|
Serial Transmission
In telecommunication and data transmission, serial communication is the process of sending data one bit at a time, sequentially, over a communication channel or computer bus. This is in contrast to parallel communication, where several bits are sent as a whole, on a link with several parallel channels. Serial communication is used for all long-haul communication and most computer networks, where the cost of cable and difficulty of synchronization make parallel communication impractical. Serial computer buses have become more common even at shorter distances, as improved signal integrity and transmission speeds in newer serial technologies have begun to outweigh the parallel bus's advantage of simplicity (no need for serializer and deserializer, or SerDes) and to outstrip its disadvantages (clock skew, interconnect density). The migration from PCI to PCI Express (PCIe) is an example. Modern high speed serial interfaces such as PCIe send data several bits at a time using modu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serial And Parallel Data Transmission
Serial may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media The presentation of works in sequential segments * Serial (literature), serialised literature in print * Serial (publishing), periodical publications and newspapers * Serial (radio and television), series of radio and television programs that rely on a continuing plot * Serial film, a series of short subjects, with a continuing story, originally shown in theaters, in conjunction with feature films, particularly in the 1930s and 1940s * Indian serial, a type of Indian television program Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * Serial (1980 film), ''Serial'' (1980 film), based on McFadden's novel, starring Martin Mull and Tuesday Weld * Serial (podcast), ''Serial'' (podcast), a podcast spinoff of radio series ''This American Life'' * ''The Serial: A Year in the Life of Marin County'', a 1977 novel by Cyra McFadden Computing and technology * SerDes, a Serializer/Deserializer (pronounced sir-deez) * Serial ATA * Serial attach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Register
''The Register'' (often also called El Reg) is a British Technology journalism, technology news website co-founded in 1994 by Mike Magee (journalist), Mike Magee and John Lettice. The online newspaper's Nameplate_(publishing), masthead Logo, sublogo is "''Biting the hand that feeds IT''." The publication's primary focus is information technology news and opinions. Situation Publishing Ltd is the site's publisher. Drew Cullen is an owner and Linus Birtles is the managing director. Andrew Orlowski was the executive editor before leaving the website in May 2019. History ''The Register'' was founded in London as an email newsletter called ''Chip Connection''. In 1998 ''The Register'' became a daily online news source. Magee left in 2001 to start competing publications ''The Inquirer'', and later the ''IT Examiner'' and ''TechEye''. In 2002, ''The Register'' expanded to have a presence in London and San Francisco, creating ''The Register USA'' at theregus.com through a joint ventu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Over Ethernet
Power over Ethernet (PoE) describes any of several technical standard, standards or ad hoc systems that pass electric power along with data on twisted-pair Ethernet cabling. This allows a single cable to provide both a data connection and enough electricity to power networked devices such as wireless access points (WAPs), IP cameras and VoIP phones. Techniques There are several common techniques for transmitting power over Ethernet cabling, defined within the broader Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) IEEE 802.3, 802.3 standard since 2003. The three techniques are: *''Alternative A'', which uses the same two of the four Balanced line, signal pairs that 10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX use for data in typical Cat 5, Cat 5 cabling. *''Alternative B'', which separates the data and the power conductors for 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX, making troubleshooting easier. *''4PPoE'', which uses all four twisted pairs in parallel, increasing the achievable power. ''Alterna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
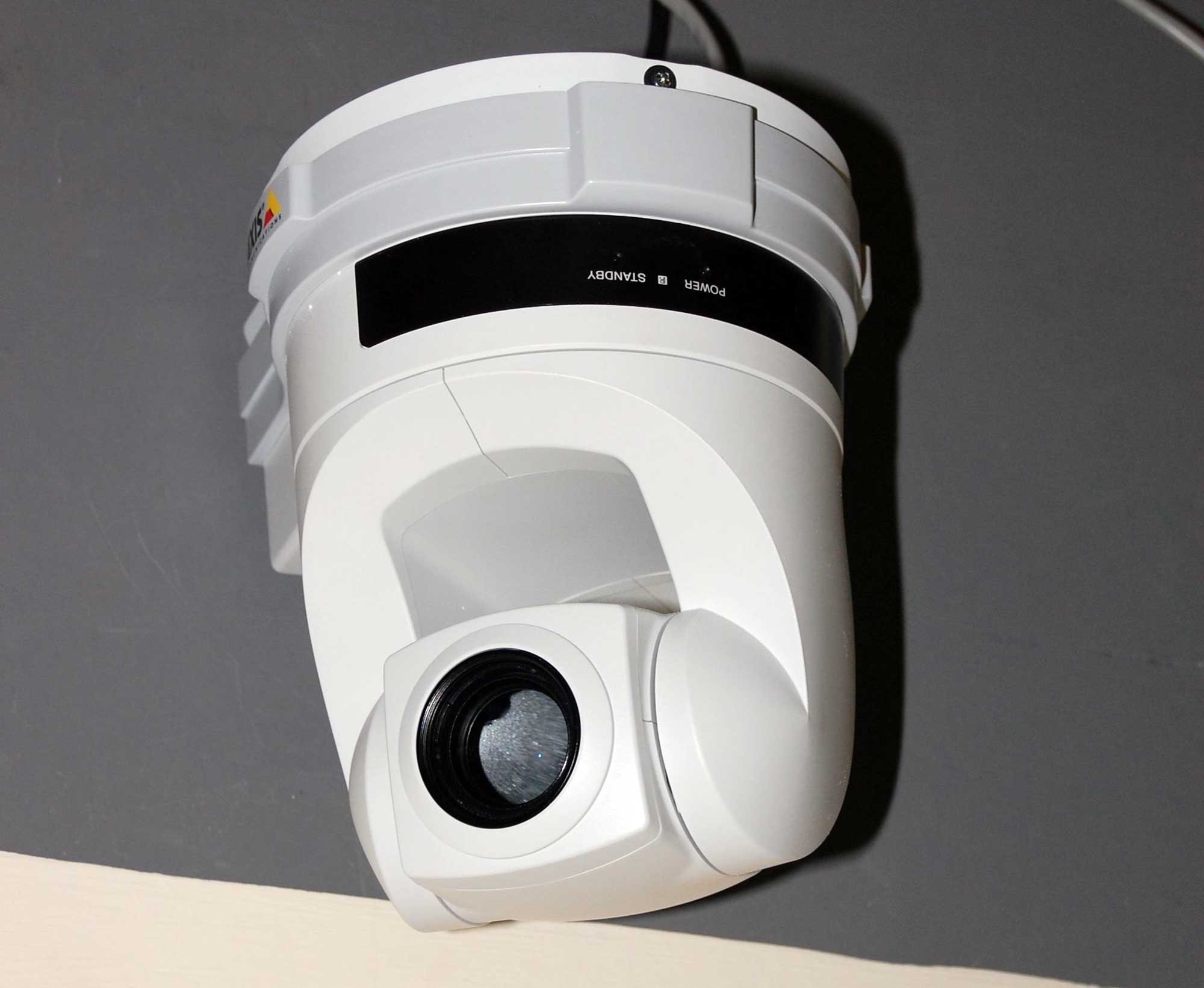
IP Camera
An Internet Protocol camera, or IP camera, is a type of digital video camera that receives control data and sends image data via an IP network. They are commonly used for surveillance, but, unlike analog closed-circuit television (CCTV) cameras, they require no local recording device, only a local area network. Most IP cameras are webcams, but the term ''IP camera'' or netcam usually applies only to those that can be directly accessed over a network connection. Some IP cameras require support of a central network video recorder (NVR) to handle the recording, video and alarm management. Others are able to operate in a decentralized manner with no NVR needed, as the camera is able to record directly to any local or remote storage media. The first IP Camera was invented by Axis Communications in 1996. History The first centralized IP camera, the ''AXIS Neteye 200'', was released in 1996 by Axis Communications. Although the product was advertised to be accessible from any ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethernet Cable
Ethernet ( ) is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 1983 as IEEE 802.3. Ethernet has since been refined to support higher bit rates, a greater number of nodes, and longer link distances, but retains much backward compatibility. Over time, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies such as Token Ring, FDDI and ARCNET. The original 10BASE5 Ethernet uses a thick coaxial cable as a shared medium. This was largely superseded by 10BASE2, which used a thinner and more flexible cable that was both less expensive and easier to use. More modern Ethernet variants use twisted pair and fiber optic links in conjunction with switches. Over the course of its history, Ethernet data transfer rates have been increased from the original to the latest , with rates up to under development. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE 1394
IEEE 1394 is an interface standard for a serial bus for high-speed communications and isochronous real-time data transfer. It was developed in the late 1980s and early 1990s by Apple in cooperation with a number of companies, primarily Sony and Panasonic. It is most commonly known by the name FireWire (Apple), though other brand names exist such as i.LINK (Sony), and Lynx (Texas Instruments). The copper cable used in its most common implementation can be up to long. Power and data is carried over this cable, allowing devices with moderate power requirements to operate without a separate power supply. FireWire is also available in Cat 5 and optical fiber versions. The 1394 interface is comparable to USB. USB was developed subsequently and gained much greater market share. USB requires a host controller whereas IEEE 1394 is cooperatively managed by the connected devices. History and development FireWire is Apple's name for the IEEE 1394 High Speed Serial Bus. Its deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Webcam
A webcam is a video camera which is designed to record or stream to a computer or computer network. They are primarily used in Videotelephony, video telephony, live streaming and social media, and Closed-circuit television, security. Webcams can be Built-in function, built-in computer hardware or Peripheral, peripheral devices, and are commonly connected to a device using USB or Internet protocol suite, wireless protocol. Webcams have been used on the Internet as early as 1993, and the first widespread commercial one became available in 1994. Early webcam usage on the Internet was primarily limited to stationary shots streamed to web sites. In the late 1990s and early 2000s, instant messaging clients added support for webcams, increasing their popularity in video conferencing. Computer manufacturers later started integrating webcams into laptop hardware. In 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic caused a shortage of webcams due to the increased number of people Remote work, working from hom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HD-SDI
SMPTE 292 is a digital video transmission line standard published by the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE). This technical standard is usually referred to as HD-SDI; it is part of a family of standards that define a serial digital interface based on a coaxial cable, intended to be used for transport of uncompressed digital video and audio in a television studio environment. SMPTE 292 expands upon SMPTE 259 and SMPTE 344 allowing for bit-rates of 1.485 Gbit/s, and 1.485/1.001 Gbit/s. These bit-rates are sufficient for and often used to transfer uncompressed high-definition video. Nomenclature The "M" designator was originally introduced to signify metric dimensions. It is no longer used in listings or filenames. Units of the International System of Units (SI) are the preferred units of measurement in all SMPTE Engineering Documents. Technical details The SMPTE 292 standard is a nominally 1.5 Gbit/s interface. Two exact bitrates are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coax Cable
Coaxial cable, or coax (pronounced ), is a type of electrical cable consisting of an inner conductor surrounded by a concentric conducting shield, with the two separated by a dielectric ( insulating material); many coaxial cables also have a protective outer sheath or jacket. The term ''coaxial'' refers to the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing a geometric axis. Coaxial cable is a type of transmission line, used to carry high-frequency electrical signals with low losses. It is used in such applications as telephone trunk lines, broadband internet networking cables, high-speed computer data buses, cable television signals, and connecting radio transmitters and receivers to their antennas. It differs from other shielded cables because the dimensions of the cable and connectors are controlled to give a precise, constant conductor spacing, which is needed for it to function efficiently as a transmission line. Coaxial cable was used in the first (1858) and follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple Desktop Bus
Apple Desktop Bus (ADB) is a proprietary bit-serial peripheral bus connecting low-speed devices to computers. It was introduced on the Apple IIGS in 1986 as a way to support low-cost devices like keyboards and mice, enabling them to be connected together in a daisy chain without the need for hubs or other devices. Apple Desktop Bus was quickly introduced on later Macintosh models, on later models of NeXT computers, and saw some other third-party use as well. Like the similar PS/2 connector used in many PC-compatibles at the time, Apple Desktop Bus was rapidly replaced by USB as that system became popular in the late 1990s; the last external Apple Desktop Bus port on an Apple product was in 1999, though it remained as an internal-only bus on some Mac models into the 2000s. History AppleBus Early during the creation of the Macintosh computer, the engineering team had selected the fairly sophisticated Zilog 8530 to supply serial communications. This was initially done to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PS/2 Port
The PS/2 port is a 6-pin mini-DIN connector used for connecting Computer keyboard, keyboards and computer mouse, mice to a PC compatible computer system. Its name comes from the IBM Personal System/2 series of personal computers, with which it was introduced in 1987. The PS/2 mouse connector generally replaced the older DE-9 connector, DE-9 RS-232 "serial mouse" connector, while the PS/2 keyboard connector replaced the larger 5-pin/180° DIN connector used in the IBM PC/AT design. The PS/2 keyboard port is electrically and logically identical to the IBM AT keyboard port, differing only in the type of electrical connector used. The PS/2 platform introduced a second port with the same design as the keyboard port for use to connect a mouse; thus the PS/2-style keyboard and mouse interfaces are electrically similar and employ the same communication protocol. However, unlike the otherwise similar Apple Desktop Bus connector used by Apple, a given system's keyboard and mouse port may n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
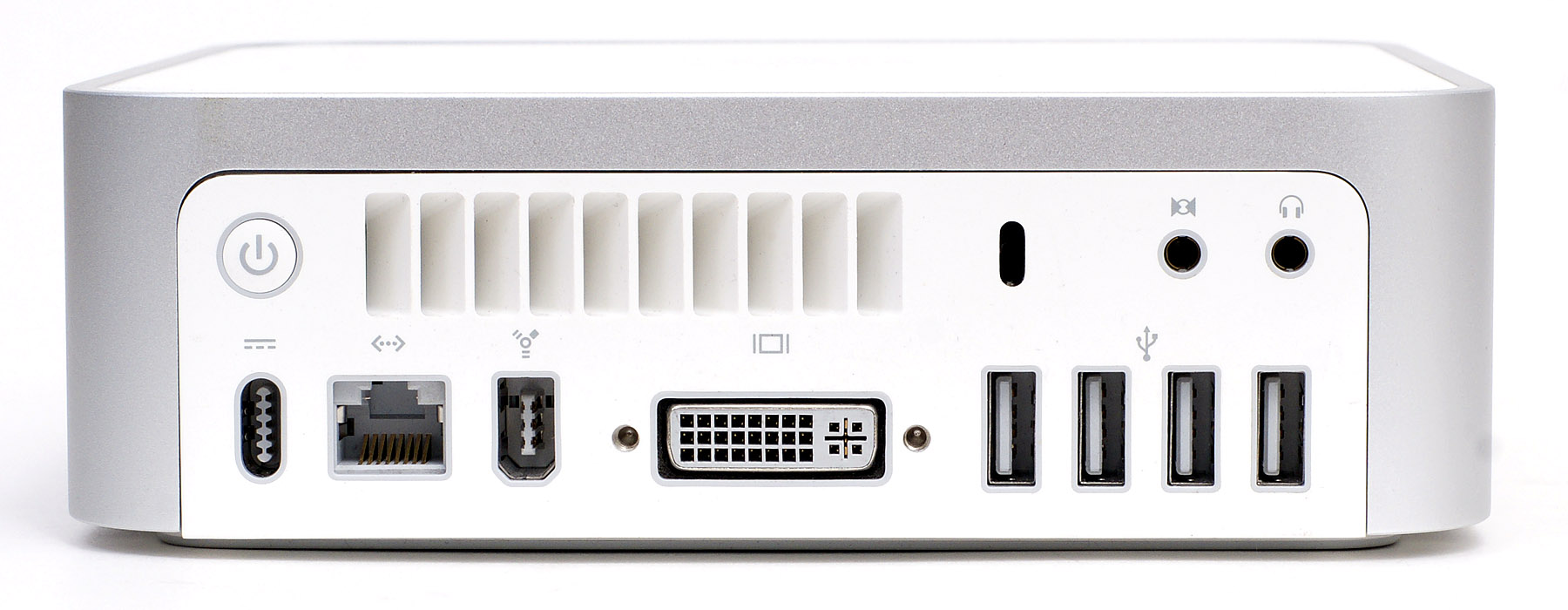
Computer Port (hardware)
A computer port is a hardware piece on a computer where an electrical connector can be plugged to link the device to external devices, such as another computer, a peripheral device or network equipment. This is a non-standard term. Electronically, the several conductors where the port and cable contacts connect, provide a method to transfer data signals between devices. Bent pins are easier to replace on a cable than on a connector attached to a computer, so it was common to use female connectors for the fixed side of an interface. Computer ports in common use cover a wide variety of shapes such as round ( PS/2, etc.), rectangular (FireWire, etc.), square ( Telephone plug), trapezoidal ( D-Sub — the old printer port was a DB-25), etc. There is some standardization to physical properties and function. For instance, most computers have a keyboard port (currently a Universal Serial Bus USB-like outlet referred to as USB Port), into which the keyboard is connected. Ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |