses and hair. Samples can be analyzed by High throughput sequencing, high-throughput DNA sequencing methods, known as metagenomics, Mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
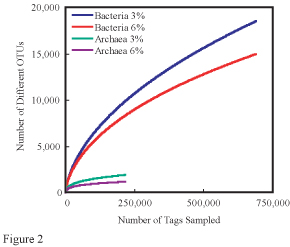
Rarefaction (ecology)
In ecology, rarefaction is a technique to assess species richness from the results of sampling. Rarefaction allows the calculation of species richness for a given number of individual samples, based on the construction of so-called rarefaction curves. This curve is a plot of the number of species as a function of the number of samples. Rarefaction curves generally grow rapidly at first, as the most common species are found, but the curves plateau as only the rarest species remain to be sampled. The issue that occurs when sampling various species in a community is that the larger the number of individuals sampled, the more species that will be found. Rarefaction curves are created by randomly re-sampling the pool of ''N'' samples multiple times and then plotting the average number of species found in each sample (1,2, ... N). "Thus rarefaction generates the expected number of species in a small collection of ''n'' individuals (or ''n'' samples) drawn at random from the large pool o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demography
Demography () is the statistical study of human populations: their size, composition (e.g., ethnic group, age), and how they change through the interplay of fertility (births), mortality (deaths), and migration. Demographic analysis examines and measures the dimensions and dynamics of populations; it can cover whole societies or groups defined by criteria such as education, nationality, religion, and ethnicity. Educational institutions usually treat demography as a field of sociology, though there are a number of independent demography departments. These methods have primarily been developed to study human populations, but are extended to a variety of areas where researchers want to know how populations of social actors can change across time through processes of birth, death, and migration. In the context of human biological populations, demographic analysis uses administrative records to develop an independent estimate of the population. Demographic analysis estima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark And Recapture
Mark and recapture is a method commonly used in ecology to estimate an animal population's size where it is impractical to count every individual. A portion of the population is captured, marked, and released. Later, another portion will be captured and the number of marked individuals within the sample is counted. Since the number of marked individuals within the second sample should be proportional to the number of marked individuals in the whole population, an estimate of the total population size can be obtained by dividing the number of marked individuals by the proportion of marked individuals in the second sample. The method assumes, rightly or wrongly, that the probability of capture is the same for all individuals. Other names for this method, or closely related methods, include capture-recapture, capture-mark-recapture, mark-recapture, sight-resight, mark-release-recapture, multiple systems estimation, band recovery, the Petersen method, and the Lincoln method. Another ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Collection
Data collection or data gathering is the process of gathering and measuring information on targeted variables in an established system, which then enables one to answer relevant questions and evaluate outcomes. Data collection is a research component in all study fields, including physical science, physical and social sciences, humanities, and business. While methods vary by discipline, the emphasis on ensuring accurate and honest collection remains the same. The goal for all data collection is to capture evidence that allows data analysis to lead to the formulation of credible answers to the questions that have been posed. Regardless of the field of or preference for defining data (Quantitative method, quantitative or Qualitative method, qualitative), accurate data collection is essential to maintain research integrity. The selection of appropriate data collection instruments (existing, modified, or newly developed) and delineated instructions for their correct use reduce the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endangered Species
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, invasive species, and climate change. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List lists the global conservation status of many species, and various other agencies assess the status of species within particular areas. Many nations have laws that protect conservation-reliant species which, for example, forbid hunting, restrict land development, or create protected areas. Some endangered species are the target of extensive conservation efforts such as captive breeding and habitat restoration. Human activity is a significant cause in causing some species to become endangered. Conservation status The conservation status of a species indicates the likelihood that it will become extinct. Multiple factors are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
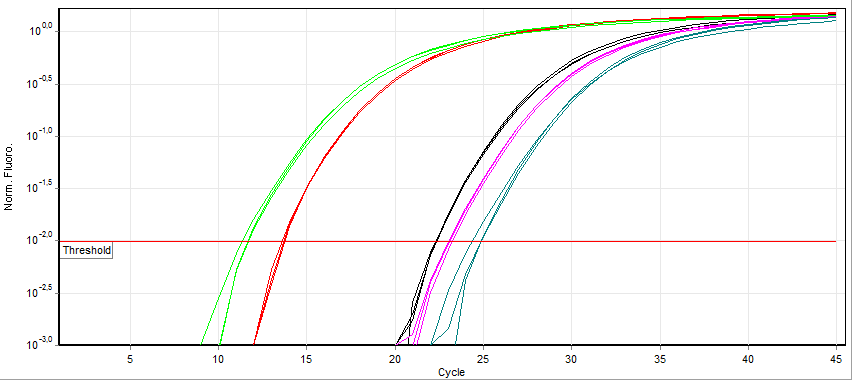
Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction
A real-time polymerase chain reaction (real-time PCR, or qPCR when used quantitatively) is a laboratory technique of molecular biology based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It monitors the amplification of a targeted DNA molecule during the PCR (i.e., in real time), not at its end, as in conventional PCR. Real-time PCR can be used quantitatively and semi-quantitatively (i.e., above/below a certain amount of DNA molecules). Two common methods for the detection of PCR products in real-time PCR are (1) non-specific fluorescent dyes that Intercalation (biochemistry), intercalate with any double-stranded DNA and (2) sequence-specific DNA probes consisting of oligonucleotides that are labelled with a fluorescence, fluorescent reporter, which permits detection only after nucleic acid hybridisation, hybridization of the probe with its complementary sequence. The Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments (MIQE) guidelines propose that the abb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
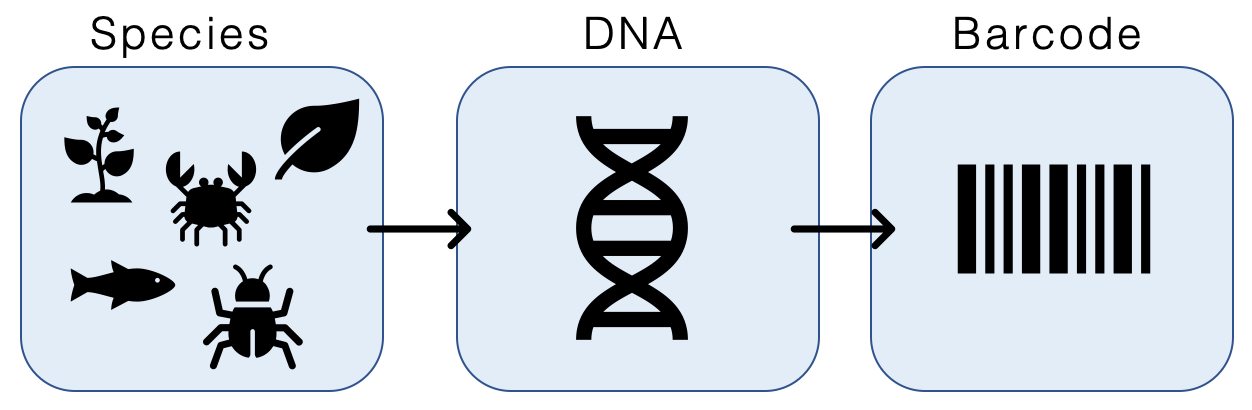
DNA Barcoding
DNA barcoding is a method of species identification using a short section of DNA from a specific gene or genes. The premise of DNA barcoding is that by comparison with a reference library of such DNA sections (also called " sequences"), an individual sequence can be used to uniquely identify an organism to species, just as a supermarket scanner uses the familiar black stripes of the UPC barcode to identify an item in its stock against its reference database. These "barcodes" are sometimes used in an effort to identify unknown species or parts of an organism, simply to catalog as many taxa as possible, or to compare with traditional taxonomy in an effort to determine species boundaries. Different gene regions are used to identify the different organismal groups using barcoding. The most commonly used barcode region for animals and some protists is a portion of the cytochrome ''c'' oxidase I (COI or COX1) gene, found in mitochondrial DNA. Other genes suitable for DNA barcoding a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bias (statistics)
In the field of statistics, bias is a systematic tendency in which the methods used to gather data and estimate a sample statistic present an inaccurate, skewed or distorted ('' biased'') depiction of reality. Statistical bias exists in numerous stages of the data collection and analysis process, including: the source of the data, the methods used to collect the data, the estimator chosen, and the methods used to analyze the data. Data analysts can take various measures at each stage of the process to reduce the impact of statistical bias in their work. Understanding the source of statistical bias can help to assess whether the observed results are close to actuality. Issues of statistical bias has been argued to be closely linked to issues of statistical validity. Statistical bias can have significant real world implications as data is used to inform decision making across a wide variety of processes in society. Data is used to inform lawmaking, industry regulation, corp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microtus Cabrerae
Cabrera's vole (''Microtus cabrerae'') is a species of vole native to Spain and Portugal. It is named for Ángel Cabrera, a mammalogist then working at the Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales in Madrid. It is the only living member of the subgenus ''Iberomys'', although two fossil species are also known, including ''M. brecciensis'', the likely direct ancestor of the living species. Description Cabrera's vole is one of the largest voles in the genus ''Microtus'', with a body length of and a tail in length. Adults weigh between , up to five times more than other voles native to Spain and Portugal. They have long, thick fur which is brownish olive over most of the body and yellowish in colour on the underparts. The guard hairs are particularly long, reaching as far as out from the body, greater than that in any other ''Microtus'' species. Internally, the caecum is longer than that in most other voles, relative to body size, a feature that may be related to its specialised diet. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |