|
Servo (radio Control)
Servos (also RC servos) are small, cheap, mass-produced servomotors or other actuators used for radio control and small-scale robotics. Most servos are rotary actuators although other types are available. Linear actuators are sometimes used, although it is more common to use a rotary actuator with a bellcrank and pushrod. Some types, originally used as sail winches for model yachting, can rotate continuously. Construction A typical servo consists of a small electric motor driving a train of reduction gears. A potentiometer is connected to the output shaft. Some simple electronics provide a closed-loop servomechanism. Operation The position of the output, measured by the potentiometer, is continually compared to the commanded position from the control (i.e., the radio control). Any difference gives rise to an error signal in the appropriate direction, which drives the electric motor either forwards or backwards, and moving the output shaft to the commanded position. When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micro Servo
Micro may refer to: Measurement * micro- (μ), a metric prefix denoting a factor of 10−6 Places * Micro, North Carolina, town in U.S. People * DJ Micro, (born Michael Marsicano) an American trance DJ and producer * Chii Tomiya (都宮 ちい, born 1991), Japanese female professional wrestler, ring name Micro * Micro, Nishimiya Yūki (born 1980), Japanese musician, member of the pop band Def Tech Arts, entertainment, and media * Micro (comics), often known as Micro, a character in Marvel Comics * ''Micro'' (novel), techno-thriller by Michael Crichton, published posthumously in 2011 * Micro (Thai band), a Thai rock band formed in 1983 * ''IEEE Micro'', a peer-reviewed scientific journal * International Symposium on Microarchitecture, an academic conference focus on microarchitecture * Micromanagement (gameplay), the handling of detailed gameplay elements, such as individual units in realtime strategy games Brands and enterprises * Micro Cars, Sri Lankan automobile comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
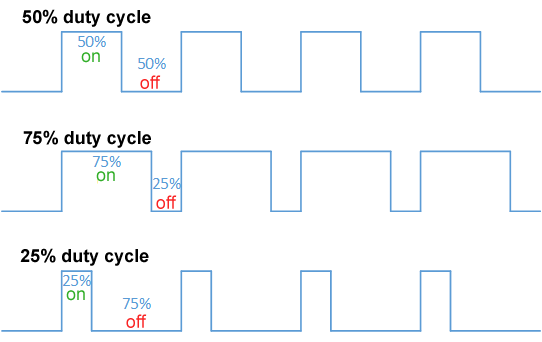
Pulse-width Modulation
Pulse-width modulation (PWM), also known as pulse-duration modulation (PDM) or pulse-length modulation (PLM), is any method of representing a signal as a rectangular wave with a varying duty cycle (and for some methods also a varying period). PWM is useful for controlling the average power or amplitude delivered by an electrical signal. The average value of voltage (and current) fed to the load is controlled by switching the supply between 0 and 100% at a rate faster than it takes the load to change significantly. The longer the switch is on, the higher the total power supplied to the load. Along with maximum power point tracking (MPPT), it is one of the primary methods of controlling the output of solar panels to that which can be utilized by a battery. PWM is particularly suited for running inertial loads such as motors, which are not as easily affected by this discrete switching. The goal of PWM is to control a load; however, the PWM switching frequency must be sele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newton (unit)
The newton (symbol: N) is the unit of force in the International System of Units (SI). Expressed in terms of SI base units, it is 1 kg⋅m/s2, the force that accelerates a mass of one kilogram at one metre per second squared. The unit is named after Isaac Newton in recognition of his work on classical mechanics, specifically his second law of motion. Definition A newton is defined as 1 kg⋅m/s2 (it is a named derived unit defined in terms of the SI base units). One newton is, therefore, the force needed to accelerate one kilogram of mass at the rate of one metre per second squared in the direction of the applied force. The units "metre per second squared" can be understood as measuring a rate of change in velocity per unit of time, i.e. an increase in velocity by one metre per second every second. In 1946, the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) Resolution 2 standardized the unit of force in the MKS system of units to be the amount need ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radian
The radian, denoted by the symbol rad, is the unit of angle in the International System of Units (SI) and is the standard unit of angular measure used in many areas of mathematics. It is defined such that one radian is the angle subtended at the centre of a circle by an Circular arc, arc that is equal in length to the radius. The unit was formerly an SI supplementary unit and is currently a dimensionless unit, dimensionless SI derived unit,: "The CGPM decided to interpret the supplementary units in the SI, namely the radian and the steradian, as dimensionless derived units." defined in the SI as 1 rad = 1 and expressed in terms of the SI base unit metre (m) as . Angles without explicitly specified units are generally assumed to be measured in radians, especially in mathematical writing. Definition One radian is defined as the angle at the center of a circle in a plane that wikt:subtend, subtends an arc whose length equals the radius of the circle. More generally, the magnit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational analogue of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. When being referred to as moment of force, it is commonly denoted by . Just as a linear force is a push or a pull applied to a body, a torque can be thought of as a twist applied to an object with respect to a chosen point; for example, driving a screw uses torque to force it into an object, which is applied by the screwdriver rotating around its axis to the drives on the head. Historical terminology The term ''torque'' (from Latin , 'to twist') is said to have been suggested by James Thomson and appeared in print in April, 1884. Usage is attested the same year by Silvanus P. Thompson in the first edition of ''Dynamo-Electric Machinery''. Thompson describes his usage of the term as follows: Today, torque is referred to using d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium-ion Polymer Battery
A lithium polymer battery, or more correctly, lithium-ion polymer battery (abbreviated as LiPo, LIP, Li-poly, lithium-poly, and others), is a rechargeable battery derived from lithium-ion and lithium-metal battery technology. The primary difference is that instead of using a liquid Lithium salt (such as lithium hexafluorophosphate, LiPF6) held in an organic solvent (such as EC/ DMC/ DEC) as the electrolyte, the battery uses a solid (or semi-solid) polymer electrolyte such as polyethylene glycol (PEG), polyacrylonitrile (PAN), poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) or poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVdF). Other terms used in the literature for this system include hybrid polymer electrolyte (HPE), where "hybrid" denotes the combination of the polymer matrix, the liquid solvent, and the salt. Polymer electrolytes can be divided into two large categories: dry solid polymer electrolytes (SPE) and gel polymer electrolytes (GPE). In comparison to liquid electrolytes and solid organic electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battery Eliminator Circuit
In battery-powered equipment, a battery eliminator circuit (BEC) is an electronic voltage regulator used to power a subsystem at a different voltage without the need for a supplemental battery. BECs are commonly used in radio-controlled models, which need separate voltages to power the motor and the RC equipment. Radio-controlled (RC) models In an electric-powered radio-controlled model, the BEC is typically part of the electronic speed control (ESC). BEC allows such a model to carry only one battery (the motive power battery) instead of two (motive power, and a separate battery to operate the RC equipment). A BEC-equipped ESC meant for airplane use often incorporates a low-voltage-cutoff (LVC) circuit which can sense the voltage drop caused when the battery has little charge left. It then cuts the power to the 'drive' motor in order to provide the 'steering' servo(s) with enough power to be able to bring the model safely back to the operator. The power to the propeller is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Speed Control
An electronic speed control (ESC) is an electronic circuit that controls and regulates the speed of an electric motor. It may also provide reversing of the motor and dynamic braking. Miniature electronic speed controls are used in electrically powered radio controlled models. Full-size electric vehicles also have systems to control the speed of their drive motors. Function An electronic speed control follows a speed reference signal (derived from a throttle lever, joystick, or other manual input) and varies the switching rate of a network of field effect transistors (FETs). By adjusting the duty cycle or switching frequency of the transistors, the speed of the motor is changed. The rapid switching of the current flowing through the motor is what causes the motor itself to emit its characteristic high-pitched whine, especially noticeable at lower speeds. Different types of speed controls are required for brushed DC motors and brushless DC motors. A brushed motor can hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PID Controller
PID or Pid may refer to: Medicine * Pelvic inflammatory disease or pelvic inflammatory disorder, an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system * Primary immune deficiency, disorders in which part of the body's immune system is missing or does not function properly * Prolapsed intervertebral disc, commonly called a herniated disc Science, technology and engineering * BBC Programme Identifier, a unique identifier for a BBC television or radio programme brand, a season or series, or an individual episode * OBD-II PIDs (on-board diagnostics parameter IDs), requests for data through an OBD connector in automotive repair * Packet Identifier, a field in a MPEG transport stream#Packet Identifier (PID), MPEG transport stream packet * Partial information decomposition, an extension of information theory * Passive infrared detector, a passive infrared sensor * Payload Interface Document (used on space engineering program for example) * Persistent identifier, a long-lastin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiplexing
In telecommunications and computer networking, multiplexing (sometimes contracted to muxing) is a method by which multiple analog or digital signals are combined into one signal over a shared medium. The aim is to share a scarce resource—a physical transmission medium. For example, in telecommunications, several telephone calls may be carried using one wire. Multiplexing originated in telegraphy in the 1870s, and is now widely applied in communications. In telephony, George Owen Squier is credited with the development of telephone carrier multiplexing in 1910. The multiplexed signal is transmitted over a communication channel such as a cable. The multiplexing divides the capacity of the communication channel into several logical channels, one for each message signal or data stream to be transferred. A reverse process, known as demultiplexing, extracts the original channels on the receiver end. A device that performs the multiplexing is called a multiplexer (MUX), and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |