|
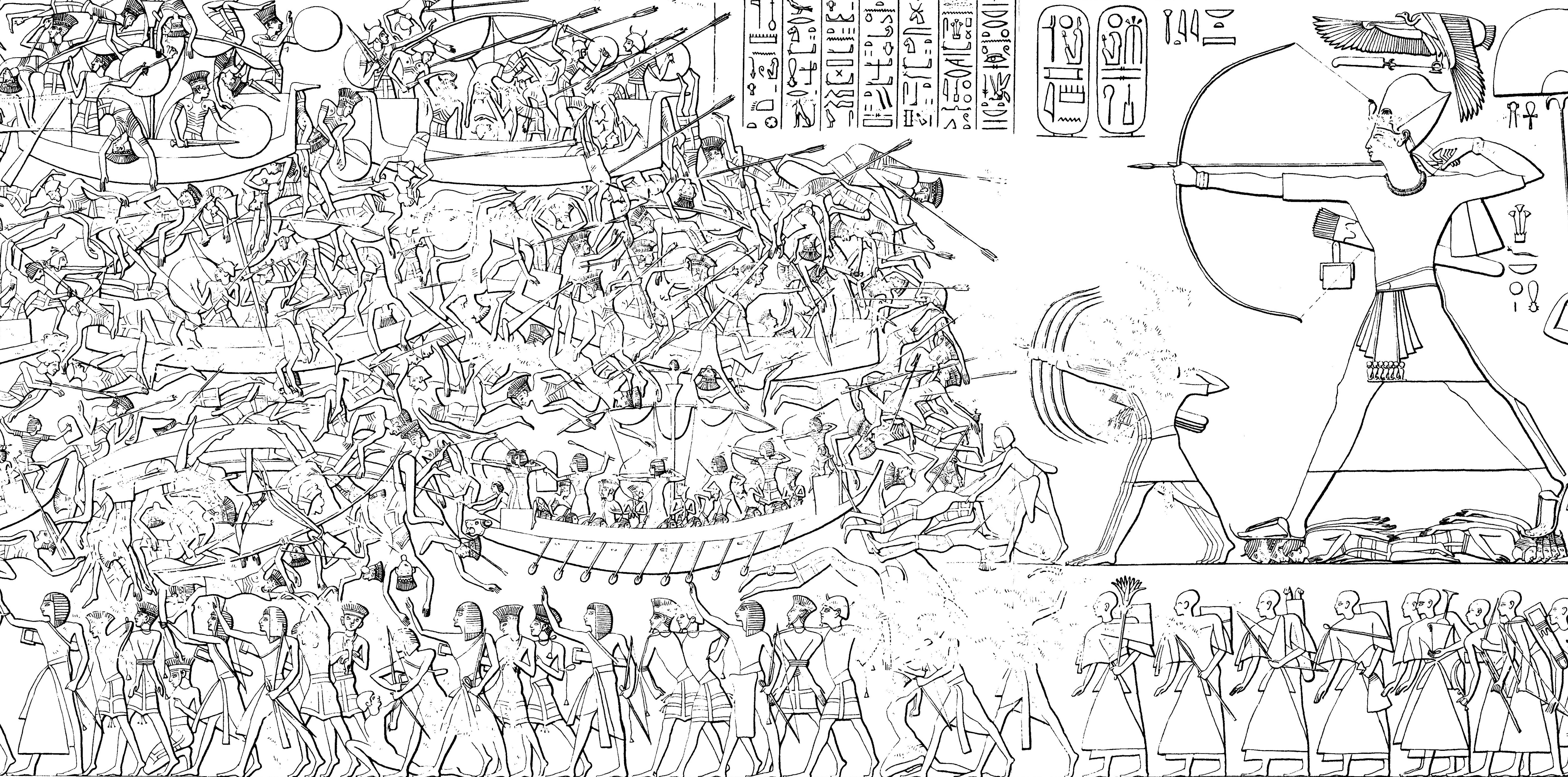
Setnakhte
Userkhaure-setepenre Setnakhte (also called Setnakht or Sethnakht) was the first pharaoh (1180s BC, 1189 BC–1180s BC, 1186 BC) of the Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt, Twentieth Dynasty of the New Kingdom of Egypt and the father of Ramesses III. Accession Setnakhte was not the son, brother or a direct descendant of either Twosret or Siptah, Merneptah Siptah—the immediately preceding two pharaohs—nor that of Siptah's predecessor Seti II, whom Ramesses III, Setnakhte's son, formally considered the last legitimate ruler in his Medinet Habu kinglist. Setnakhte was a man of unknown origins who seized the throne during a time of crisis and political unrest likely from Twosret and he was presumably a minor descendant of Ramesses II through a separate family line from that of Seti II, Siptah and Twosret. As Aidan Dodson writes, Setnakhte's accession to power as an usurper is confirmed by a victory stela at Elephantine at Aswan, which shows his rise to power was accompanied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twosret
Tausret, also spelled ''Tawosret'' or ''Twosret'' (d. 1189 BCE) was the last known ruler and the final pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt. She is recorded in Manetho's ''Epitome'' as "Thuoris, who in Homer is called Polybus, husband of Alcandra, and in whose time Troy was taken."J. Tyldesley, Chronicle of the Queens of Egypt, 2006, Thames & Hudson She was said to have ruled Egypt for seven years, but this figure included the nearly six-year reign of Siptah, her predecessor. Tausret simply assumed Siptah's regnal years as her own. While her sole independent reign would have lasted for perhaps one to one and a half years, from 1191-89 BC, this number now appears more likely to be two full years instead, possibly longer. Excavation work by the Richard H. Wilkinson, University of Arizona Egyptian Expedition on her memorial temple ("temple of millions of years") at Gournah strongly suggests that it was completed and functional during her reign and that Tausret started a regnal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twentieth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XX, alternatively 20th Dynasty or Dynasty 20) is the third and last dynasty of the Ancient Egyptian New Kingdom period, lasting from 1189 BC to 1077 BC. The 19th and 20th Dynasties together constitute an era known as the Ramesside period owing to the predominance of rulers with the given name "Ramesses". This dynasty is generally considered to mark the beginning of the decline of Ancient Egypt at the transition from the Late Bronze to Iron Age. During the period of the Twentieth Dynasty, Ancient Egypt faced the crisis of invasions by Sea Peoples. The dynasty successfully defended Egypt, while sustaining heavy damage. History After the death of the last pharaoh of the 19th Dynasty, Queen Twosret, Egypt entered into a period of civil war. Because of lost historical records, the cause of the civil war is unknown. The war was ended with the accession to the throne by Setnakhte, who founded the 20th Dynasty of Egypt. From the reign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiy-Merenese
Tiy-Merenese,J. Tyldesley, Chronicle of the Queens of Egypt, 2006, Thames & Hudson Teye-Merenaset,Grajetski, Ancient Egyptian Queens: a hieroglyphic dictionary, Golden House Publications Tiye-MerenisetAidan Dodson & Dyan Hilton, The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt, Thames & Hudson (2004) ''(Tiy, Beloved of Isis)'' was the Great Royal Wife of pharaoh Setnakhte and mother of Ramesses III of the Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt. She is the only known wife of Setnakhte. She was depicted together with her husband on a stela A stele ( ) or stela ( )The plural in English is sometimes stelai ( ) based on direct transliteration of the Greek, sometimes stelae or stelæ ( ) based on the inflection of Greek nouns in Latin, and sometimes anglicized to steles ( ) or stela ... in Abydos. A priest named Meresyotef is shown adoring Setnakhte and Tiy-Merenese and their son Ramesses III is shown making offerings. Tiye-Merenese also appears on blocks found in Abydos which were reused in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KV14
Tomb KV14 is a joint tomb, used originally by Tausert and then reused and extended by Setnakhte. It has been open since antiquity, but was not properly recorded until Hartwig Altenmüller excavated it from 1983 to 1987. Located in the main body of the Valley of the Kings, it has two burial chambers, the later extensions making the tomb one of the largest of the Royal Tombs, at over 112 metres long. The original decoration showing the female Twosret was replaced with those of the male Setnakhte. It is possible that Seti II was also buried in KV14 before being subsequently moved to the hastily finished KV15, perhaps by Setnakhte, in order to take over KV14 for his own tomb. Gallery File:Burial Chamber of Tomb KV14.jpg, Sarcophagus view File:Égypte, Vallée des Rois, Nécropole thébaine, Tombe de la reine Taousert Setnakht (KV 14), Anubis (49835127627).jpg, Anubis File:Égypte, Vallée des Rois, Nécropole thébaine, Tombe de la reine Taousert Setnakht (KV 14) (49835129007) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramesses III
Usermaatre Meryamun Ramesses III was the second Pharaoh of the Twentieth dynasty of Egypt, Twentieth Dynasty in Ancient Egypt. Some scholars date his reign from 26 March 1186 to 15 April 1155 BC, and he is considered the last pharaoh of the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom to have wielded substantial power. His long reign saw the decline of Egyptian political and economic power, linked to a series of invasions and internal economic problems that also plagued pharaohs before him. This coincided with a decline in the cultural sphere of Ancient Egypt. However, his successful defense was able to slow down the decline, although it still meant that his successors would have a weaker military. He has also been described as a "warrior Pharaoh" due to his strong military strategies. He led the way by defeating the invaders known as "the Sea Peoples", who had caused destruction in other civilizations and empires. He was able to save Egypt from collapsing at the time when Late Bronze Age c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Per (hieroglyph)
Pr (𓉐 Gardiner sign listed no. O1) is the hieroglyph for 'house', the floor-plan of a walled building with an open doorway. While its original pronunciation is not known with certainty, modern Egyptology assigns it the value of ''per'', but purely on the basis of a convention specific to the discipline. However, the Ancient Greek rendering of the title ''pr-`3'' as suggests the reconstruction of the historical (Late Egyptian) pronunciation as *''par'', see Pharaoh#Etymology. Pr combined with an associated "personal name", god, or location becomes the ''"house of .... ."'' An example for pharaoh Setnakhte is the city of: Pr-Atum, (city of Pithom). Pr and ankh-(life) is a "combination hieroglyph" and is the "word" for ''house of life''. The "house of life" is a library for papyrus books-(scrolls), as well as a possible scriptorium. The shape of ''pr'' in beginning dynasties had variations in the shape of a square, with the opening. See Garrett Reference for tomb of ''O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Kingdom Of Egypt
The New Kingdom, also called the Egyptian Empire, refers to ancient Egypt between the 16th century BC and the 11th century BC. This period of History of ancient Egypt, ancient Egyptian history covers the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth, Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Nineteenth, and Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt, Twentieth dynasties. Through radiocarbon dating, the establishment of the New Kingdom has been placed between 1570 and 1544 BC. The New Kingdom followed the Second Intermediate Period of Egypt, Second Intermediate Period and was succeeded by the Third Intermediate Period of Egypt, Third Intermediate Period. It was the most prosperous time for the Egyptians#History, Egyptian people and marked the peak of Egypt's power. In 1845, the concept of a "New Kingdom" as Periodization of ancient Egypt, one of three "golden ages" was coined by German scholar Christian Charles Josias von Bunsen; the original definition would evolve significantly throughout the 19th and 20th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nineteenth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XIX), also known as the Ramessid dynasty, is classified as the second Dynasty of the Ancient Egyptian New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom period, lasting from 1292 BC to 1189 BC. The 19th Dynasty and the 20th Dynasty furthermore together constitute an era known as the ''Ramesside period''. This Dynasty was founded by Vizier (Ancient Egypt), Vizier Ramesses I, whom Pharaoh Horemheb chose as his successor to the throne. History Background The warrior kings of the early Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, 18th Dynasty had encountered only little resistance from neighbouring kingdoms, allowing them to expand their realm of influence easily, but the international situation had changed radically towards the end of the dynasty. The Hittites had gradually extended their influence into Syria and Canaan to become a major power in international politics, a power that both Seti I and his son Ramesses II would confront in the future. 19th Dynasty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zahi Hawass
Zahi Abass Hawass (; born May 28, 1947) is an Egyptians, Egyptian archaeology, archaeologist, Egyptology, Egyptologist, and former Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities (Egypt), Minister of Tourism and Antiquities, a position he held twice. He has worked at archaeological sites in the Nile Delta, the Western Desert (Egypt), Western Desert and the Upper and Lower Egypt, Upper Nile Valley. Early life Hawass was born in a small village near Damietta, Egypt. Although he originally dreamed of becoming an attorney, he obtained a Bachelor of Arts degree in Greek and Roman Archaeology from Alexandria University in 1967. In 1979, Hawass earned a diploma in Egyptology from Cairo University. He then worked at the Great Pyramids as an inspector—a combination of administrator and archaeologist. When he was 33 years old, Hawass was awarded a Fulbright Fellowship to attend the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia to study Egyptology, earning a Master of Arts degree in the subject and also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartzite
Quartzite is a hard, non- foliated metamorphic rock that was originally pure quartz sandstone.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak, p 182 Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tectonic compression within orogenic belts, and hence quartzite is a metasandstone. Pure quartzite is usually white to grey, though quartzites often occur in various shades of pink and red due to varying amounts of hematite. Other colors, such as yellow, green, blue and orange, are due to other minerals. The term ''quartzite'' is also sometimes used for very hard but unmetamorphosed sandstones that are composed of quartz grains thoroughly cemented with additional quartz. Such sedimentary rock has come to be described as orthoquartzite to distinguish it from metamorphic quartzite, which is sometimes called metaquartzite to emphasize its metamorphic origins. Quartzite is very resistant to chemical weathering and often forms ridges and resist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Ahram Weekly
''Al-Ahram Weekly'' is an English-language weekly broadsheet printed by the Al-Ahram Publishing House in Cairo, Egypt. History and profile ''Al Ahram Weekly'' was established in 1991 by the ''Al-Ahram'' newspaper, which also runs a French-language weekly version, '' Al-Ahram Hebdo''. Between 1991 and 2003, founder Hosni Guindi, served as the editor-in-chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The editor-in-chief heads all departments of the organization and is held accoun ... and Hani Shukrallah as managing editor and co-founder Mona Anis as deputy editor-in-chief. After Hosni's death in 2003, Shukrallah succeeded him as acting editor. In 2005 Egypt's Shura Council appointed Assem El-Qersh as the paper's editor-in-chief, replacing Shukrallah. In June 2014, Galal Nassar was appointed editor-in-chief of the weekly. The circulation of the magazine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmose I
Ahmose I (''Amosis'', ''Aahmes''; meaning "Iah (the Moon) is born") was a pharaoh and founder of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt in the New Kingdom of Egypt, the era in which ancient Egypt achieved the peak of its power. His reign is usually dated to the mid-16th century BC at the beginning of the Late Bronze Age. During his reign, Ahmose completed the conquest and expulsion of the Hyksos, restored Theban rule over Lower- and Upper Egypt, and successfully reasserted Egyptian power in its formerly subject territories of Nubia and Canaan. He then reorganized the administration of the country, reopened quarry, quarries, mining, mines and trade routes and began massive construction projects of a type that had not been undertaken since the time of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom. This building program culminated in the construction of the last Egyptian pyramids, pyramid built by native Egyptian rulers. Ahmose's reign laid the foundations for the New Kingdom of Egypt, New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |