|
Service Integration Maturity Model
{{Dablink, This article is about a business transformation model. For other uses of the abbreviation SIMM, see SIMM (other). The Service Integration Maturity Model (SIMM) is a standardized model for organizations to guide their transformation to a service based business model. By having a standard maturity model, it becomes possible for the organizations or industry to benchmark their SIMM levels, to have a roadmap for transformation to assist their planning and for vendors to offer services and software against these benchmarks. SIMM may also serve as a framework for the transformation process that can be customized to suit the specific needs of organizations and assessments. This process is a simple sequence of steps: configure the assessment framework, determine the initial level of maturity, and determine the target level of maturity and a transformation path from initial to target level. The Service Integration Maturity Model (SIMM) helps an organization create a roa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
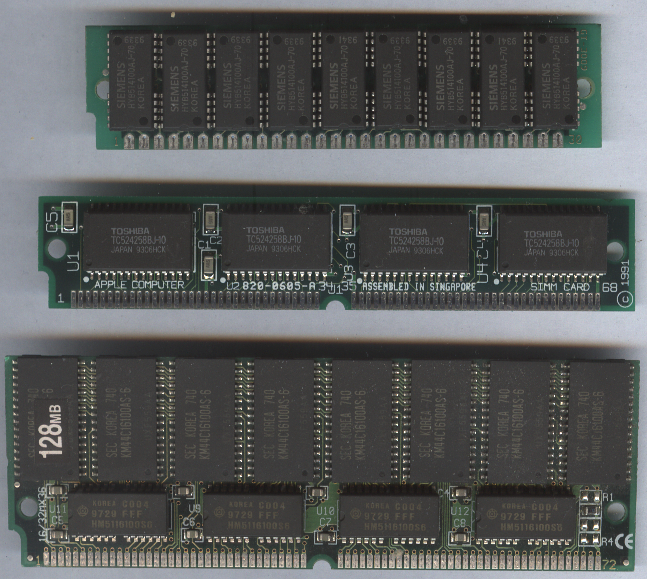
SIMM (other)
A SIMM (single in-line memory module) is a type of memory module containing random-access memory used in computers from the early 1980s to the early 2000s. It differs from a dual in-line memory module (DIMM), the most predominant form of memory module since the late 1990s, in that the contacts on a SIMM are redundant on both sides of the module. SIMMs were standardised under the JEDEC JESD-21C standard. Most early PC motherboards (8088-based PCs, XTs, and early ATs) used socketed DIP chips for DRAM. As computer memory capacities grew, memory modules were used to save motherboard space and ease memory expansion. Instead of plugging in eight or nine single DIP chips, only one additional memory module was needed to increase the memory of the computer. History SIMMs were invented in 1982 by James J. Parker at Zenith Microcircuits and the first Zenith Microcircuits customer was Wang Laboratories. Wang Laboratories tried to patent it and were granted a patent in April 1987. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Service Design
Service design is the activity of planning and arranging people, infrastructure, communication and material components of a service in order to improve its quality, and the interaction between the service provider and its users. Service design may function as a way to inform changes to an existing service or create a new service entirely. The purpose of service design methodologies is to establish the most effective practices for designing services, according to both the needs of users and the competencies and capabilities of service providers. If a successful method of service design is adapted then the service will be user-friendly and relevant to the users, while being sustainable and competitive for the service provider. For this purpose, service design uses methods and tools derived from different disciplines, ranging from ethnography to information and management science to interaction design. Service design concepts and ideas are typically portrayed visually, using differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maturity Model
Maturity is a measurement of the ability of an organization for continuous improvement in a particular discipline (as defined in O-ISM3 ). The higher the maturity, the higher will be the chances that incidents or errors will lead to improvements either in the quality or in the use of the resources of the discipline as implemented by the organization. Most maturity models assess qualitatively people/culture, processes/structures, and objects/technology. Two approaches for implementing maturity models exist. With a top-down approach, such as proposed by Becker et al., a fixed number of maturity stages or levels is specified first and further corroborated with characteristics (typically in form of specific assessment items) that support the initial assumptions about how maturity evolves. When using a bottom-up approach, such as suggested by Lahrmann et al., distinct characteristics or assessment items are determined first and clustered in a second step into maturity levels to induce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Group
The Open Group is a global consortium that seeks to "enable the achievement of business objectives" by developing "open, vendor-neutral technology standards and certifications." It has over 840 member organizations and provides a number of services, including strategy, management, innovation and research, standards, certification, and test development. It was established in 1996 when X/Open merged with the Open Software Foundation. The Open Group is the certifying body for the UNIX trademark, and publishes the Single UNIX Specification technical standard, which extends the POSIX standards. The Open Group also develops and manages the TOGAF® standard, which is an industry standard enterprise architecture framework. Members The over 840 members include a range of technology vendors and buyers as well as government agencies, including, for example, Capgemini, Fujitsu, HPE, Orbus Software, IBM, Huawei, Philips, the U.S. Department of Defense, and NASA. There is no obligation on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |